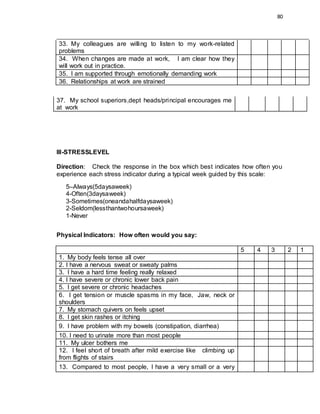
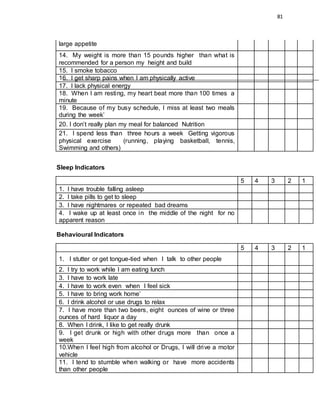
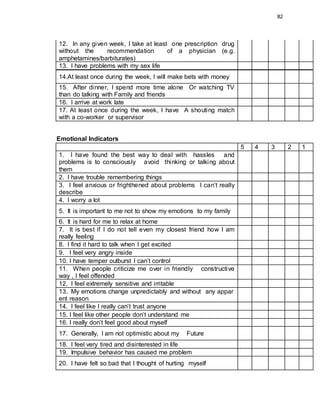
This document provides background information on a study about the relationship between teachers' working conditions and stress levels. It discusses relevant theories on work motivation and stress. The study aims to determine how teachers describe their working conditions and assess their stress levels across physical, sleep, behavioral, and emotional indicators. It also seeks to understand if there is a relationship between working conditions and personal stress levels. The study focuses on teachers from two large public schools in Quezon City, Philippines, with student populations of around 6,000 each.