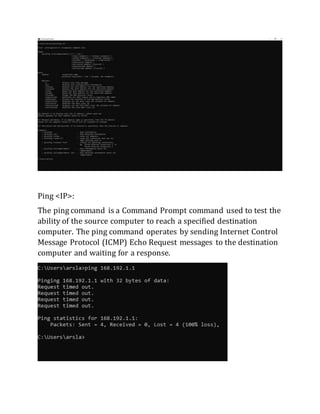
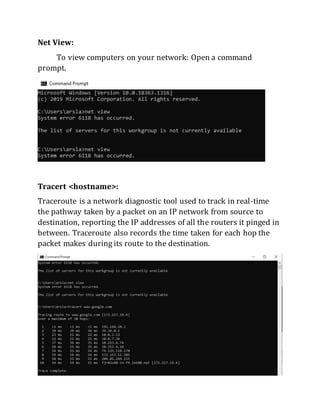
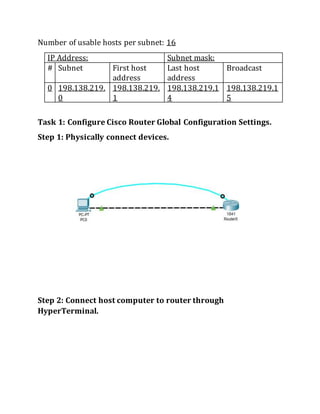
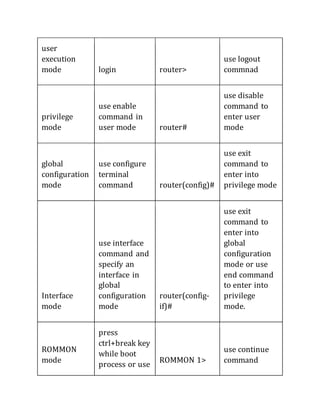
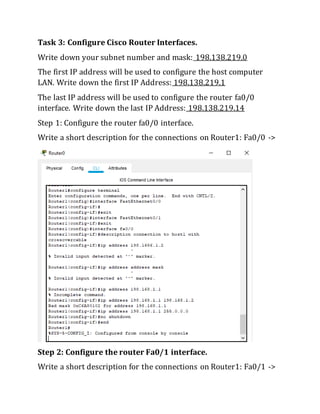
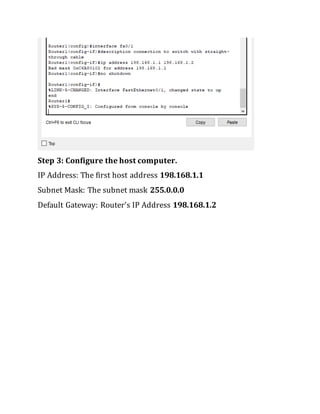
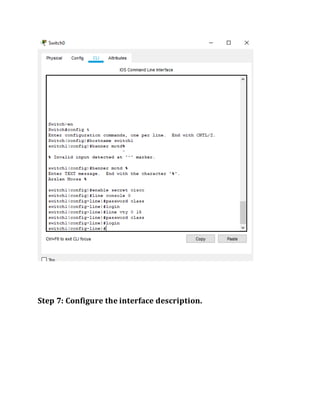
This document contains instructions and configuration steps for configuring Cisco routers and switches. It discusses configuring global settings like hostname and MOTD banners on routers. It also provides steps for configuring router passwords, interfaces with IP addresses, and saving configurations. The document contains tasks for configuring a switch interface description and saving the RAM configuration to NVRAM.