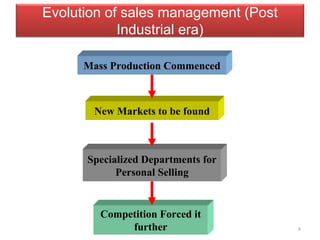
This document outlines the chapter on sales management from a textbook. It discusses the objectives of sales management, the personal selling process, developing personal selling strategies for different competitive environments, determining sales force size and structure, and qualities of successful sales executives. The chapter covers topics like prospecting, approaching customers, presenting, handling objections, and closing sales. It also describes different types of sales organizations and factors to consider when establishing a sales force.