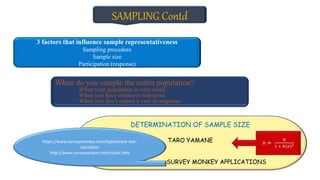
The document discusses various sampling techniques used in research, distinguishing between probability and non-probability sampling methods. It outlines the process of sampling, factors that influence sample representativeness, and when to sample an entire population. Additionally, the document provides a guide on determining sample size and describes specific sampling methods such as simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and others.