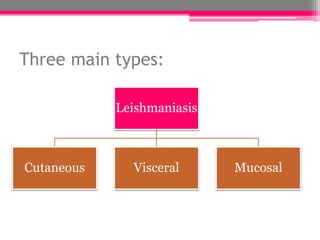
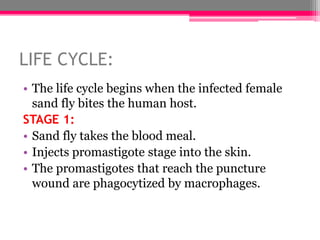
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease spread by the bites of infected sand flies. It is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Leishmania and is endemic in many parts of the world. There are three main clinical forms: cutaneous, visceral, and mucosal. Cutaneous leishmaniasis causes skin sores, visceral leishmaniasis affects internal organs and can be fatal if not treated, and mucosal leishmaniasis destroys mucous membranes in the nose, throat or mouth. The parasite has a multi-stage life cycle alternating between the sand fly vector and a mammalian host like humans. Diagnosis involves microscopic identification of the parasite, antibody detection, or
![k.Shalini [B.sc MB]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leishmaniasis-200916182320/85/Leishmaniasis-1-320.jpg)

















![TREATMENT:
• The only food and drug administration[FAD]
approved medications for treatment of
leishmaniasis are intravenous liposomal
amphotericin B [L-AmB] for VL .
• oral miltefosine for CL, ML AND VL caused by
particular species.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leishmaniasis-200916182320/85/Leishmaniasis-21-320.jpg)




