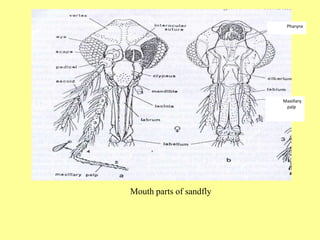
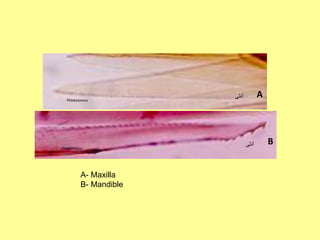
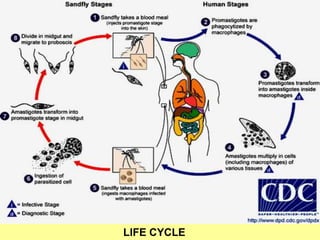
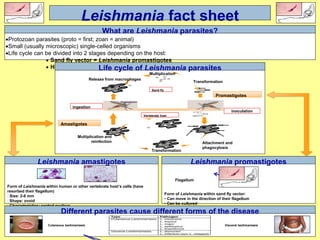
1. Leishmaniasis is transmitted by the bite of female phlebotomine sand flies which inject infective promastigotes during blood meals.
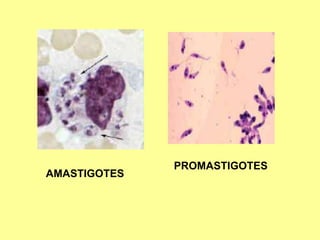
2. Inside the human host, promastigotes are phagocytosed by macrophages and transform into amastigotes, multiplying within infected cells and affecting different tissues.
3. The life cycle continues when female sand flies ingest infected macrophages during a blood meal, and the parasites transform and multiply and migrate to the fly's proboscis as promastigotes.