Stoke pathophysiology-1228539935337551-8
•Download as DOC, PDF•
5 likes•6,659 views
There are several types of strokes caused by blocked or ruptured blood vessels in the brain. Ischemic strokes are caused by blocked arteries, cutting off blood flow and oxygen to brain tissue. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when blood vessels rupture, either within the brain itself (intracerebral hemorrhage) or in the space surrounding the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage). Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) involve a temporary blockage but no permanent damage. Risk factors for strokes include hypertension, smoking, heart disease, and diabetes.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Schematic Pathophysiology Cva

This document outlines the schematic pathophysiology of stroke. It lists predisposing factors like age, heredity, and prior medical conditions that can increase risk. Precipitating factors include hypertension, smoking, diabetes, and atrial fibrillation. The path begins with atherosclerosis causing plaque deposits and potentially thrombosis blocking blood flow. If not managed, this can lead to cerebral hemorrhage or ischemia. The progression of effects is described depending on management or lack thereof, including increased intracranial pressure, metabolic acidosis, hypoxia, and ultimately brain tissue damage.
Pathophysiology of left basal ganglia hemorrhage

This document discusses the pathophysiology of left basal ganglia hemorrhage or intracerebral hemorrhage. It lists precipitating factors like hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and high blood glucose that can cause vasoconstriction and blockage of blood vessels, restricting oxygen and nutrient supply. This decreased cerebral perfusion results in intracerebral bleeding that irritates nerves and tissues, causing signs and symptoms such as changes in movement, weakness, cognitive deficits, headaches, and personality changes.
December 2012 NLE Tips Funda

1. The document provides an overview of key concepts in fundamentals of nursing that may be covered in the upcoming December 2012 Philippine Nurse Licensure Examination (PNLE), including nursing theorists, the nursing process, roles of nurses, and concepts of health, disease, and illness transmission.
2. Some of the nursing theorists discussed are Florence Nightingale, Virginia Henderson, Faye Abdellah, and nursing models like the environmental theory, 14 basic human needs theory, and patient-centered approaches.
3. The nursing process is also summarized, outlining the assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation phases.
4. The roles and functions of professional nurses
Future of Nursing - Crown Point

The document discusses the future of nursing and healthcare. It outlines challenges facing the US healthcare system including rising costs and access issues. It also discusses challenges and opportunities for nursing including an aging population, need for higher levels of education, and calls to expand nursing's leadership role. The IOM report on nursing recommends increasing the proportion of nurses with bachelor's degrees and doubling the number with doctorates by 2020 to help transform the healthcare system and improve outcomes.
Nursing care plan chronic renal failure

Chronic renal failure can result from diabetes, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, or other causes leading to irreversible kidney damage and decreased glomerular filtration rate. Key nursing priorities include monitoring for excess fluid retention and electrolyte imbalances, ensuring adequate nutrition given potential nausea or appetite changes, and supporting patient mobility despite possible fatigue. Outcome goals are normal fluid balance, adequate nutritional intake without signs of malnutrition, and activity levels within the patient's capabilities.
Urinary Retention

Urinary retention occurs when a person is unable to empty their bladder fully. It can be caused by immobility, medications, anxiety, or pathological conditions that decrease muscle tone in the bladder and abdomen. Nursing care involves assessing for contributing factors, monitoring intake and output, relieving pain, promoting mobility, and implementing intermittent catheterization if needed to empty the bladder fully and prevent complications like overflow incontinence. The goals are for the patient to experience relief of pain, empty their bladder completely without residuals, and demonstrate behavior changes to prevent future issues.
Neuro Nursing

This document provides an overview of neurologic nursing lecture notes. It covers:
1. The divisions of the nervous system including the central nervous system (CNS), peripheral nervous system (PNS), and autonomic nervous system (ANS).
2. An overview of the structure and function of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves, and spinal nerves.
3. Sympathetic and parasympathetic responses including effects on heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, gastrointestinal function, urinary function and more.
4. Toxic substances that can pass the blood-brain barrier such as bilirubin, lead, ammonia, and carbon monoxide.
Dec 2012 NLE TIPS MS (A)

1) The document discusses perioperative nursing, including types of surgical procedures, classifications of procedures, informed consent, preoperative medications and teachings, and the surgical team.
2) It also discusses postoperative complications involving various body systems like respiratory, circulatory, and wounds. Principles of surgical asepsis and PACU/RR care are outlined.
3) Oncology nursing is discussed, differentiating benign and malignant neoplasms. Recommendations for cancer screening and warning signs of cancer are provided. Internal radiation therapy and nursing management are summarized.
Recommended
Schematic Pathophysiology Cva

This document outlines the schematic pathophysiology of stroke. It lists predisposing factors like age, heredity, and prior medical conditions that can increase risk. Precipitating factors include hypertension, smoking, diabetes, and atrial fibrillation. The path begins with atherosclerosis causing plaque deposits and potentially thrombosis blocking blood flow. If not managed, this can lead to cerebral hemorrhage or ischemia. The progression of effects is described depending on management or lack thereof, including increased intracranial pressure, metabolic acidosis, hypoxia, and ultimately brain tissue damage.
Pathophysiology of left basal ganglia hemorrhage

This document discusses the pathophysiology of left basal ganglia hemorrhage or intracerebral hemorrhage. It lists precipitating factors like hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and high blood glucose that can cause vasoconstriction and blockage of blood vessels, restricting oxygen and nutrient supply. This decreased cerebral perfusion results in intracerebral bleeding that irritates nerves and tissues, causing signs and symptoms such as changes in movement, weakness, cognitive deficits, headaches, and personality changes.
December 2012 NLE Tips Funda

1. The document provides an overview of key concepts in fundamentals of nursing that may be covered in the upcoming December 2012 Philippine Nurse Licensure Examination (PNLE), including nursing theorists, the nursing process, roles of nurses, and concepts of health, disease, and illness transmission.
2. Some of the nursing theorists discussed are Florence Nightingale, Virginia Henderson, Faye Abdellah, and nursing models like the environmental theory, 14 basic human needs theory, and patient-centered approaches.
3. The nursing process is also summarized, outlining the assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation phases.
4. The roles and functions of professional nurses
Future of Nursing - Crown Point

The document discusses the future of nursing and healthcare. It outlines challenges facing the US healthcare system including rising costs and access issues. It also discusses challenges and opportunities for nursing including an aging population, need for higher levels of education, and calls to expand nursing's leadership role. The IOM report on nursing recommends increasing the proportion of nurses with bachelor's degrees and doubling the number with doctorates by 2020 to help transform the healthcare system and improve outcomes.
Nursing care plan chronic renal failure

Chronic renal failure can result from diabetes, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, or other causes leading to irreversible kidney damage and decreased glomerular filtration rate. Key nursing priorities include monitoring for excess fluid retention and electrolyte imbalances, ensuring adequate nutrition given potential nausea or appetite changes, and supporting patient mobility despite possible fatigue. Outcome goals are normal fluid balance, adequate nutritional intake without signs of malnutrition, and activity levels within the patient's capabilities.
Urinary Retention

Urinary retention occurs when a person is unable to empty their bladder fully. It can be caused by immobility, medications, anxiety, or pathological conditions that decrease muscle tone in the bladder and abdomen. Nursing care involves assessing for contributing factors, monitoring intake and output, relieving pain, promoting mobility, and implementing intermittent catheterization if needed to empty the bladder fully and prevent complications like overflow incontinence. The goals are for the patient to experience relief of pain, empty their bladder completely without residuals, and demonstrate behavior changes to prevent future issues.
Neuro Nursing

This document provides an overview of neurologic nursing lecture notes. It covers:
1. The divisions of the nervous system including the central nervous system (CNS), peripheral nervous system (PNS), and autonomic nervous system (ANS).
2. An overview of the structure and function of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves, and spinal nerves.
3. Sympathetic and parasympathetic responses including effects on heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, gastrointestinal function, urinary function and more.
4. Toxic substances that can pass the blood-brain barrier such as bilirubin, lead, ammonia, and carbon monoxide.
Dec 2012 NLE TIPS MS (A)

1) The document discusses perioperative nursing, including types of surgical procedures, classifications of procedures, informed consent, preoperative medications and teachings, and the surgical team.
2) It also discusses postoperative complications involving various body systems like respiratory, circulatory, and wounds. Principles of surgical asepsis and PACU/RR care are outlined.
3) Oncology nursing is discussed, differentiating benign and malignant neoplasms. Recommendations for cancer screening and warning signs of cancer are provided. Internal radiation therapy and nursing management are summarized.
Cva

A cerebrovascular accident (CVA), also known as a stroke, is caused by the loss of blood flow to an area of the brain resulting in cell death. It is a leading cause of death and disability. The majority of strokes are ischemic and caused by blockage of an artery by a clot or debris. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding into or around the brain. Treatment focuses on prevention through risk factor control as well as acute interventions like clot-busting drugs. Rehabilitation aims to maximize recovery of function and independence.
July 2012 nle tips funda

1. The document provides an overview of key topics that may be covered in the upcoming July 2012 Philippine Nurse Licensure Examination (PNLE), including nursing theorists, the nursing process, nursing roles and functions, and isolation precautions.
2. It discusses several influential nursing theorists and their models, such as Florence Nightingale, Virginia Henderson, and Jean Watson. It also outlines the main steps and considerations for the nursing process: assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention/implementation, and evaluation.
3. The roles and functions of professional nurses are defined, including direct care provider, communicator, teacher, counselor, client advocate, change agent, leader, and manager.
4. Standard precautions,
July 2012 nle tips chn and cd

The document provides information about community health nursing for the upcoming Philippine Nurse Licensure Examination (PNLE) in July 2012. It discusses the Department of Health's vision and mission, levels of prevention, common herbal medicines used in the Philippines, and key topics that may be covered in the exam such as the Family Health Service Information System (FHSIS) and maternal, infant, and neonatal mortality rates.
July 2012 nle tips ms

The document discusses the surgical team and perioperative nursing. It describes:
1) The major types of pathologic processes requiring surgery such as obstruction, perforation, erosion, and tumors.
2) The classification of surgical procedures according to purpose such as diagnostic, exploratory, curative, and palliative, and according to urgency such as emergent, urgent, elective, and non-urgent.
3) The roles of the surgical team which includes the surgeon, assistant surgeon, anesthesiologist, scrub nurse, and circulating nurse. The roles and responsibilities of each member are outlined.
The CNL Role in Critical Care

What can a Clinical Nurse Leader do for your critical care nursing unit? Plenty! Consider this new nursing role as one that can improve patient outcomes and increase satisfaction for both clients and staff. Successful microsystems begin with empowering patients, families and front line nurses.
July 2012 nle tips palmer

The document provides information on the Professional Adjustment, Leadership & Management, and Research (PALMER) section of the Philippine Nursing Licensure Examination (PNLE). Some key topics that may appear on the upcoming July 2012 PNLE include:
- Patient's bill of rights
- Organization and responsibilities of the Board of Nursing
- Requirements and qualifications for nursing licensure, practice, and education
- Nursing jurisprudence including laws affecting the nursing profession, negligence, malpractice, and informed consent
- Restraints, living wills, and advance directives
Nursing crib.com nursing care plan renal failure

The nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing renal failure who presents with edema, fatigue, and weakness, and notes an assessment of fluid overload and compromised renal function. The plan includes monitoring intake and output, daily weighing, skin assessments for edema, oral fluid replacement within restrictions, and administering diuretics and antihypertensives as needed to manage fluid levels, reduce edema, and treat hypertension. The expected outcomes are appropriate urinary output, stable weight and vital signs, and resolution of edema.
July 2012 nle tips mchn

The document provides information on various diagnostic tests performed during pregnancy including amniocentesis, chorionic villi sampling, ultrasound, and alpha-fetoprotein screening. It discusses signs and symptoms of pregnancy such as breast changes, nausea, and a positive pregnancy test. Common discomforts of pregnancy like heartburn and constipation are also outlined along with recommended health teachings. The document concludes with an overview of electronic fetal monitoring including the non-stress test to monitor fetal heart rate.
PHARMA-THE NURSING PROCESS

3. Observe for adverse effects and report
immediately.
5. Document administration accurately and
completely.
7. Report any errors immediately to the
nurse manager/supervisor.
9. Evaluate effectiveness of medication.
11. Teach client about medication.
13. Respect client's right to refuse medication.
15. Maintain confidentiality.
17. Report any changes in client's condition.
19. Respect cultural and religious beliefs.
21. Encourage questions about medications.
23. Monitor for drug interactions.
25. Respect client's right to participate in own care.
27. Evaluate understanding of teaching.
29. Respect
Legal issues in nursing practice

This document discusses legal issues related to nursing practice. It covers sources of laws at federal, state and local levels. Criminal and civil laws are described as well as tort law, including elements of professional negligence. Strategies to prevent incidents and standards of care are presented. Selected laws around informed consent, controlled substances, and good Samaritan laws are covered. The roles of nurse practice acts, licensing, and regulatory boards are explained. Standards of nursing practice from organizations like ANA are also summarized.
Trends in critical care nursing

This document discusses trends in critical care nursing. It begins by defining critical care nursing and describing the responsibilities of critical care nurses, which include advocating for patients, using clinical judgment, and collaborating with a multidisciplinary team. It then discusses the evolution of critical care from the 1800s to present day and how critical care nursing developed as a specialty. The document outlines standards of care and professional practice for critical care nurses. It describes the changing roles of critical care nurses and how they can function as staff nurses, educators, managers, and more. Finally, it discusses the importance of holistic care in critical care nursing.
Community health

This document discusses the concepts and principles of community health nursing. It defines community health nursing as applying nursing skills, public health, and social assistance through organized community efforts to promote health, prevent disease, and ensure access to healthcare. The key goals are to raise the level of health in communities and maximize their potential for wellness through participation and self-reliance. Community health nursing focuses on serving individuals, families, populations, and communities across all ages and levels of healthcare.
Newman’s theory of health as expanding consciousness

The theory of health as expanding consciousness stimulated by concern for those for whom health as the absence of disease or disability is not possible, (Newman, 2010).
The theory has progressed to include the health of all persons regardless of the presence or absence of disease, (Newman, 2010).
The theory asserts that every person in every situation, no matter how disordered and hopeless it may seem, is part of the universal process of expanding consciousness, (Newman, 2010).
July 2012 nle tips psych

1. This document provides information on psychiatric nursing for the July 2012 PNLE exam, including topics on neurotransmitters, therapeutic and non-therapeutic communication techniques, defense mechanisms, the nurse-patient relationship, anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, mood disorders, schizophrenia, and antidepressant medications.
2. Key aspects of neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, acetylcholine, and GABA are discussed. Therapeutic communication techniques include silence, reflection, and clarification, while non-therapeutic techniques include reassurance and advising.
3. Common defense mechanisms, the phases of the nurse-patient relationship, levels of anxiety and interventions, and assessments and treatments for various mood and
Respiratory Nursing

This document provides lecture notes on the respiratory system prepared by Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN. It begins with the anatomy of the respiratory system including the upper respiratory tract, lower respiratory tract, lungs and pulmonary circulation. It then discusses the physiology of the respiratory system including ventilation, gas exchange, neurochemical control and the driving force for air flow. Finally, it outlines the respiratory examination and assessment including inspection of breathing patterns, cyanosis, the hands, face, trachea and chest as well as relevant medical history.
Fdar charting

This document contains sample focus charting from a nurse's notes. It includes 3 entries with the date, focus, and progress notes in the DAR (Data, Action, Response) format. The focuses included pain, hyperthermia, and fatigue. The summaries provided nursing assessments, interventions, and the patient's response for each focus area in 3 sentences or less.
Nursing Care of Clients with Stroke

Stroke is a medical condition where blood supply to part of the brain is decreased, causing loss of brain function. It is a leading cause of death and disability. There are two main types - ischemic (caused by clots) and hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding). Risk factors include hypertension, heart disease, smoking, diabetes and obesity. Prevention involves controlling risk factors through lifestyle changes and medications. Anyone experiencing symptoms like weakness or numbness on one side of the body should seek immediate medical attention.
Gastrointestinal Nursing

This document provides an overview of the gastrointestinal system including its structure and function. It discusses several common gastrointestinal disorders such as parotitis, appendicitis, liver cirrhosis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and cholelithiasis. For each disorder, it describes the etiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostics, and nursing management. The document is authored by Mark Fredderick Abejo RN, MAN and intended to educate nurses on gastrointestinal disorders and their treatment.
1.5. critical care ethical and legal responsibilities

This document discusses the ethical and legal responsibilities of critical care nurses. It begins by distinguishing between ethical and legal standards, with ethical standards based on principles of right and wrong and legal standards based on written law.
It then outlines some common ethical dilemmas nurses may face including end-of-life decisions, patient care issues, and human rights issues. It also discusses legal decisions around topics like medical documentation, use of restraints, and declaring brain death.
The document provides recommendations for resolving ethical dilemmas and outlines practical principles for ethical decision making including effective communication and determining patient desires. It emphasizes the importance of shared decision making at end-of-life.
Stroke

Stroke is the third leading cause of death in Malaysia. The document defines stroke, classifies its types, and outlines its diagnosis and management. Key points include that stroke is caused by blocked blood flow to the brain, and risk factors include age, gender, family history, hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, smoking, and high cholesterol. Diagnostic tests include CT/MRI scans and angiograms to determine the cause. Treatment focuses on rehabilitation, managing risk factors, and preventing future strokes.
Cva

A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, caused by a blood clot blocking a vessel, and hemorrhagic, caused by a bleeding vessel in the brain. Symptoms include sudden numbness, confusion, trouble seeing or walking, and severe headaches. If experienced, one must get immediate medical help to treat the stroke and prevent further damage. Risk factors include conditions like hypertension, smoking, diabetes, age, and heredity.
More Related Content
What's hot
Cva

A cerebrovascular accident (CVA), also known as a stroke, is caused by the loss of blood flow to an area of the brain resulting in cell death. It is a leading cause of death and disability. The majority of strokes are ischemic and caused by blockage of an artery by a clot or debris. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding into or around the brain. Treatment focuses on prevention through risk factor control as well as acute interventions like clot-busting drugs. Rehabilitation aims to maximize recovery of function and independence.
July 2012 nle tips funda

1. The document provides an overview of key topics that may be covered in the upcoming July 2012 Philippine Nurse Licensure Examination (PNLE), including nursing theorists, the nursing process, nursing roles and functions, and isolation precautions.
2. It discusses several influential nursing theorists and their models, such as Florence Nightingale, Virginia Henderson, and Jean Watson. It also outlines the main steps and considerations for the nursing process: assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention/implementation, and evaluation.
3. The roles and functions of professional nurses are defined, including direct care provider, communicator, teacher, counselor, client advocate, change agent, leader, and manager.
4. Standard precautions,
July 2012 nle tips chn and cd

The document provides information about community health nursing for the upcoming Philippine Nurse Licensure Examination (PNLE) in July 2012. It discusses the Department of Health's vision and mission, levels of prevention, common herbal medicines used in the Philippines, and key topics that may be covered in the exam such as the Family Health Service Information System (FHSIS) and maternal, infant, and neonatal mortality rates.
July 2012 nle tips ms

The document discusses the surgical team and perioperative nursing. It describes:
1) The major types of pathologic processes requiring surgery such as obstruction, perforation, erosion, and tumors.
2) The classification of surgical procedures according to purpose such as diagnostic, exploratory, curative, and palliative, and according to urgency such as emergent, urgent, elective, and non-urgent.
3) The roles of the surgical team which includes the surgeon, assistant surgeon, anesthesiologist, scrub nurse, and circulating nurse. The roles and responsibilities of each member are outlined.
The CNL Role in Critical Care

What can a Clinical Nurse Leader do for your critical care nursing unit? Plenty! Consider this new nursing role as one that can improve patient outcomes and increase satisfaction for both clients and staff. Successful microsystems begin with empowering patients, families and front line nurses.
July 2012 nle tips palmer

The document provides information on the Professional Adjustment, Leadership & Management, and Research (PALMER) section of the Philippine Nursing Licensure Examination (PNLE). Some key topics that may appear on the upcoming July 2012 PNLE include:
- Patient's bill of rights
- Organization and responsibilities of the Board of Nursing
- Requirements and qualifications for nursing licensure, practice, and education
- Nursing jurisprudence including laws affecting the nursing profession, negligence, malpractice, and informed consent
- Restraints, living wills, and advance directives
Nursing crib.com nursing care plan renal failure

The nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing renal failure who presents with edema, fatigue, and weakness, and notes an assessment of fluid overload and compromised renal function. The plan includes monitoring intake and output, daily weighing, skin assessments for edema, oral fluid replacement within restrictions, and administering diuretics and antihypertensives as needed to manage fluid levels, reduce edema, and treat hypertension. The expected outcomes are appropriate urinary output, stable weight and vital signs, and resolution of edema.
July 2012 nle tips mchn

The document provides information on various diagnostic tests performed during pregnancy including amniocentesis, chorionic villi sampling, ultrasound, and alpha-fetoprotein screening. It discusses signs and symptoms of pregnancy such as breast changes, nausea, and a positive pregnancy test. Common discomforts of pregnancy like heartburn and constipation are also outlined along with recommended health teachings. The document concludes with an overview of electronic fetal monitoring including the non-stress test to monitor fetal heart rate.
PHARMA-THE NURSING PROCESS

3. Observe for adverse effects and report
immediately.
5. Document administration accurately and
completely.
7. Report any errors immediately to the
nurse manager/supervisor.
9. Evaluate effectiveness of medication.
11. Teach client about medication.
13. Respect client's right to refuse medication.
15. Maintain confidentiality.
17. Report any changes in client's condition.
19. Respect cultural and religious beliefs.
21. Encourage questions about medications.
23. Monitor for drug interactions.
25. Respect client's right to participate in own care.
27. Evaluate understanding of teaching.
29. Respect
Legal issues in nursing practice

This document discusses legal issues related to nursing practice. It covers sources of laws at federal, state and local levels. Criminal and civil laws are described as well as tort law, including elements of professional negligence. Strategies to prevent incidents and standards of care are presented. Selected laws around informed consent, controlled substances, and good Samaritan laws are covered. The roles of nurse practice acts, licensing, and regulatory boards are explained. Standards of nursing practice from organizations like ANA are also summarized.
Trends in critical care nursing

This document discusses trends in critical care nursing. It begins by defining critical care nursing and describing the responsibilities of critical care nurses, which include advocating for patients, using clinical judgment, and collaborating with a multidisciplinary team. It then discusses the evolution of critical care from the 1800s to present day and how critical care nursing developed as a specialty. The document outlines standards of care and professional practice for critical care nurses. It describes the changing roles of critical care nurses and how they can function as staff nurses, educators, managers, and more. Finally, it discusses the importance of holistic care in critical care nursing.
Community health

This document discusses the concepts and principles of community health nursing. It defines community health nursing as applying nursing skills, public health, and social assistance through organized community efforts to promote health, prevent disease, and ensure access to healthcare. The key goals are to raise the level of health in communities and maximize their potential for wellness through participation and self-reliance. Community health nursing focuses on serving individuals, families, populations, and communities across all ages and levels of healthcare.
Newman’s theory of health as expanding consciousness

The theory of health as expanding consciousness stimulated by concern for those for whom health as the absence of disease or disability is not possible, (Newman, 2010).
The theory has progressed to include the health of all persons regardless of the presence or absence of disease, (Newman, 2010).
The theory asserts that every person in every situation, no matter how disordered and hopeless it may seem, is part of the universal process of expanding consciousness, (Newman, 2010).
July 2012 nle tips psych

1. This document provides information on psychiatric nursing for the July 2012 PNLE exam, including topics on neurotransmitters, therapeutic and non-therapeutic communication techniques, defense mechanisms, the nurse-patient relationship, anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, mood disorders, schizophrenia, and antidepressant medications.
2. Key aspects of neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, acetylcholine, and GABA are discussed. Therapeutic communication techniques include silence, reflection, and clarification, while non-therapeutic techniques include reassurance and advising.
3. Common defense mechanisms, the phases of the nurse-patient relationship, levels of anxiety and interventions, and assessments and treatments for various mood and
Respiratory Nursing

This document provides lecture notes on the respiratory system prepared by Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN. It begins with the anatomy of the respiratory system including the upper respiratory tract, lower respiratory tract, lungs and pulmonary circulation. It then discusses the physiology of the respiratory system including ventilation, gas exchange, neurochemical control and the driving force for air flow. Finally, it outlines the respiratory examination and assessment including inspection of breathing patterns, cyanosis, the hands, face, trachea and chest as well as relevant medical history.
Fdar charting

This document contains sample focus charting from a nurse's notes. It includes 3 entries with the date, focus, and progress notes in the DAR (Data, Action, Response) format. The focuses included pain, hyperthermia, and fatigue. The summaries provided nursing assessments, interventions, and the patient's response for each focus area in 3 sentences or less.
Nursing Care of Clients with Stroke

Stroke is a medical condition where blood supply to part of the brain is decreased, causing loss of brain function. It is a leading cause of death and disability. There are two main types - ischemic (caused by clots) and hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding). Risk factors include hypertension, heart disease, smoking, diabetes and obesity. Prevention involves controlling risk factors through lifestyle changes and medications. Anyone experiencing symptoms like weakness or numbness on one side of the body should seek immediate medical attention.
Gastrointestinal Nursing

This document provides an overview of the gastrointestinal system including its structure and function. It discusses several common gastrointestinal disorders such as parotitis, appendicitis, liver cirrhosis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and cholelithiasis. For each disorder, it describes the etiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostics, and nursing management. The document is authored by Mark Fredderick Abejo RN, MAN and intended to educate nurses on gastrointestinal disorders and their treatment.
1.5. critical care ethical and legal responsibilities

This document discusses the ethical and legal responsibilities of critical care nurses. It begins by distinguishing between ethical and legal standards, with ethical standards based on principles of right and wrong and legal standards based on written law.
It then outlines some common ethical dilemmas nurses may face including end-of-life decisions, patient care issues, and human rights issues. It also discusses legal decisions around topics like medical documentation, use of restraints, and declaring brain death.
The document provides recommendations for resolving ethical dilemmas and outlines practical principles for ethical decision making including effective communication and determining patient desires. It emphasizes the importance of shared decision making at end-of-life.
What's hot (20)
Newman’s theory of health as expanding consciousness

Newman’s theory of health as expanding consciousness
1.5. critical care ethical and legal responsibilities

1.5. critical care ethical and legal responsibilities
Similar to Stoke pathophysiology-1228539935337551-8
Stroke

Stroke is the third leading cause of death in Malaysia. The document defines stroke, classifies its types, and outlines its diagnosis and management. Key points include that stroke is caused by blocked blood flow to the brain, and risk factors include age, gender, family history, hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, smoking, and high cholesterol. Diagnostic tests include CT/MRI scans and angiograms to determine the cause. Treatment focuses on rehabilitation, managing risk factors, and preventing future strokes.
Cva

A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, caused by a blood clot blocking a vessel, and hemorrhagic, caused by a bleeding vessel in the brain. Symptoms include sudden numbness, confusion, trouble seeing or walking, and severe headaches. If experienced, one must get immediate medical help to treat the stroke and prevent further damage. Risk factors include conditions like hypertension, smoking, diabetes, age, and heredity.
Cardiovascular pathology coronary heart disease finale

1. The document discusses coronary heart disease, which is caused by impaired blood flow due to atherosclerosis in most cases.
2. Diseases of the coronary arteries can cause angina, heart attack, cardiac dysrhythmias, conduction defects, heart failure, and sudden death.
3. The pathogenesis of coronary heart disease involves LDL cholesterol entering the arterial wall and being taken up by scavenger cells, forming fatty streaks and atheromatous plaques that can progress and restrict blood flow.
Heart diseases

The document discusses the structure and function of the normal human heart. It describes key details like the layers of the heart, cardiac muscle cell structures, blood supply, age-related changes, and more. Diseases covered include ischemic heart disease, heart failure, effects of aging on the heart, and abnormalities that can cause cardiac dysfunction. Pathologies like myocardial infarction and atherosclerosis are explained in terms of causes, pathogenesis, morphological changes, and treatment options like thrombolytic therapy.
@ Stroke seminar

Stroke is caused by interrupted blood flow to the brain and can be ischemic (blockage of blood flow) or hemorrhagic (bleeding in the brain). The main symptoms include sudden weakness or numbness, trouble speaking or understanding, vision changes, and severe headache. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol, and atrial fibrillation. Diagnosis involves CT or MRI imaging of the brain along with medical history and exam. Treatment depends on the type of stroke but may include managing blood pressure, anticoagulants, surgery to repair burst blood vessels, and rehabilitation therapy.
Heart disorders

This document summarizes several common heart disorders:
- Coronary heart disease is caused by plaque buildup in the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. Atherosclerosis is a similar condition where plaques develop inside arterial walls.
- Chest pain called angina occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the heart. Arrhythmias happen when the heart's electrical system malfunctions, causing irregular heartbeats.
- Congestive heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Other disorders discussed include stroke, myocardial infarction, hypotension, hypertension, rheumatic heart disease, and congenital heart disease. Risk factors and treatments are also outlined.
approach to a patient with stroke.pdf

The document defines various terms related to strokes, including stroke, TIA, progressive stroke, completed stroke, and hemorrhagic vs ischemic stroke. It discusses the epidemiology, risk factors, types, clinical features, investigations, and differential diagnosis of strokes. Specifically, it provides details on the clinical presentations and neurological deficits associated with occlusion of different arteries in the anterior and posterior circulations. It also outlines the objectives and modalities used to investigate a potential stroke, including non-invasive tests like CT, MRI, and Doppler ultrasound and invasive tests like angiography.
stroke ( ischemic stroke )

Is characterized by the sudden loss of blood circulation to an area of the brain, resulting in a corresponding loss of neurologic function. Acute ischemic stroke is caused by thrombotic or embolic occlusion of a cerebral artery and is more common than hemorrhagic stroke.
It can occur
in the carotid
artery of the
neck as well as
other arteries.
When an artery is acutely occluded by thrombus or embolus, the area of the CNS supplied by it will undergo infarction if there is no adequate collateral blood supply.
Surrounding a central necrotic zone, an ‘ischemic penumbra’ remains viable for a time, i.e. it may recover function if blood flow is restored.
CNS ischemia may be accompanied by swelling for two reasons:
● cytotoxic oedema – accumulation of water in damaged glial cells and neurones,
● vasogenic oedema – extracellular fluid accumulation as a result of breakdown of the blood–brain barrier.
In the brain, this swelling may be sufficient to produce clinical deterioration in the days following a major stroke, as a result of a rise in intracranial pressure and compression of adjacent structures.
Stroke (Ischemic and Hemorrhagic)

In this presentation, I have described stroke and its subtypes, the ischemic stroke and the hemorrhagic stroke, their diagnosis, clinical manifestations and treatments.
93084257 pathophsiology-summary

The document summarizes several topics related to pathophysiology:
1. It discusses the structure of the heart and key features like the foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus that normally close after birth.
2. It summarizes the conduction system of the heart and locations like the PMI.
3. Several conditions are summarized like hypertension, heart failure, arrhythmias, and kidney function and disorders. Causes, signs, treatments, and important details are provided for each topic.
Cardiovascular disease

Cardiovascular disease Hypertension ,types, stages,risk factors, complications,and Atherosclerosis- causes, pathogenesis, micro and macroscopic features
Cardiac dysrhythmias

This document provides information on cardiac dysrhythmias or arrhythmias. It defines arrhythmias as abnormalities in heart rate, rhythm or impulse origin/conduction. Various types of arrhythmias are described including supraventricular arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation, ventricular arrhythmias like premature ventricular contractions, and bradyarrhythmias. Causes or risk factors of arrhythmias include age, family history, heart disease, medications and substances like caffeine. The document also discusses various inherited arrhythmia conditions.
Cardiomyopathy 

Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that weaken and enlarge the heart muscle, making it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body. There are three main types: dilated cardiomyopathy which causes the heart chambers to enlarge and the heart walls to thin; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick; and restrictive cardiomyopathy which causes the heart muscles to stiffen. Symptoms vary depending on the type but can include fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, and heart palpitations. Diagnosis involves echocardiograms, electrocardiograms, and cardiac imaging to examine the structure and function of the heart. Treatment may include medications, medical devices, and
Anti-Ischemics | Mechanism | Ischemia | Signs & Symptoms

This presentation provides a knowledge about Ischemic heart Disease, Ischemia, Mechanism of Action, signs and symptoms, Causes of Ischemia, Ischemia in different body parts, Angina, Myocardial Infarction, Artherosclerosis, Drugs used to treat ischemia and recent discovery related to Cardiac ischemia. An assignment for the subject, Advanced Pharmacology-I, 1st year M.Pharm, 1st semester.
Lecture 18 cardiovascular system 

This document summarizes various cardiovascular conditions including coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, hypertension, and pericardial diseases. It describes the pathophysiology of coronary atherosclerosis leading to decreased blood supply and angina. Myocardial infarction results from coronary thrombosis and presents as areas of necrosis. Hypertension can be primary/benign or malignant, causing hypertrophy and damage to organs over time. Pericarditis commonly results from infection, rheumatic fever or myocardial infarction, and tuberculous pericarditis can lead to constrictive pericarditis.
Cerebrovascular accident

Cerebrovascular accident refers to a stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted. The document discusses the causes, types, symptoms, risk factors, and diagnostic evaluation of strokes. It also summarizes hypertension, myocardial infarction, and coronary artery disease - all of which can increase the risk of strokes if not properly managed.
CVD

Cerebrovascular disease (CVD) refers to a group of brain dysfunctions related to diseases of the blood vessels supplying the brain. The most important cause is hypertension, which damages blood vessel linings. Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, diabetes, smoking, high alcohol intake, atrial fibrillation, and hypercoagulability. CVD includes cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke), intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attack (TIA). Diagnosis involves patient history and imaging tests. Treatment focuses on thrombolytic therapy, blood pressure control, preventing brain edema, anticoagulation, surgery, and rehabilitation.
Syncope dr yate

Syncope is defined as a brief, self-limited loss of consciousness due to reduced cerebral blood flow. It is characterized by rapid onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. The document discusses the various causes of syncope including neurally-mediated (vasovagal), orthostatic, cardiac, and others. It outlines the evaluation process including history, physical exam, ECG, and cardiac monitoring. Further tests like tilt table testing and electrophysiology studies may be used depending on the suspected cause to determine the etiology and appropriate treatment. The history is critical to differentiate syncope from other mimics and identify high-risk patients who require more extensive cardiac evaluation and monitoring.
Heart pathology

This document discusses various types of heart disease, including myocarditis, arrhythmia, cardiac failure, ischemic heart disease, and myocardial infarction. It provides details on:
- Causes of myocarditis including various infectious and non-infectious agents
- Classification of myocarditis and cardiac failure based on factors like duration, etiology, and location of failure
- Symptoms of cardiac failure like shortness of breath, fatigue, and edema
- Causes, symptoms, and signs of arrhythmias, ischemic heart disease, and myocardial infarction
- Types of arrhythmias based on the cardiac function affected - automatism, conductivity, excitability, or contractility
Stroke management 

This is a short presentation at Down Town Hospital clinical meeting for DNB Medicine students. It dose not cover the all aspects of stroke care especially Thrombolysis, since it is difficult to practice for Medical specialist, and ischemic stroke is not common in North East India
Similar to Stoke pathophysiology-1228539935337551-8 (20)
Cardiovascular pathology coronary heart disease finale

Cardiovascular pathology coronary heart disease finale
Anti-Ischemics | Mechanism | Ischemia | Signs & Symptoms

Anti-Ischemics | Mechanism | Ischemia | Signs & Symptoms
More from jilly17
Presentation community prep sept 2011

This document provides information about community nursing placements for students, including an overview of community healthcare services, the roles of various community-based healthcare professionals, potential learning opportunities in a community placement, guidance on medication administration, and contact details for placement supervisors. Students may provide care to patients with long-term conditions and observe coordinated case management approaches. While students cannot practice independently, they can gain supervised experience administering some medications and providing other direct care.
References 2203 keep

This document provides 10 references related to research on mixed-sex hospital wards and patient privacy and dignity. The references are from nursing and medical journals, news articles, and books on research methods from 2010 back to 1994. Sources include qualitative and quantitative studies, literature reviews, and guidance documents from the UK Department of Health.
References 2730

This document provides 27 references on topics related to clinical governance, interprofessional working, high quality care, dignity in healthcare, and the relationship between environment and health. Some key references include Donaldson and Gray (1988) on clinical governance, Hewson (2004) on interprofessional working, and Mackay, Soothill, and Wedd (1995) on the context for interprofessional collaboration. The references cover a range of years from 1988 to 2005 and include journal articles, books, reports, and websites.
References for critiquing research

This document provides 6 references for critiquing nursing research, including books and journal articles. The references include Parahoo's book on nursing research principles and processes, an article by Caldwell et al. on developing a framework for critiquing health research, an online source from Holland and Rees on nursing evidence-based practice skills, guidelines from the Royal College of Nursing on peri-operative fasting, and books by Strauss and Corbin on grounded theory and Kvale on qualitative research interviewing.
Research critique front page

This research critique analyzes a study on pre-operative fasting for elective surgical patients. The critique was written by Jill Wilkes for her NIP 2203 course, with a word count of 1,903 words. The tutor for the assignment was Chrysli Leliopoulou.
Sampling1[1]![Sampling1[1]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Sampling1[1]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of a population to make inferences about the whole population. It allows researchers to study populations that would be too large or impractical to study in their entirety. There are two main types of sampling - probability sampling, which allows results to be generalized to the larger population, and non-probability sampling, which is typically used for qualitative research where generalizability is not the goal. Sample size and how representative the sample is of the overall population impacts how well results can be generalized.
Shortened placement handbook updated sept 2011

The document provides guidance and learning opportunities for nursing students completing community placements. It discusses several types of community placements including primary health care, sexual health clinics, practice nursing, community nursing, palliative care, and placements with health visitors. For each placement type, it lists the services provided, roles of healthcare professionals, and potential learning opportunities for students such as observing clinical procedures, developing communication skills, and exploring multidisciplinary teamwork. Guidelines are also provided on home visiting, practice nursing, and medicine administration in the community setting.
Group work of research

This feasibility presentation discusses language barriers faced by non-English speaking patients in healthcare environments. It notes issues such as poor communication, increased patient stress, and negative impacts on healthcare experiences due to language barriers. The presentation recommends further intervention and comparative studies are needed to develop new solutions to address the increasing challenge of language barriers within primary care consultations.
Gastro

This document discusses the management of acute upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage. It notes that close monitoring is needed to determine the degree of blood loss, source of bleeding, and risk of early re-bleeding. It also stresses the importance of clear communication and management plans between physicians, surgeons, and staff. The nurse must focus on monitoring the patient's condition through frequent observations and reassuring signs like decreasing pulse and resolving hypotension or respiratory issues. Intensive monitoring may distress elderly patients, so constant reassurance and explanations are important. Nursing staff must be available to assist weak and debilitated patients who are at risk of further bleeding.
Feasibility study

1) The author conducted a feasibility study on whether patients' dignity is compromised on mixed-sex wards. They observed placements that single-sex wards provided a more comfortable environment.
2) The author searched literature databases using the PICO framework with keywords like "dignity", "patients", "mixed-sex wards", and narrowed results by changing Boolean operators.
3) Five relevant articles were identified that focused on the research question and used qualitative methods like interviews to understand perspectives of patients and nurses. The literature provided evidence that most patients and nurses prefer single-sex wards.
More from jilly17 (10)
Recently uploaded
Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...

Learn about body grief and ways to cope with it. We will also explore methods to heal from this challenging experience.
ABDOMINAL TRAUMA in pediatrics part one.

Abdominal trauma in pediatrics refers to injuries or damage to the abdominal organs in children. It can occur due to various causes such as falls, motor vehicle accidents, sports-related injuries, and physical abuse. Children are more vulnerable to abdominal trauma due to their unique anatomical and physiological characteristics. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, tenderness, distension, vomiting, and signs of shock. Diagnosis involves physical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Management depends on the severity and may involve conservative treatment or surgical intervention. Prevention is crucial in reducing the incidence of abdominal trauma in children.
Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade

Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidadeProf. Marcus Renato de Carvalho
Recomendações da OMS sobre cuidados maternos e neonatais para uma experiência pós-natal positiva.
Em consonância com os ODS – Objetivos do Desenvolvimento Sustentável e a Estratégia Global para a Saúde das Mulheres, Crianças e Adolescentes, e aplicando uma abordagem baseada nos direitos humanos, os esforços de cuidados pós-natais devem expandir-se para além da cobertura e da simples sobrevivência, de modo a incluir cuidados de qualidade.
Estas diretrizes visam melhorar a qualidade dos cuidados pós-natais essenciais e de rotina prestados às mulheres e aos recém-nascidos, com o objetivo final de melhorar a saúde e o bem-estar materno e neonatal.
Uma “experiência pós-natal positiva” é um resultado importante para todas as mulheres que dão à luz e para os seus recém-nascidos, estabelecendo as bases para a melhoria da saúde e do bem-estar a curto e longo prazo. Uma experiência pós-natal positiva é definida como aquela em que as mulheres, pessoas que gestam, os recém-nascidos, os casais, os pais, os cuidadores e as famílias recebem informação consistente, garantia e apoio de profissionais de saúde motivados; e onde um sistema de saúde flexível e com recursos reconheça as necessidades das mulheres e dos bebês e respeite o seu contexto cultural.
Estas diretrizes consolidadas apresentam algumas recomendações novas e já bem fundamentadas sobre cuidados pós-natais de rotina para mulheres e neonatos que recebem cuidados no pós-parto em unidades de saúde ou na comunidade, independentemente dos recursos disponíveis.
É fornecido um conjunto abrangente de recomendações para cuidados durante o período puerperal, com ênfase nos cuidados essenciais que todas as mulheres e recém-nascidos devem receber, e com a devida atenção à qualidade dos cuidados; isto é, a entrega e a experiência do cuidado recebido. Estas diretrizes atualizam e ampliam as recomendações da OMS de 2014 sobre cuidados pós-natais da mãe e do recém-nascido e complementam as atuais diretrizes da OMS sobre a gestão de complicações pós-natais.
O estabelecimento da amamentação e o manejo das principais intercorrências é contemplada.
Recomendamos muito.
Vamos discutir essas recomendações no nosso curso de pós-graduação em Aleitamento no Instituto Ciclos.
Esta publicação só está disponível em inglês até o momento.
Prof. Marcus Renato de Carvalho
www.agostodourado.com
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Swisschem Dermacare has mentioned the List of The Best Antifungal Soap In India 2022. All of these soaps are trusted by various Dermatology Experts.
How STIs Influence the Development of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.pptx

STIs may cause PID. For the both disease, herbal medicine Fuyan Pill can be a solution.
Best Ayurvedic medicine for Gas and Indigestion

Here is the updated list of Top Best Ayurvedic medicine for Gas and Indigestion and those are Gas-O-Go Syp for Dyspepsia | Lavizyme Syrup for Acidity | Yumzyme Hepatoprotective Capsules etc
#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun W...

#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun W...chandankumarsmartiso
#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun Women Seeking Service
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/kqbnxVAZs-0
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/SINlygW1Mpc
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
Histololgy of Female Reproductive System.pptx

Dive into an in-depth exploration of the histological structure of female reproductive system with this comprehensive lecture. Presented by Dr. Ayesha Irfan, Assistant Professor of Anatomy, this presentation covers the Gross anatomy and functional histology of the female reproductive organs. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in medical science, this lecture provides clear explanations, detailed diagrams, and valuable insights into female reproductive system. Enhance your knowledge and understanding of this essential aspect of human biology.
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

It includes regulation of combination products and medical devices. FDA and industry liaisons.
Recently uploaded (20)
Thyroid Gland- Gross Anatomy by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Thyroid Gland- Gross Anatomy by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...

Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...
Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade

Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India
How STIs Influence the Development of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.pptx

How STIs Influence the Development of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.pptx
Vestibulocochlear Nerve by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Vestibulocochlear Nerve by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun W...

#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun W...
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx
Stoke pathophysiology-1228539935337551-8
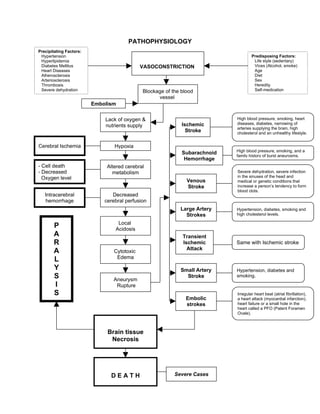
- 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Predisposing Factors: Hyperlipidemia Life style (sedentary) Diabetes Mellitus VASOCONSTRICTION Vices (Alcohol, smoke) Heart Diseases Age Atherosclerosis Diet Arteriosclerosis Sex Thrombosis Heredity Severe dehydration Blockage of the blood Self-medication vessel Embolism Lack of oxygen & High blood pressure, smoking, heart Ischemic diseases, diabetes, narrowing of nutrients supply arteries supplying the brain, high Stroke cholesterol and an unhealthy lifestyle. Cerebral Ischemia Hypoxia High blood pressure, smoking, and a Subarachnoid family history of burst aneurysms. Hemorrhage - Cell death Altered cerebral - Decreased metabolism Severe dehydration, severe infection Oxygen level in the sinuses of the head and Venous medical or genetic conditions that Stroke increase a person’s tendency to form blood clots. Intracerebral Decreased hemorrhage cerebral perfusion Large Artery Hypertension, diabetes, smoking and Strokes high cholesterol levels. Local P Acidosis A Transient R Ischemic Same with Ischemic stroke Attack A Cytotoxic L Edema Y Small Artery Hypertension, diabetes and S Aneurysm Stroke smoking. I Rupture S Irregular heart beat (atrial fibrillation), Embolic a heart attack (myocardial infarction), strokes heart failure or a small hole in the heart called a PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale). Brain tissue Necrosis DEATH Severe Cases
- 2. A stroke is caused by a blocked or bleeding artery in the brain. Most strokes are due to blocked arteries that supply blood to the brain and are called ischemic strokes. Strokes due to bursting of brain blood vessels are called hemorrhagic strokes. Intracerebral hemorrhage is caused by bleeding into the brain itself, while subarachnoid hemorrhage is due to bleeding around the base of the brain. A TIA (transient ischemic attack) is caused by a temporary blockage of blood flow to a blood vessel to the brain lasting less than 24 hours. Another, rarer, form of stroke can occur when a vein (that drains blood out of the brain) is blocked. This is called a venous stroke. Ischemic Stroke This type of stroke is caused by blockage of a blood vessel (artery) supplying the brain. Brain tissue that no longer receives its blood supply can die within a few hours unless something is done to stop the damage. The blockage of arteries can occur in large arteries in the neck or the base of the brain, or in small arteries inside the brain itself. A blood clot can form in the brain or it can form elsewhere and be carried to the brain by an artery and after having an ischemic stroke and the majority of survivors have some long term disability. There are many conditions that increase a person's risk of ischemic stroke. These include high blood pressure, smoking, heart diseases, diabetes, narrowing of arteries supplying the brain, high cholesterol and an unhealthy lifestyle. Treating these conditions can decrease stroke risk. Intracerebral Hemorrhage This type of stroke is caused by the bleeding of a blood vessel within the brain. As a result of the bleeding a blood clot forms in the brain, which puts pressure on the brain and damages it. Although intracerebral hemorrhage is less common than ischemic stroke and it is more serious. The most common cause of intracerebral hemorrhage is high blood pressure. Another cause, especially in younger people with intracerebral hemorrhages, is abnormally formed blood vessels in the brain (vascular malformations or aneurysms).
- 3. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Subarachnoid hemorrhage results from the bleeding of an artery around the base of the brain. It is the least common stroke type, accounting for about 5% of all strokes. The most frequent cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding from an aneurysm. An aneurysm is a weakening and ballooning of a short portion of an artery (similar to a bubble on the side of an old hose). The factors that can increase a person’s risk of this type of stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, and a family history of burst aneurysms. TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) A TIA is like a temporary ischemic stroke. An artery is temporarily blocked, preventing blood from reaching a part of the brain. This lack of blood flow causes that part of the brain to stop functioning. The symptoms of a TIA are the same as symptoms of an ischemic stroke. In a TIA, the blood vessel opens up again, before any permanent injury to the brain occurs and the patient recovers completely. Most TIA symptoms last less than 30 minutes. People who suffer TIA’s are at HIGH RISK OF STROKE soon thereafter. A TIA should lead to immediate medical evaluation to determine its cause and a treatment plan to prevent a stroke from following soon after. Venous Stroke Venous stroke is caused by a blood clot blocking the veins that allow blood to drain out of the brain. (All other strokes are caused by abnormalities of arteries carrying blood to the brain). Venous stroke causes a “back pressure” effect that leads to the stroke. These strokes can be either ischemic or hemorrhagic. Some causes of venous stroke include severe dehydration, severe infection in the sinuses of the head and medical or genetic conditions that increase a person’s tendency to form blood clots.