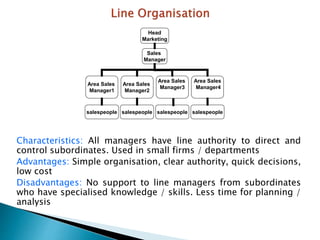
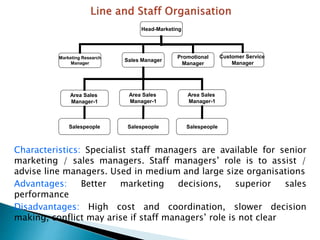
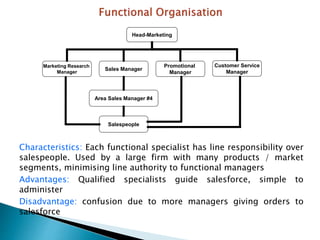
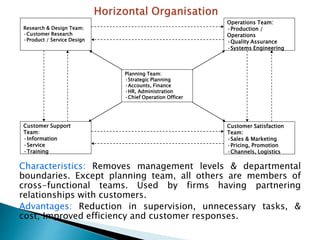
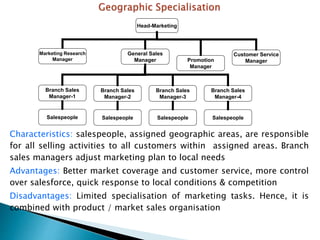
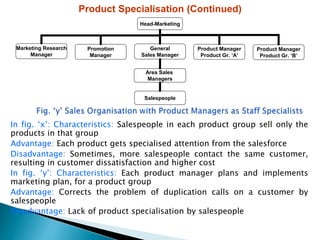
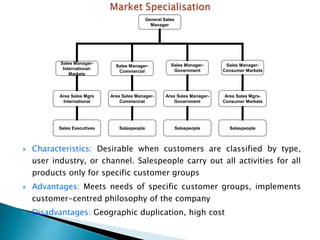
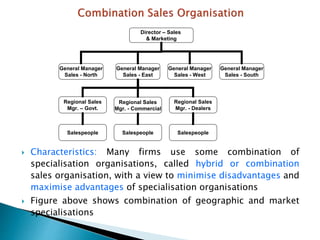
The document discusses various sales management structures and organizations. It describes line, line and staff, functional, horizontal, and specialized (geographical, product, market) organizational structures. Specialized structures can be combined to form hybrid structures. The key aspects of each structure are outlined, including their advantages and disadvantages. Overall, the document provides an overview of different approaches to organizing sales management functions within a company.