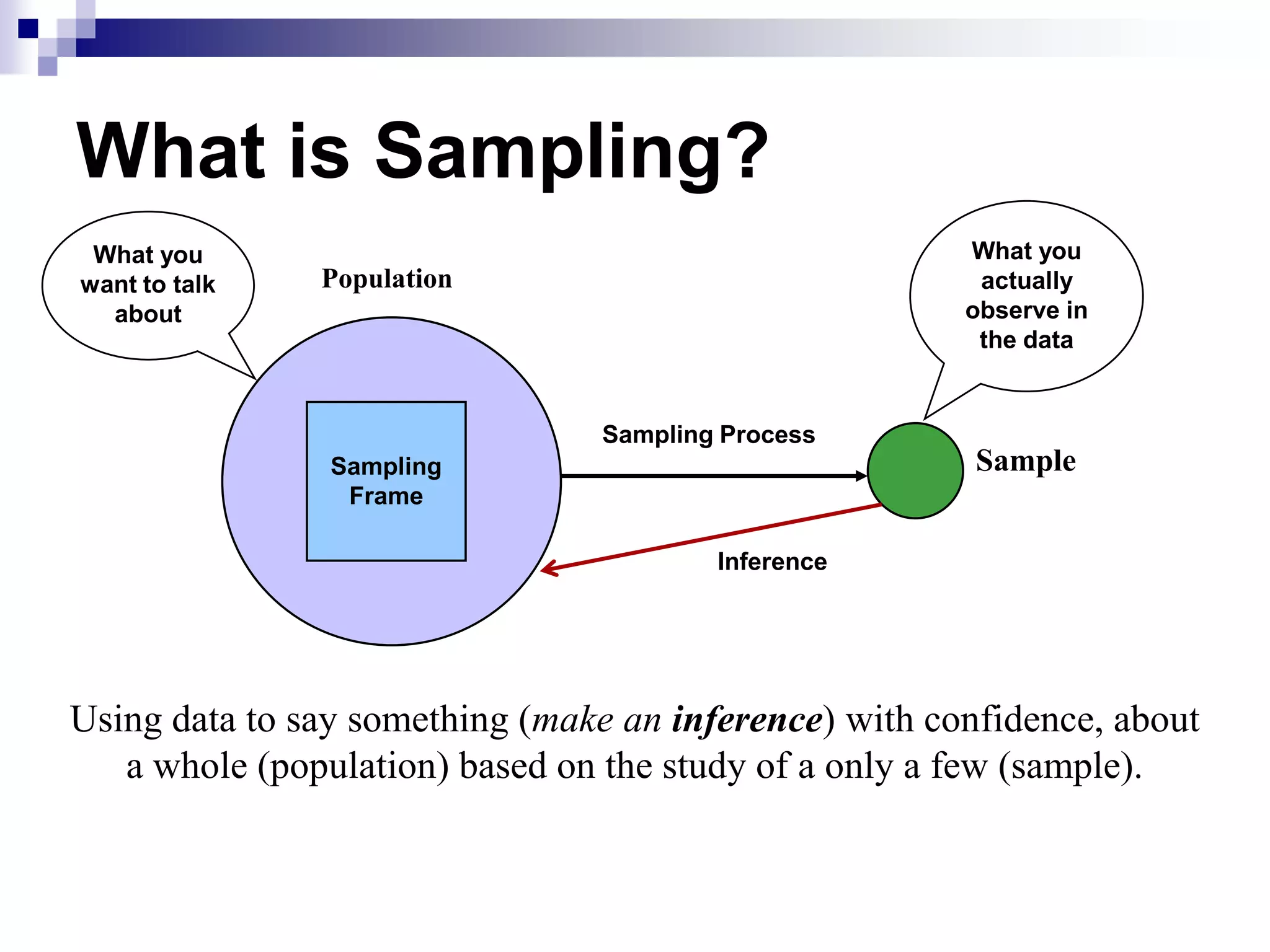
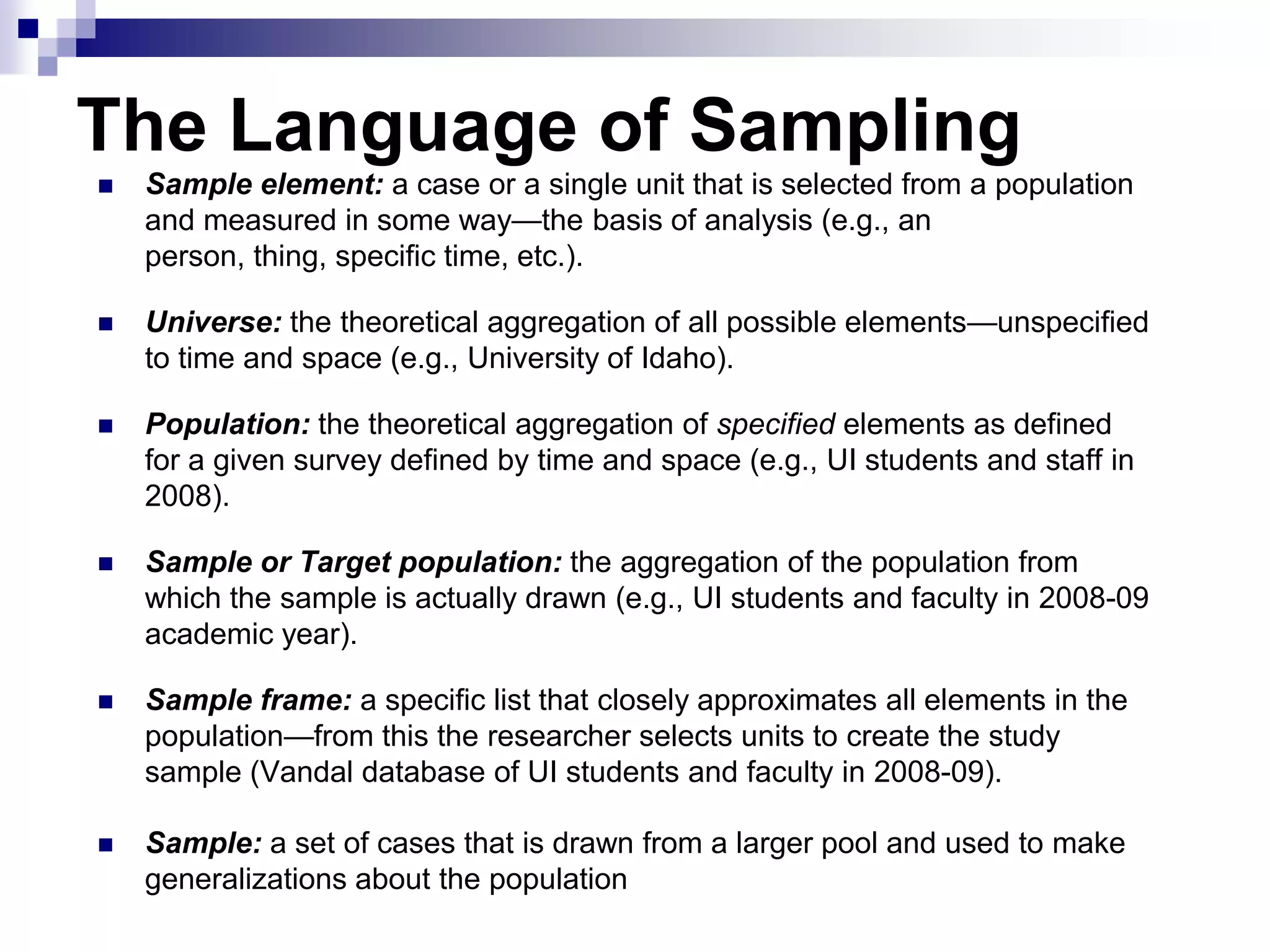
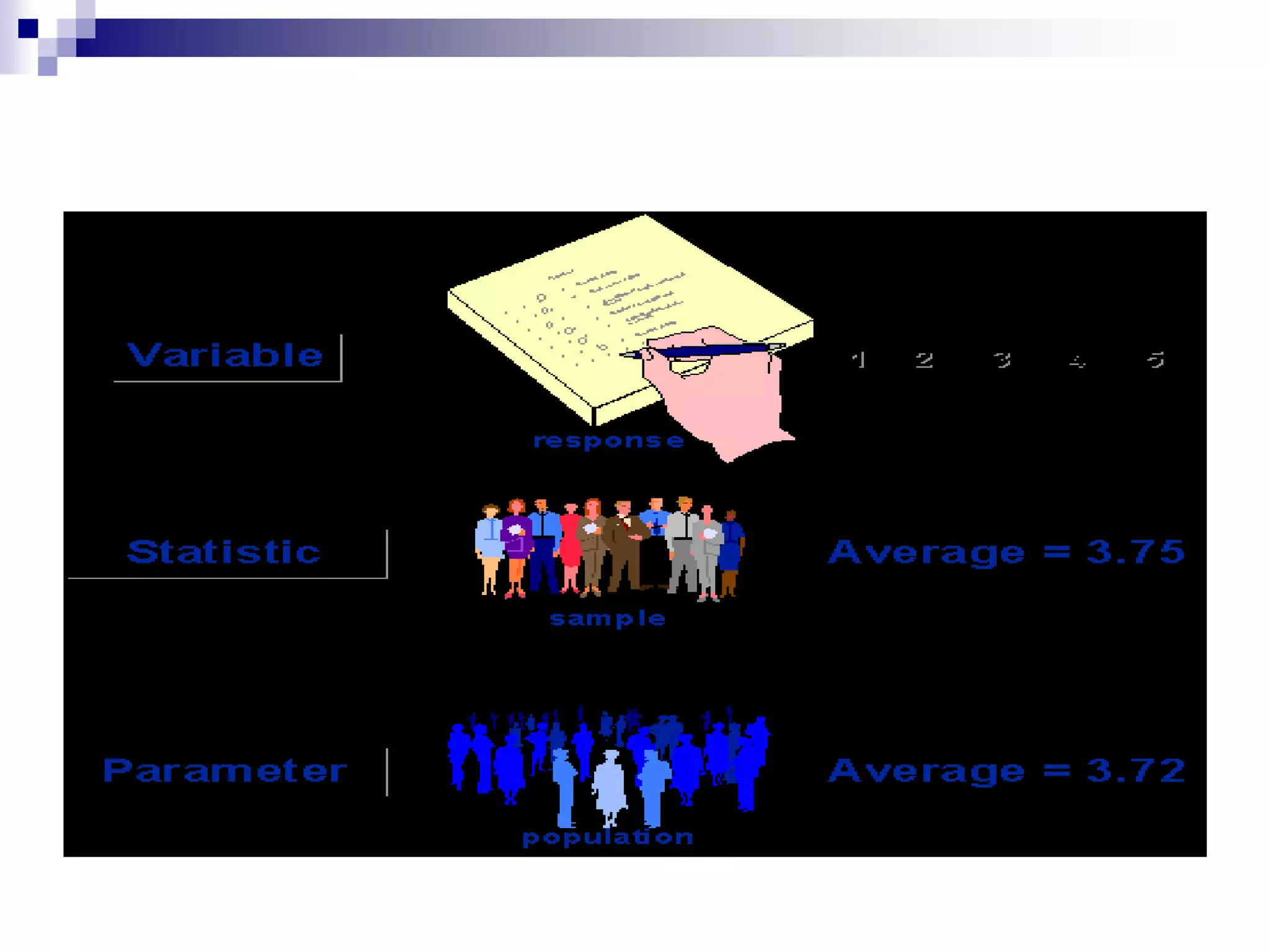
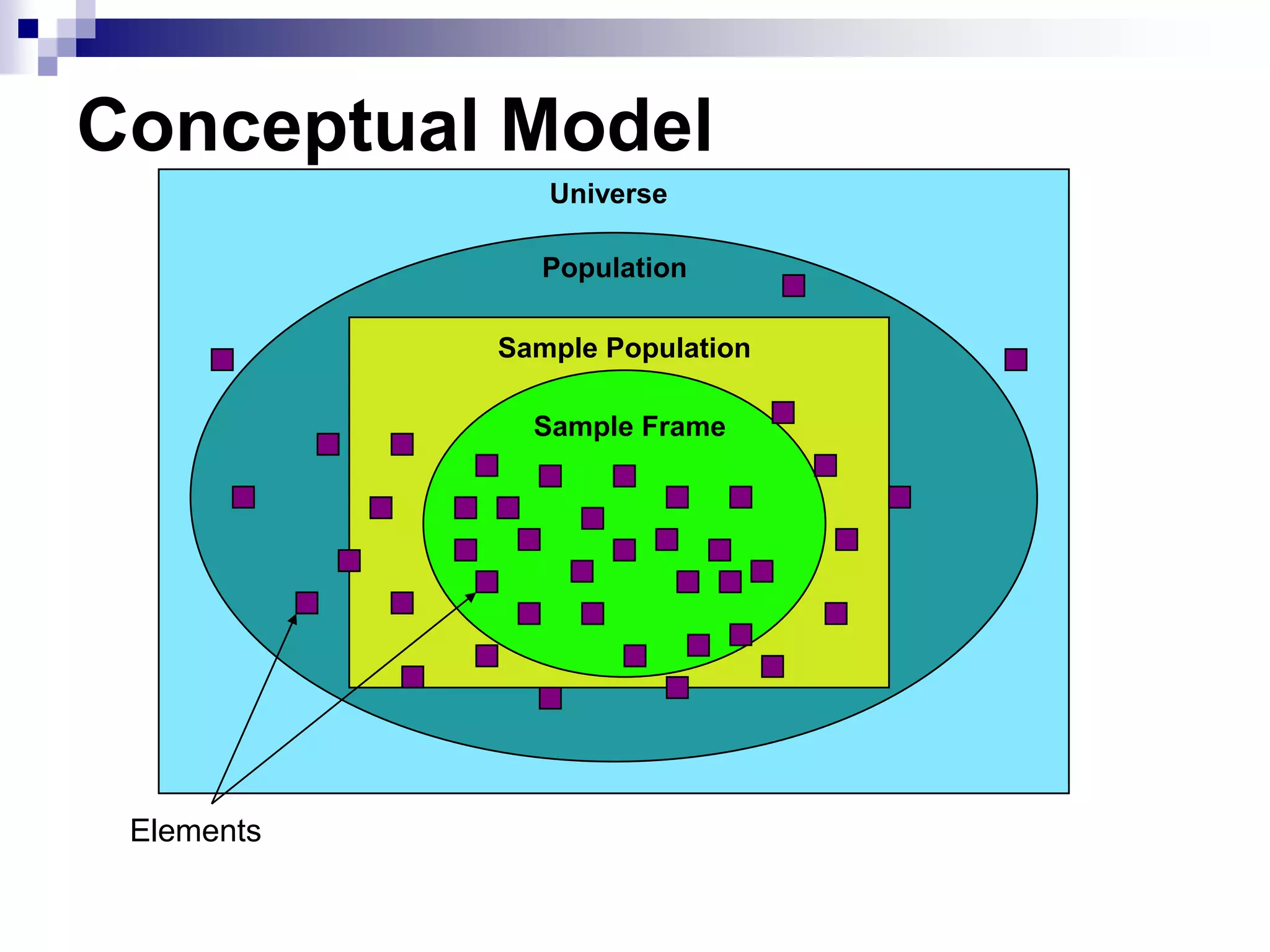
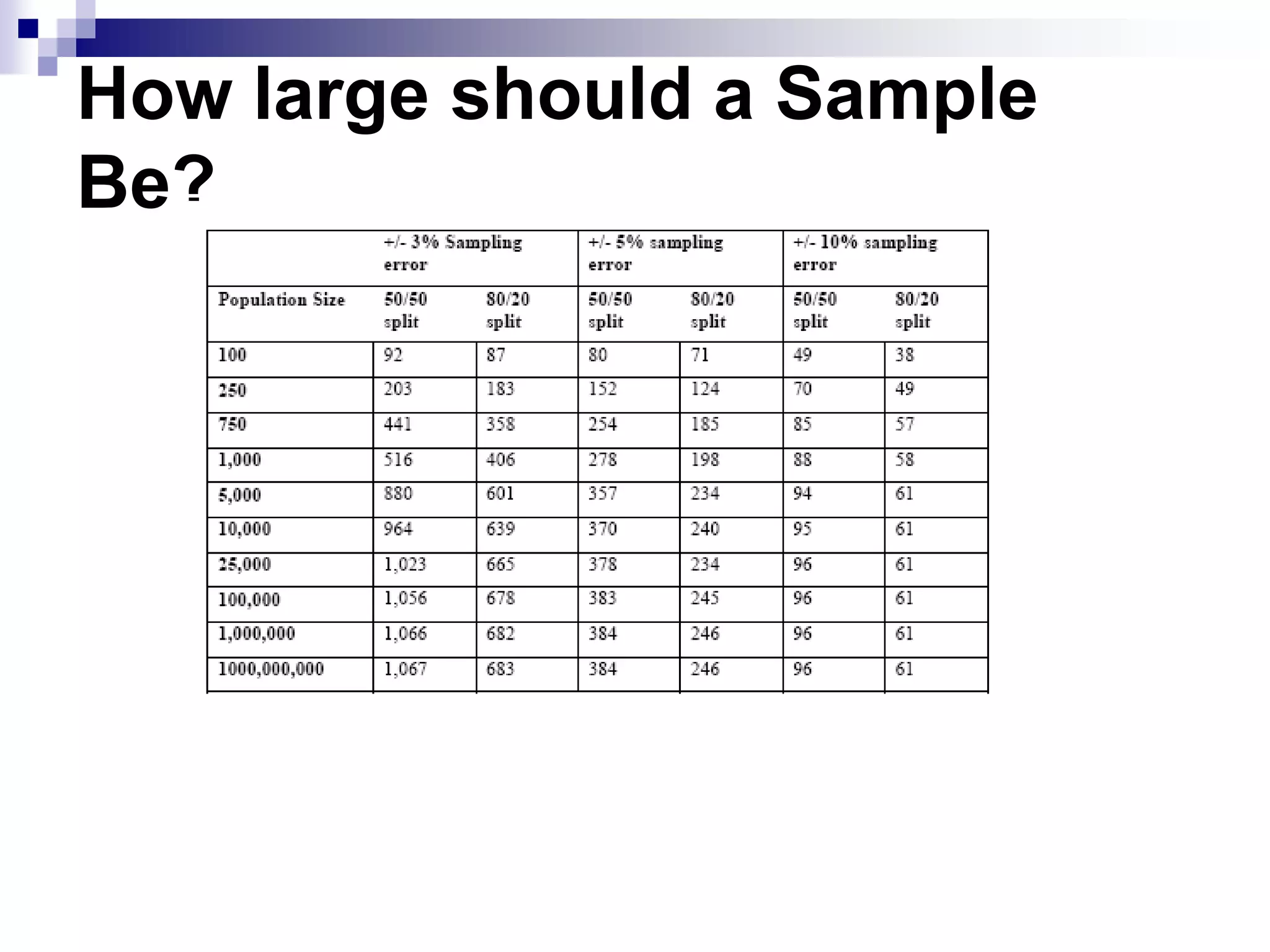
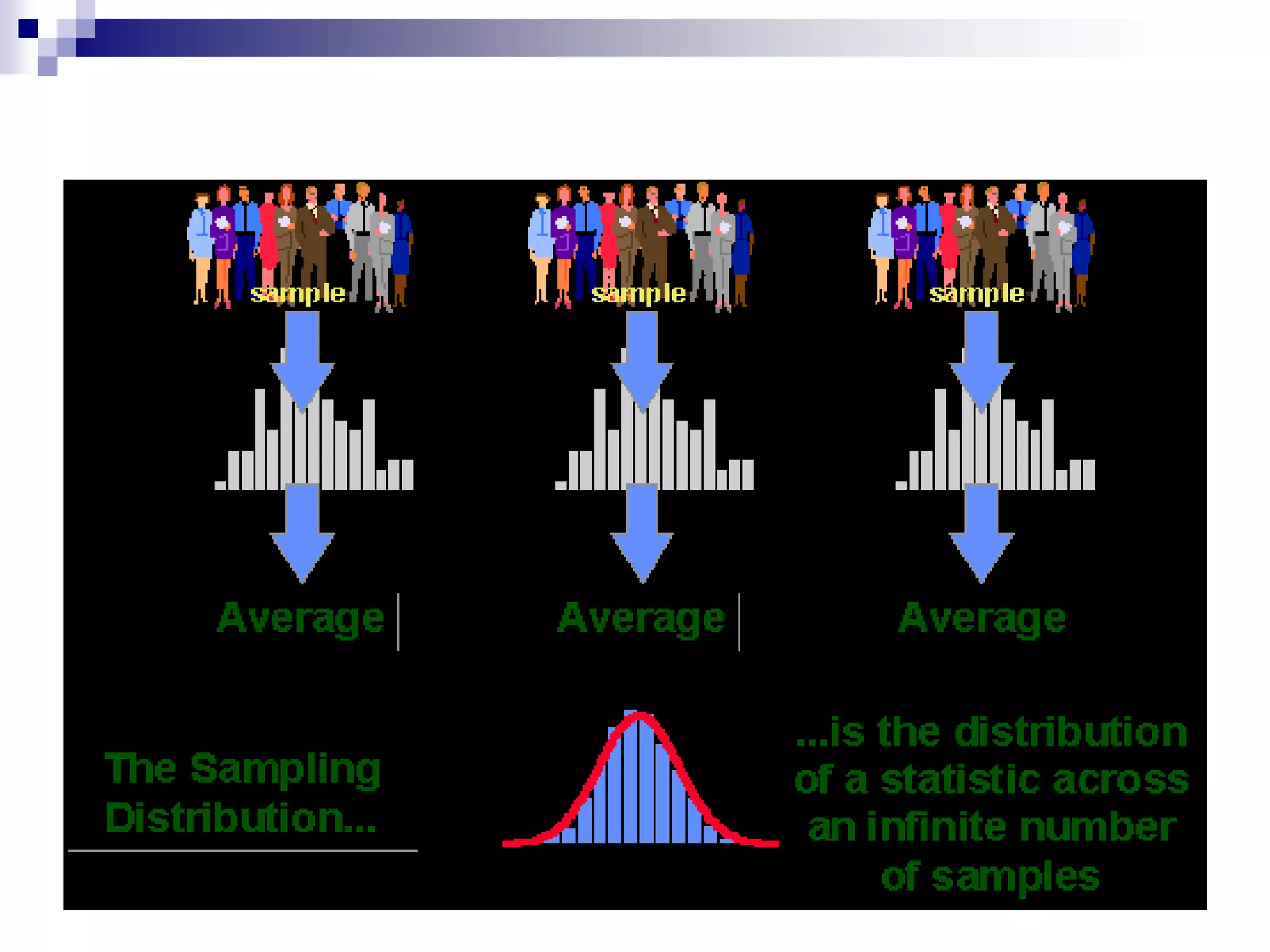
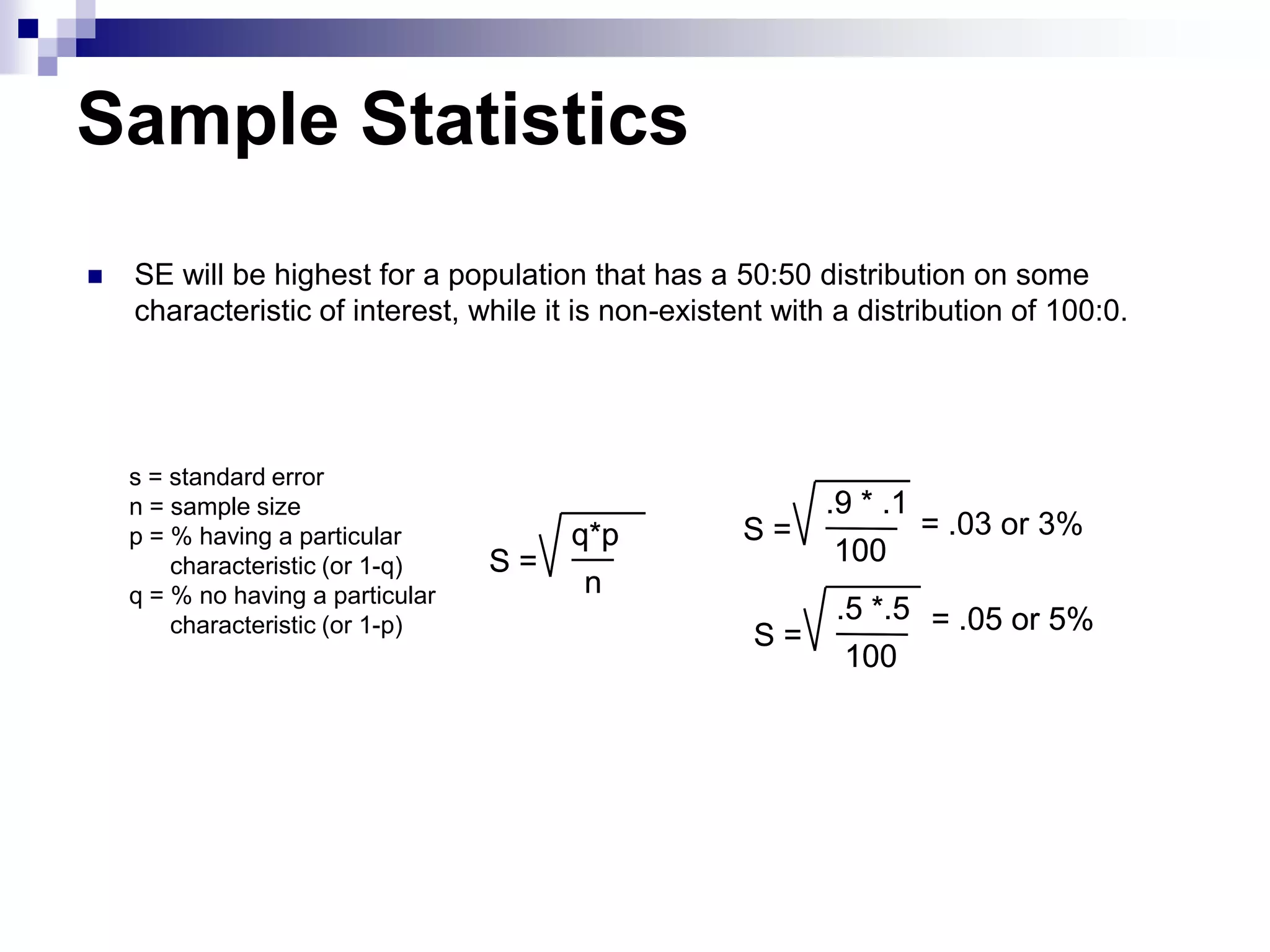
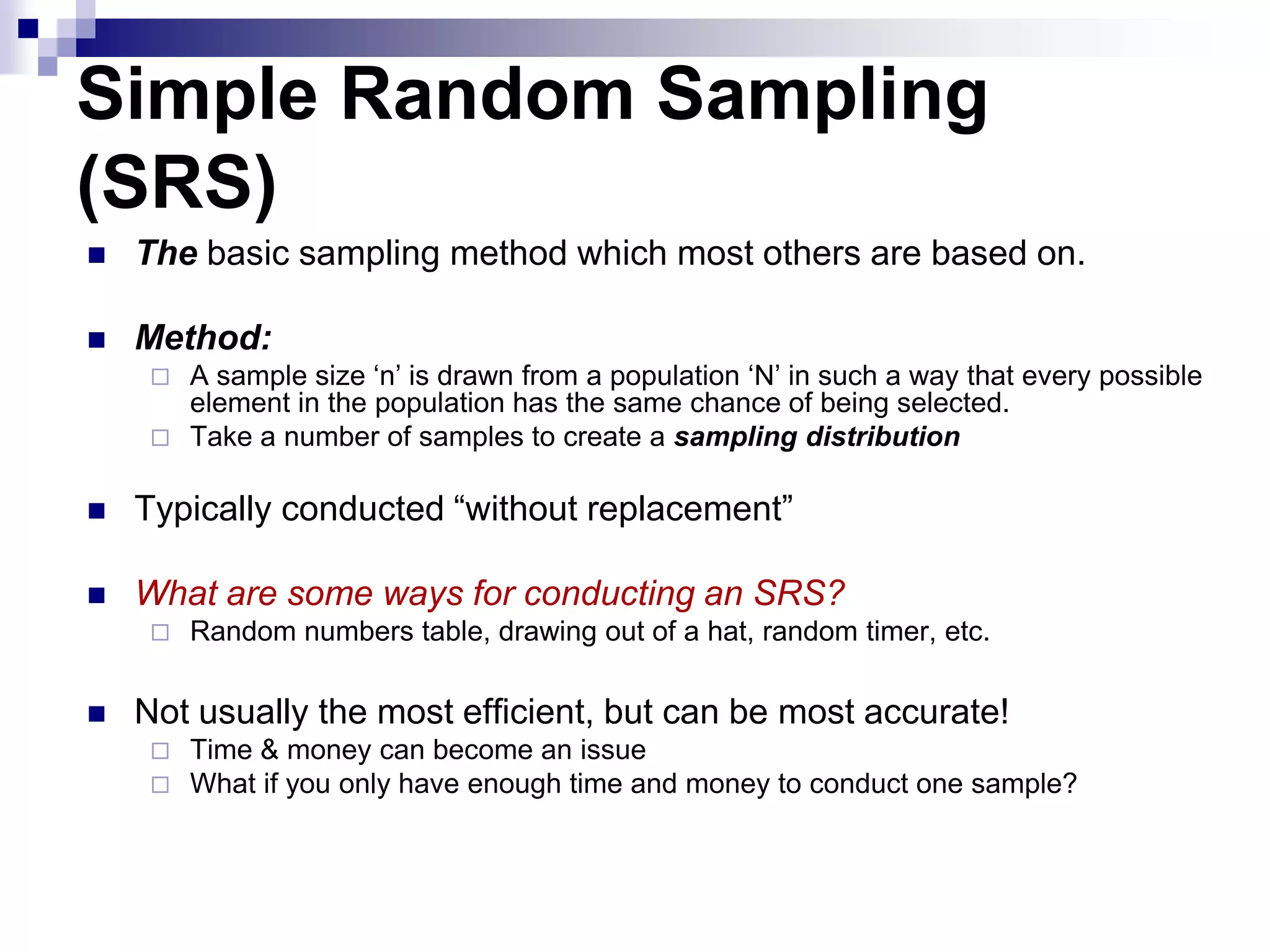
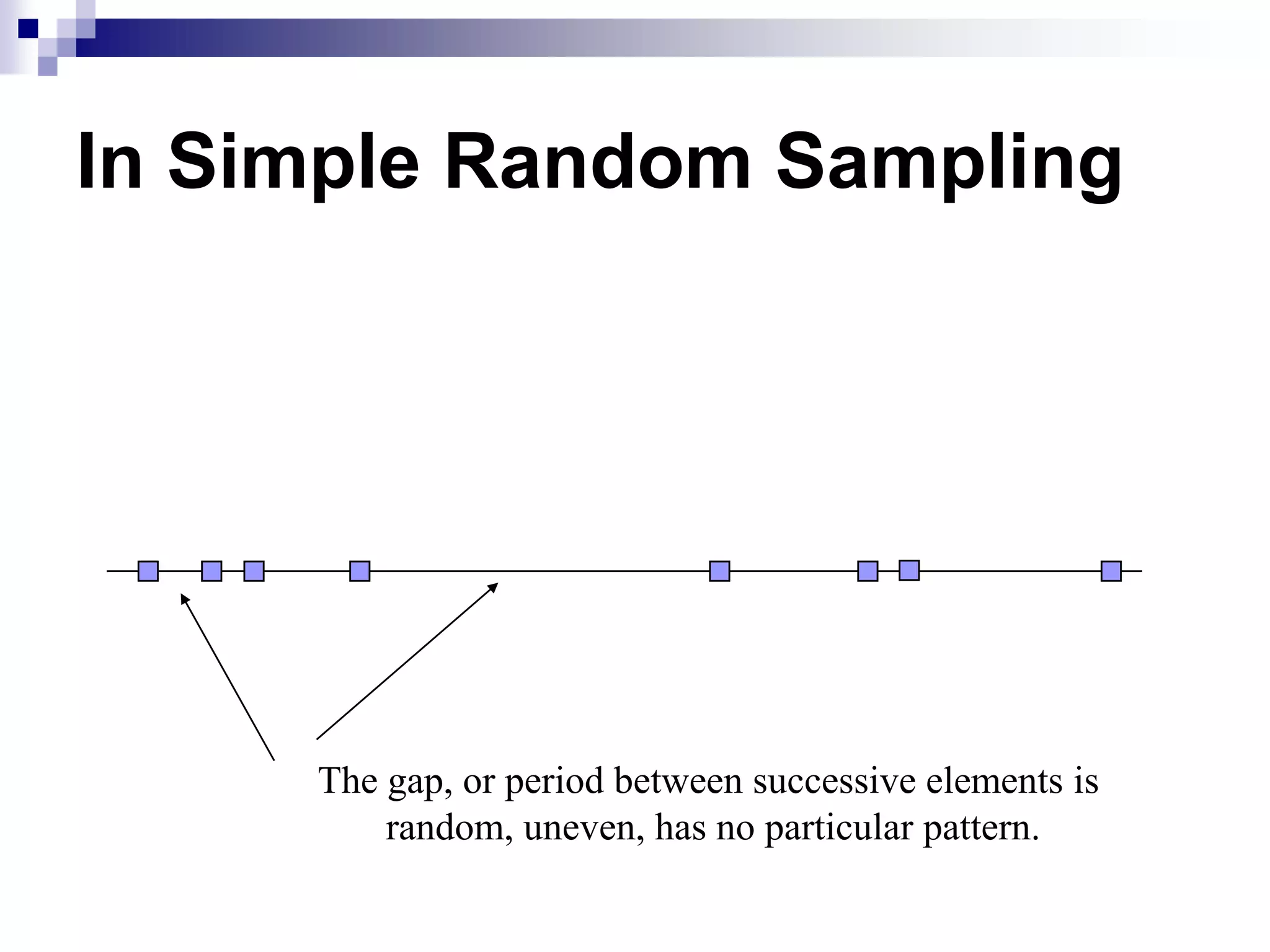
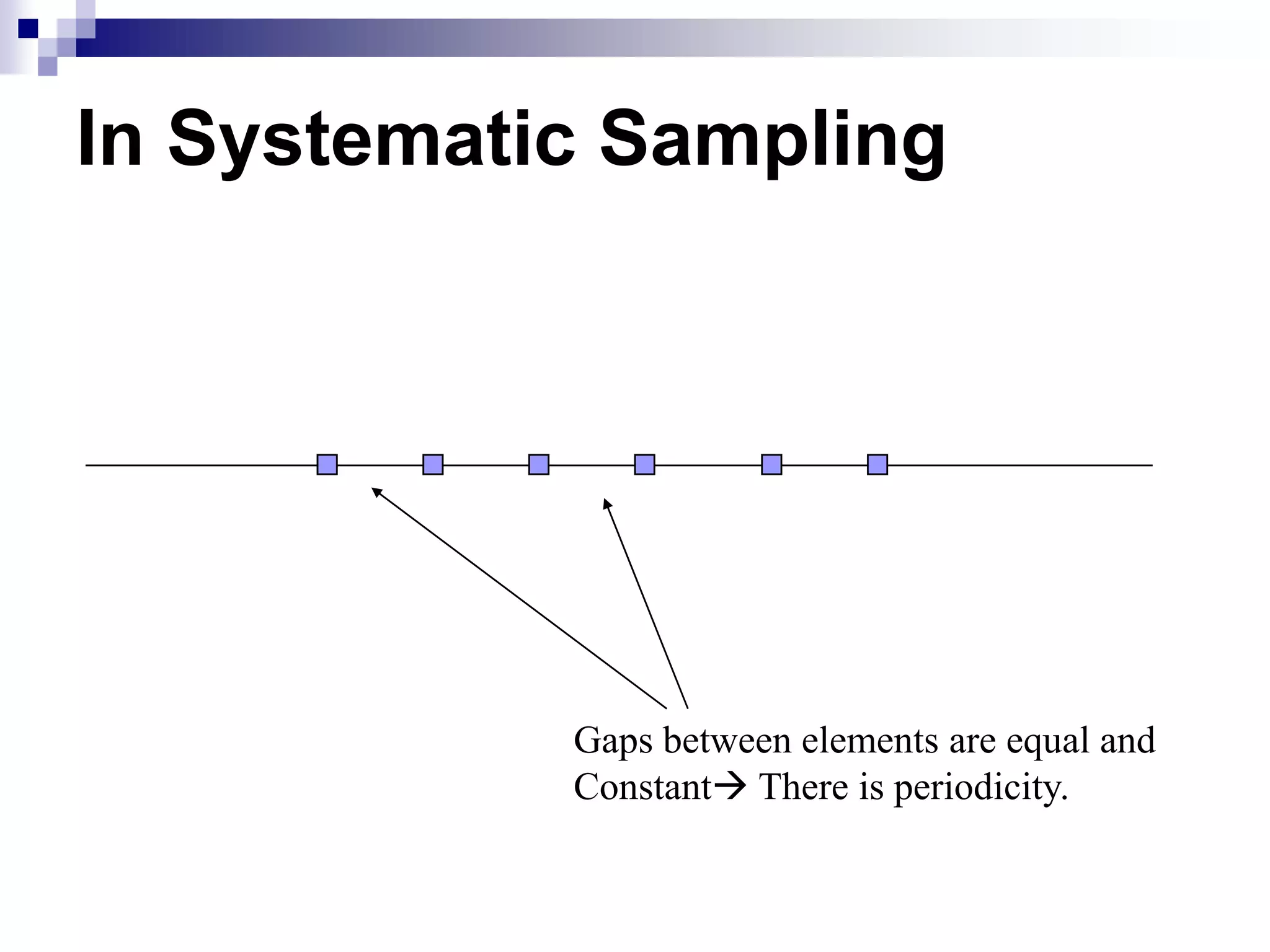
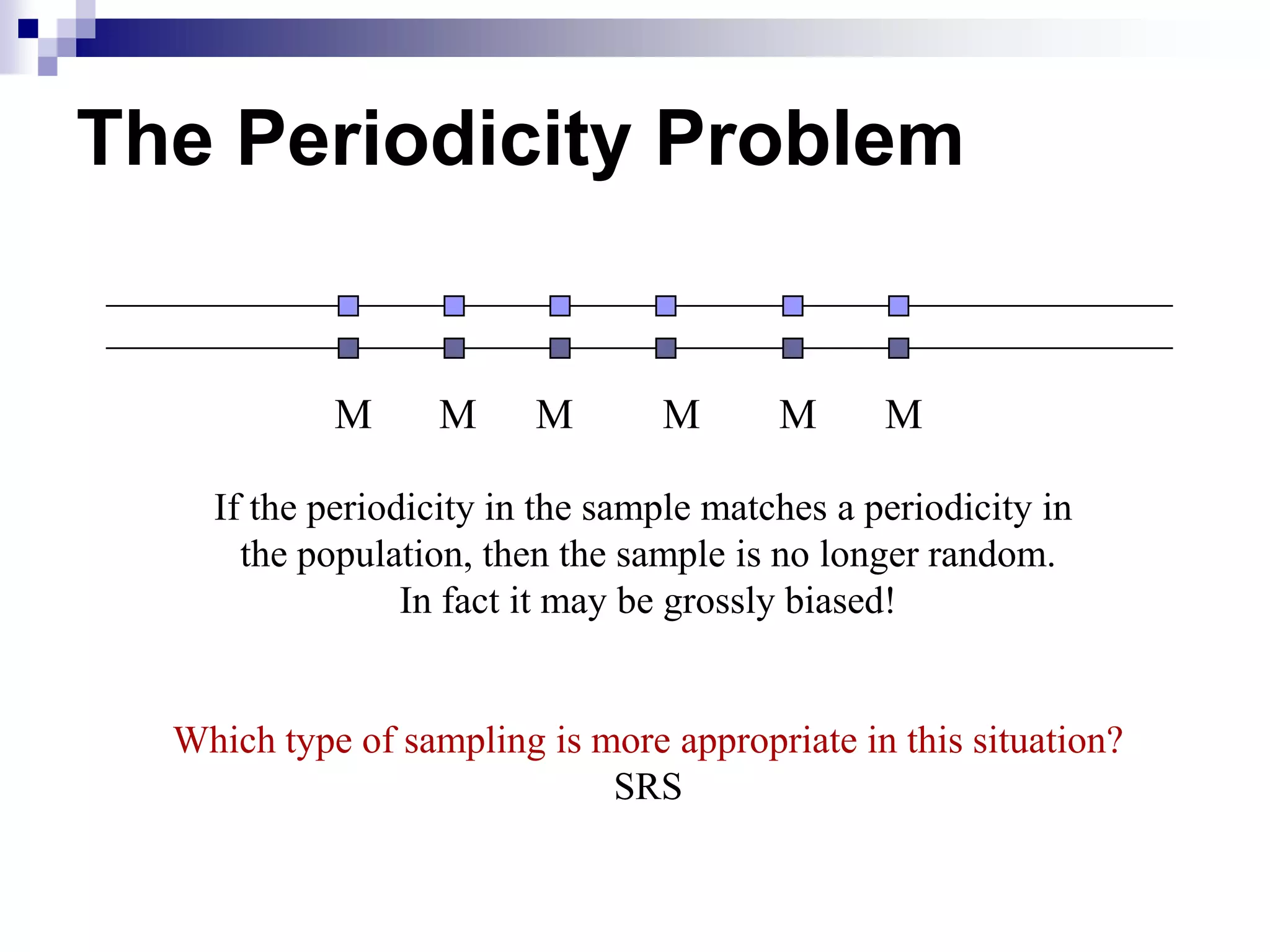
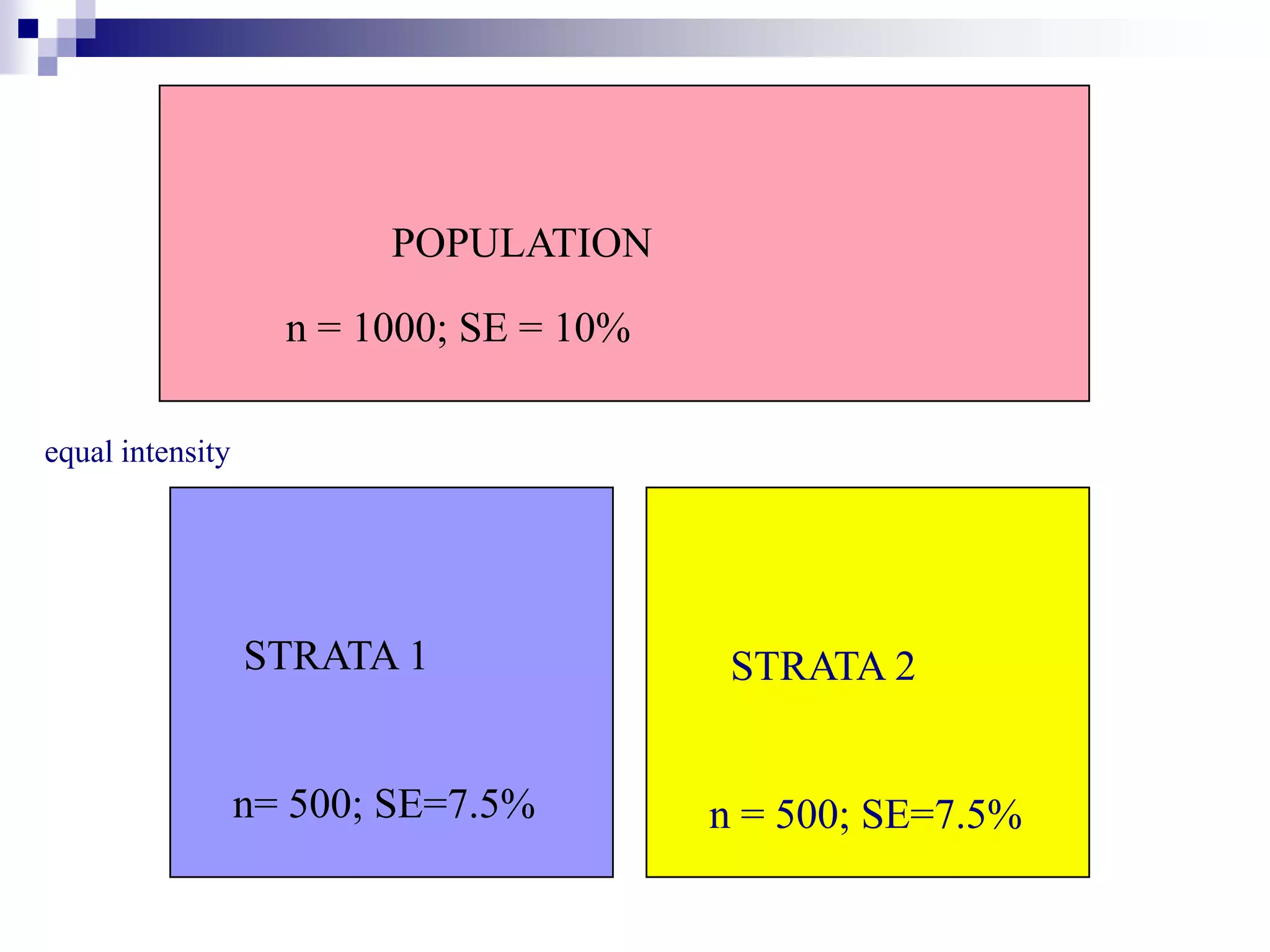
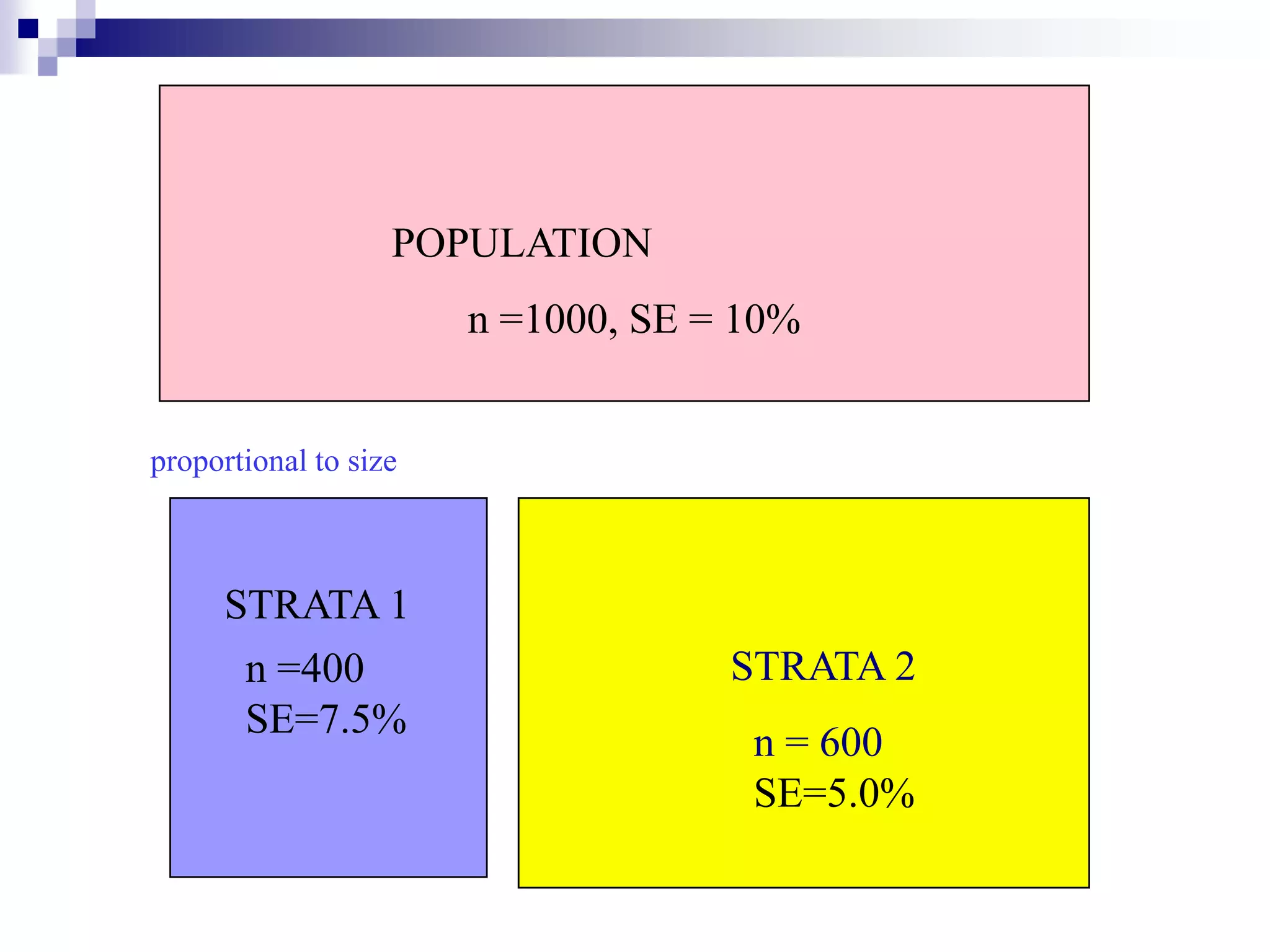
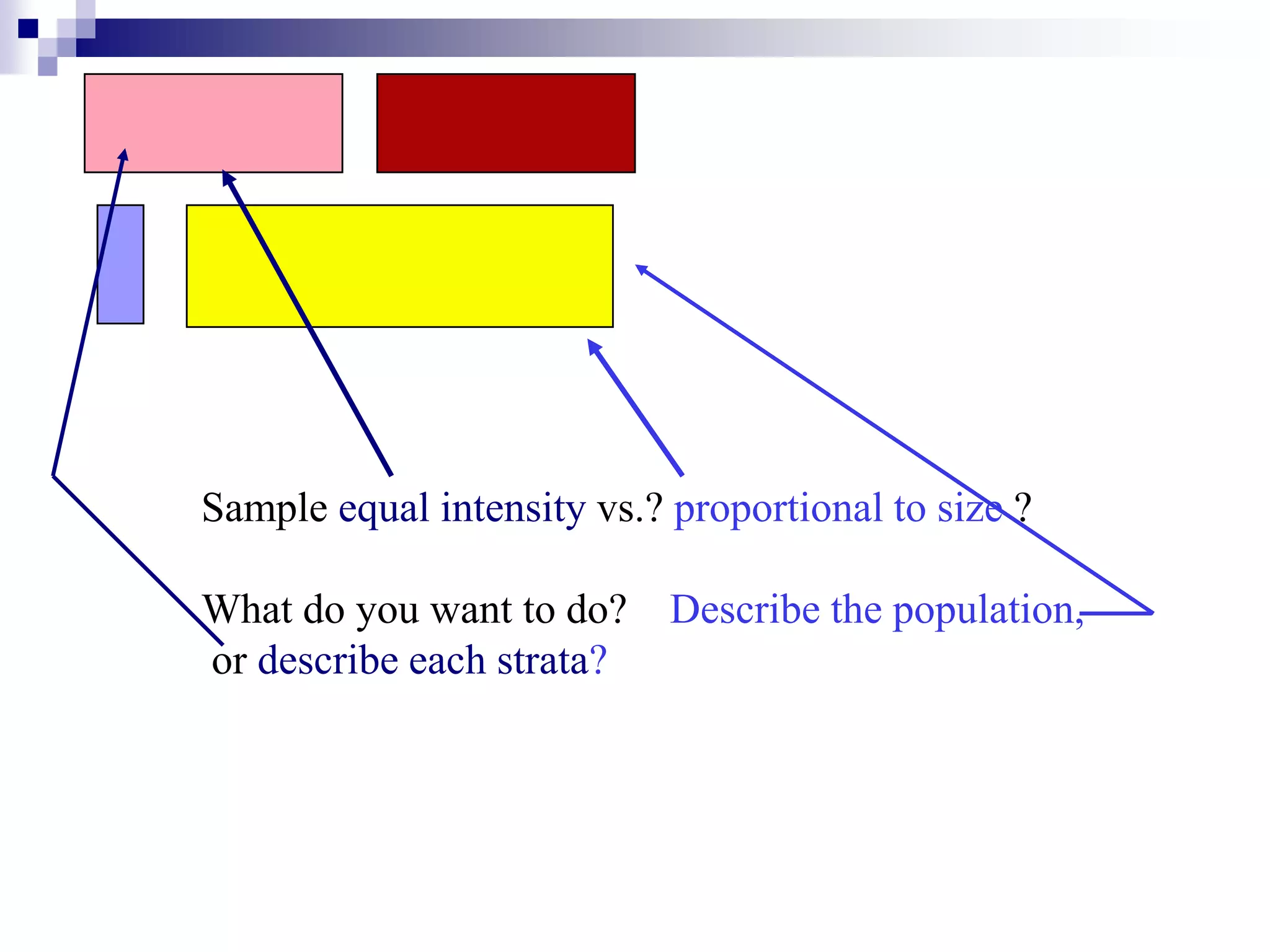
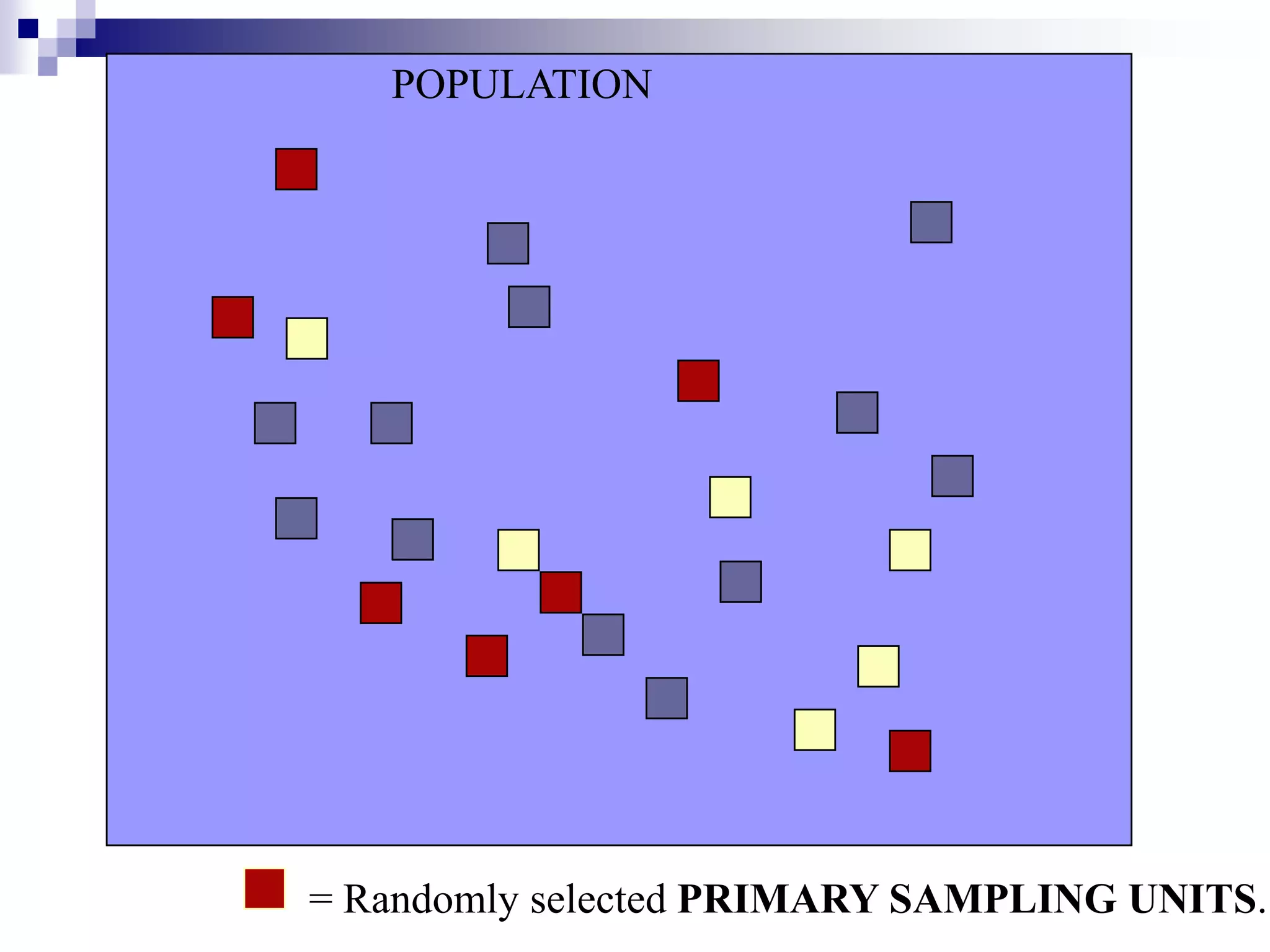
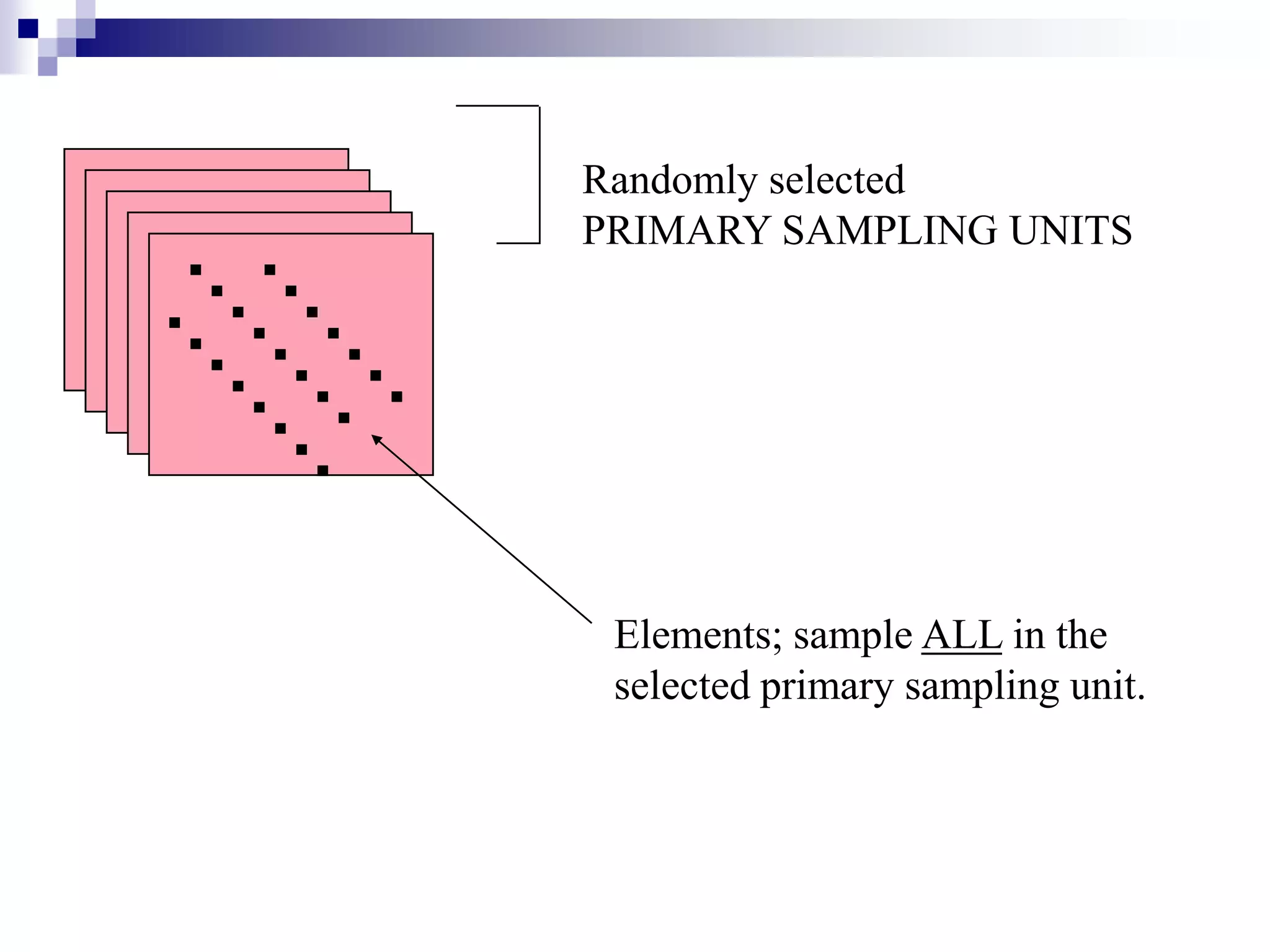
This document discusses key concepts and terminology related to probability sampling. It defines sampling as selecting observations from a population to make inferences about the entire population without bias. There are two main types of sampling: probability and non-probability. Probability sampling involves giving every member of the population an equal chance of being selected, which allows for more accurate inferences. Key concepts discussed include population, sample, parameter, estimate, sampling error, and standard error. The document also covers different probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. It explains how and when each method should be used.