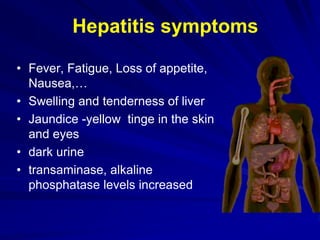
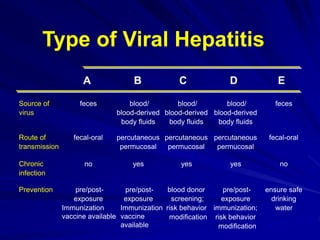
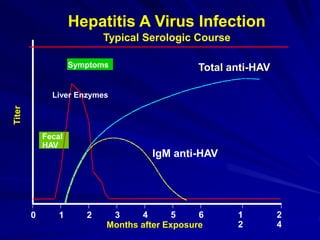
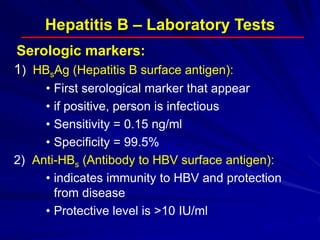
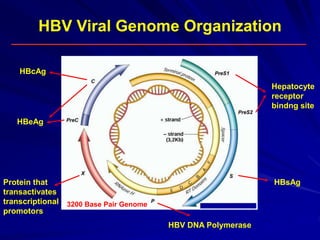
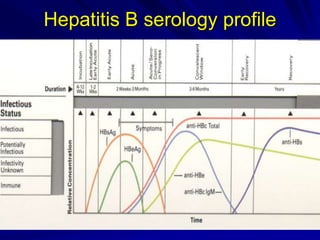
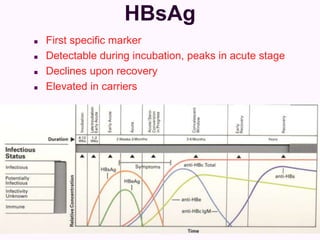
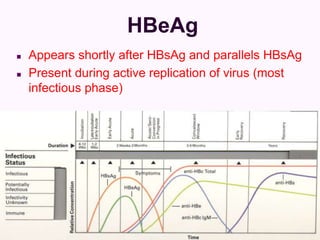
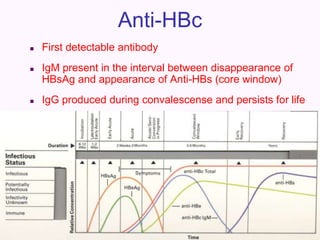
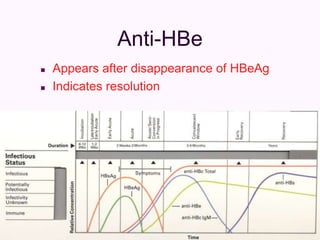
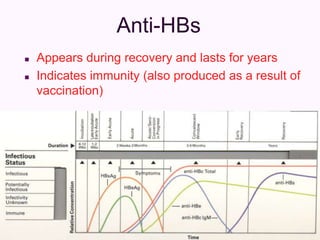
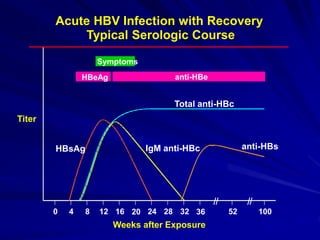
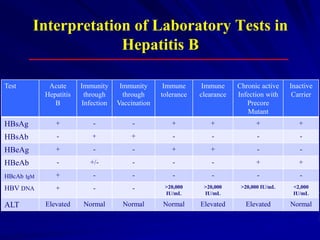
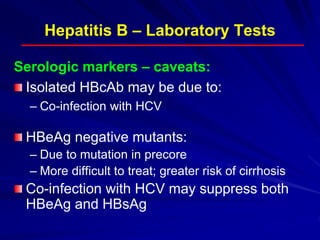
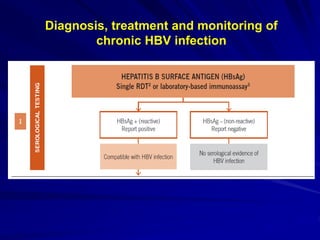
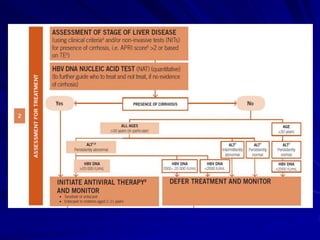
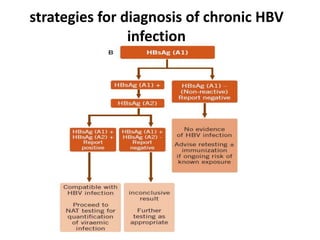
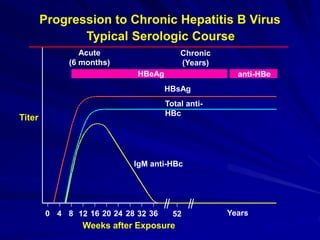
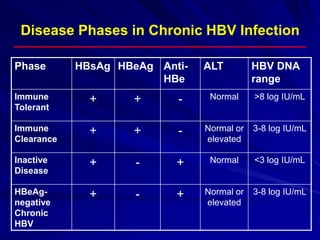
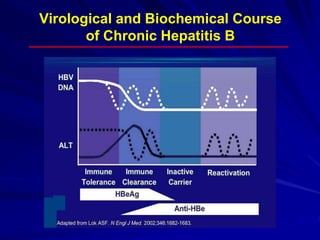
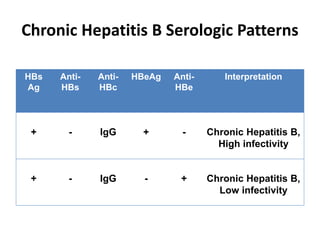
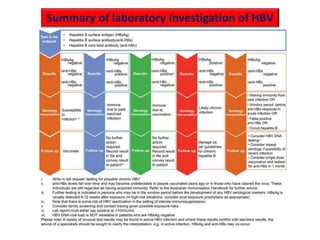
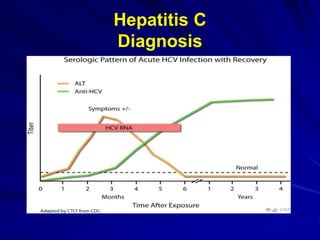
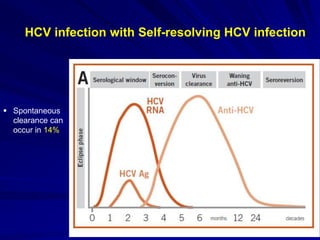
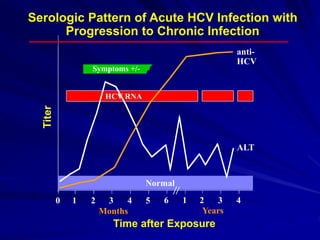
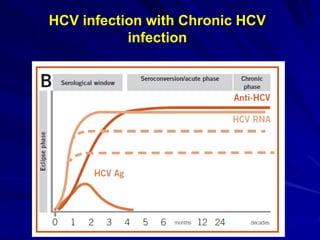
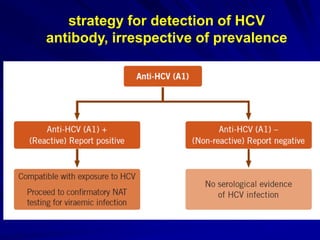
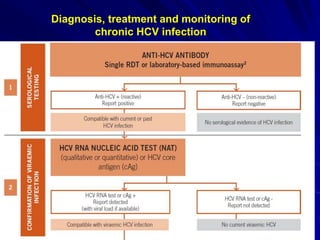
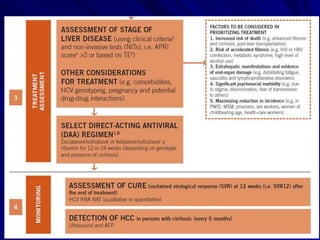
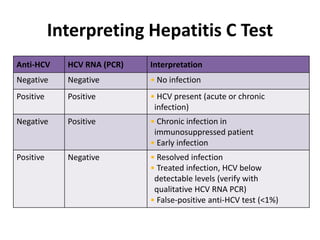
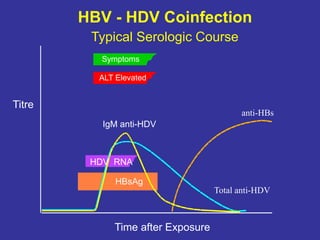
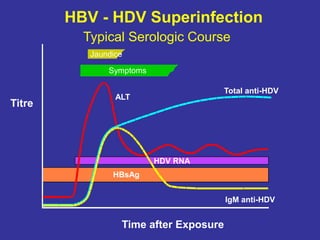
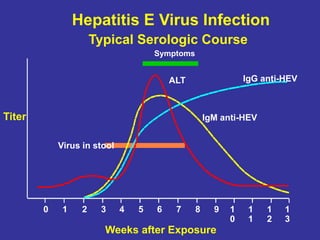
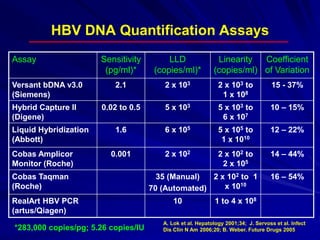
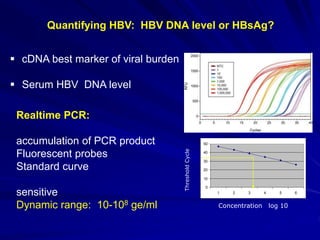
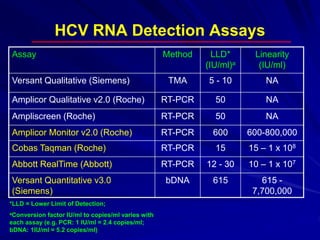
Laboratory diagnostics play an important role in identifying and characterizing hepatitis infections. Serologic tests detect viral antigens and antibodies, helping determine if a virus is present, past infection occurred, or immunity exists. Molecular tests like PCR directly detect viral RNA or DNA, and can quantify viral load levels. Hepatitis A, B, C, and D each have distinct virologic properties and transmission routes, requiring a customized diagnostic approach through various serologic and molecular markers over time to distinguish between acute and chronic infection states. Proper diagnosis is crucial for guiding patient management and public health interventions.