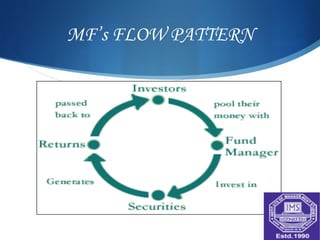
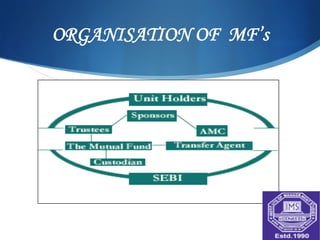
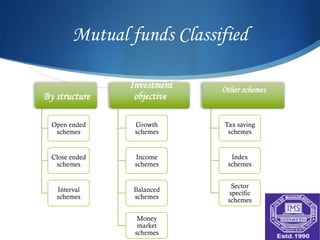
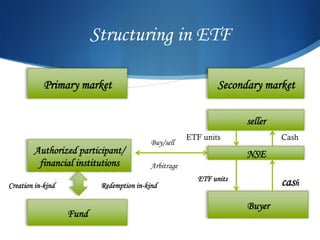
A mutual fund is a vehicle for collective investment that pools money from many investors and invests it in stocks, bonds, and other securities. The document discusses the key entities involved in mutual funds like sponsors, trustees, asset management companies, custodians, and registrars. It also covers the various types of mutual fund schemes such as open-ended, close-ended, index funds, ETFs, tax saving schemes, and more. The advantages of mutual funds include diversification, professional management, liquidity, and lower costs. However, mutual funds also have fees and less control over taxes.