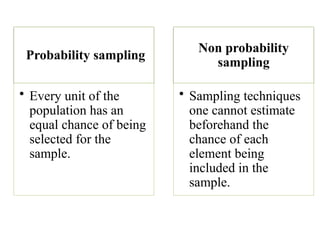
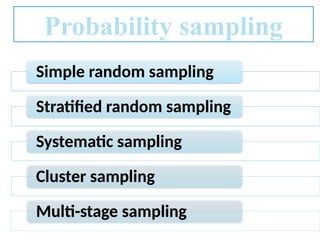
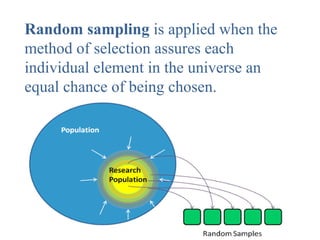
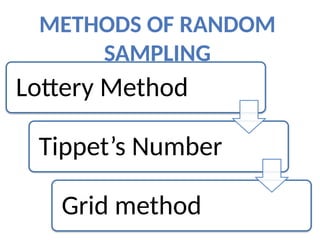
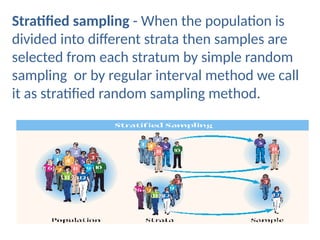
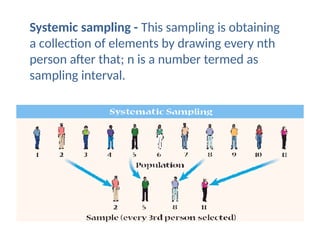
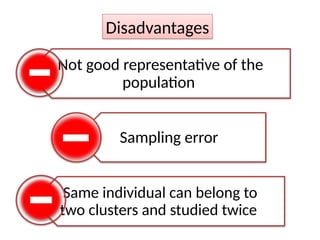
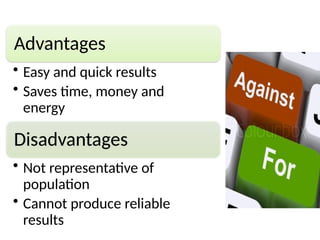
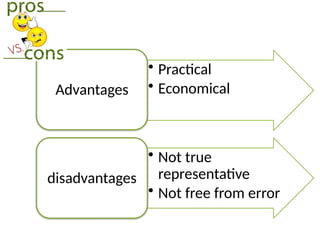
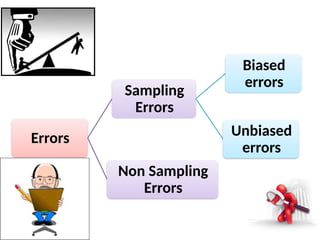
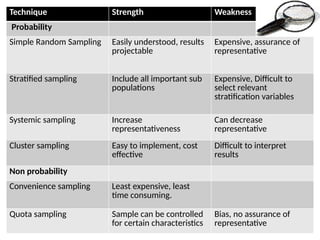
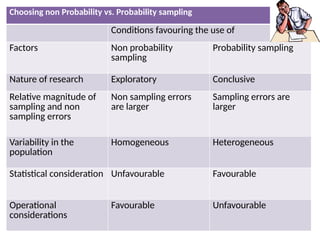
The document discusses various sampling techniques in research, defining population and sample while highlighting the importance of sampling for accuracy, efficiency, and control of errors. It categorizes sampling methods into probability and non-probability techniques, detailing their advantages and disadvantages, including approaches like simple random, stratified, systematic, cluster, and purposive sampling. The text contrasts the circumstances favoring the use of each type based on the nature of research and operational considerations.