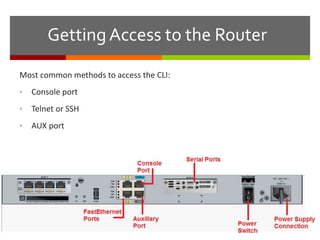
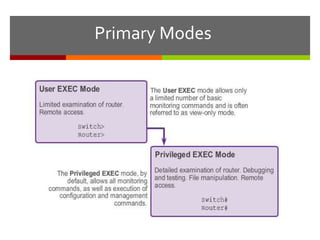
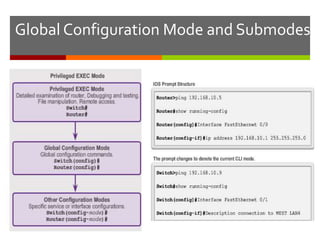
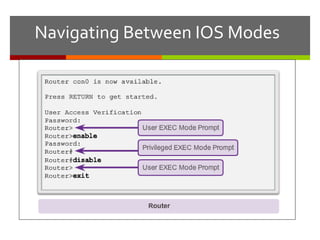
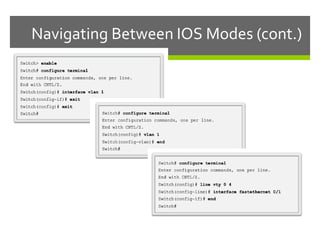
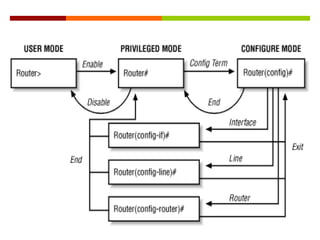
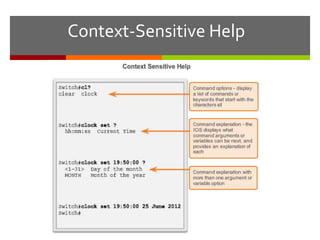
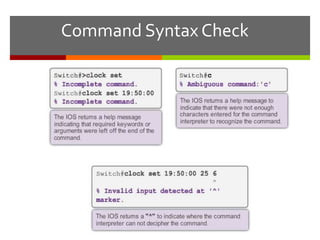
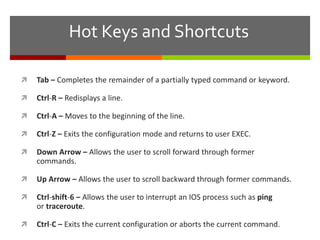
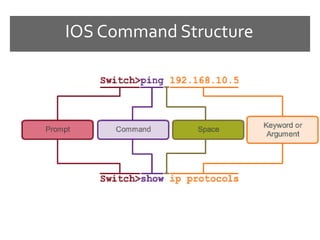
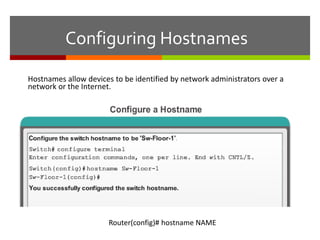
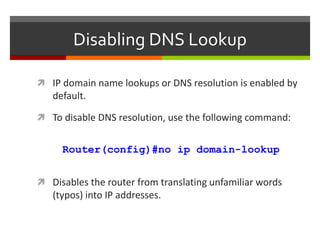
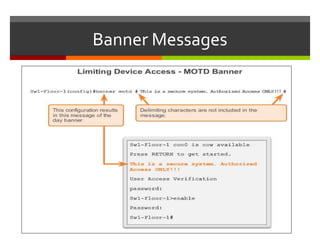
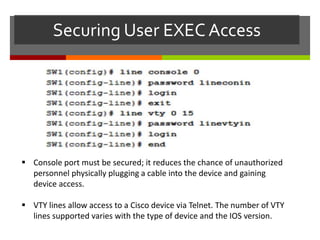
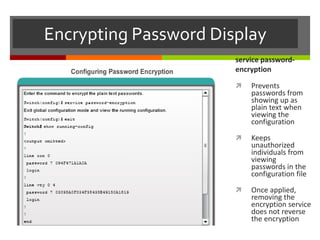
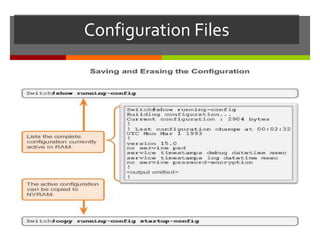
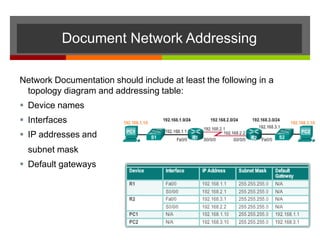
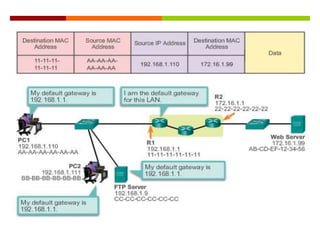
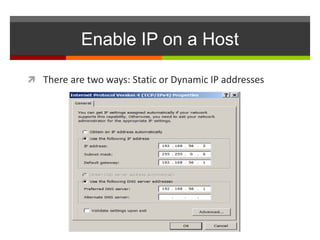
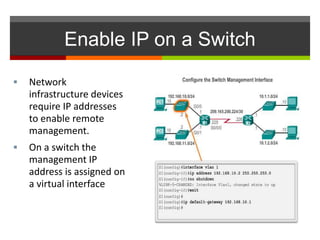
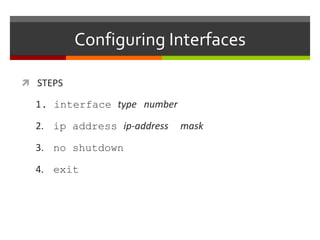
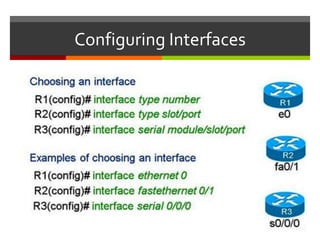
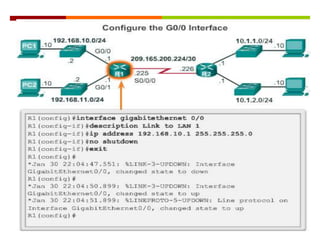
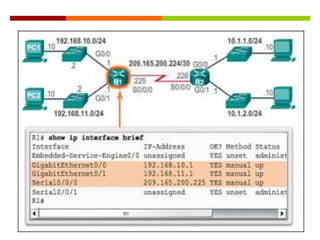
The document discusses router configurations, including accessing the router through the command line interface, different command modes like user EXEC and privileged EXEC, and basic router configurations like setting the hostname, enabling IP on interfaces, and verifying interface settings. It provides instructions on securing device access with passwords, saving configuration files, and documenting network addressing.