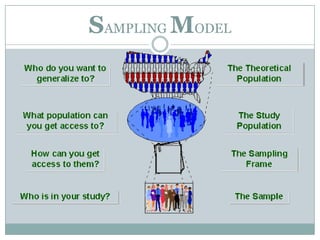
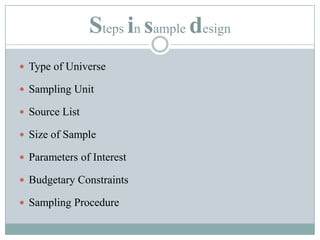
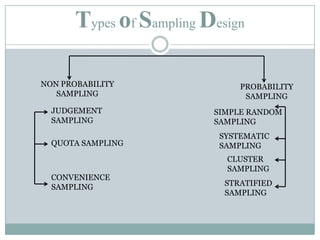
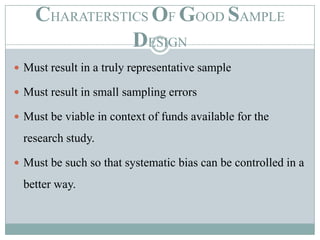
Sampling is used to learn about a population by studying a subset of it. It allows researchers to gather information in a time and cost-effective manner. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every item has an equal chance of being selected, and non-probability sampling, which has no basis for estimating selection probabilities. Some common sampling designs include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and quota sampling. Good sample design ensures representativeness, adequacy, independence, and homogeneity while accounting for resources and study goals.