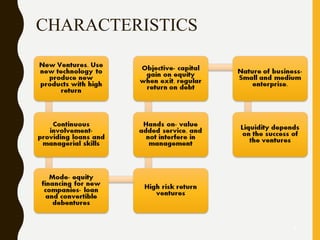
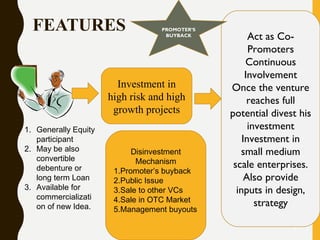
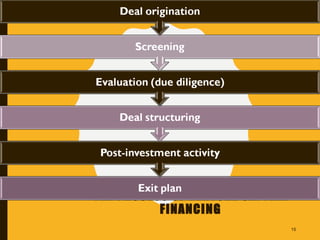
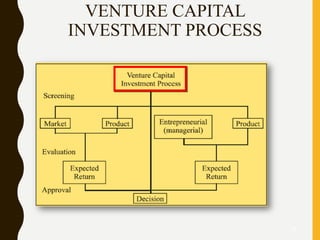
The document provides an overview of venture capital financing, including its definitions, features, characteristics, and stages involved in the financing process. It discusses the evolution of venture capital from the 19th century, its introduction in India in 1987, and various investment methods and regulations. Additionally, it explores the role of venture capitalists, criteria for evaluation, and future prospects in different sectors.