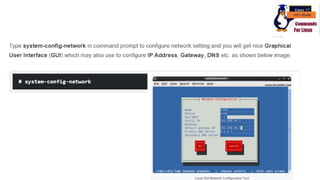
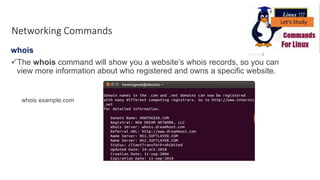
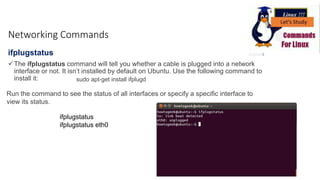
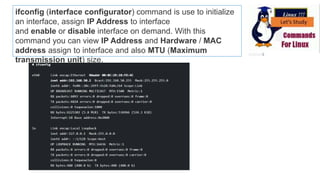
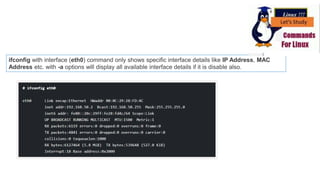
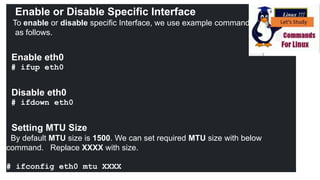
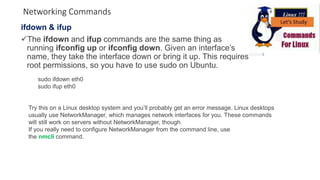
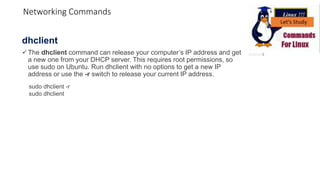
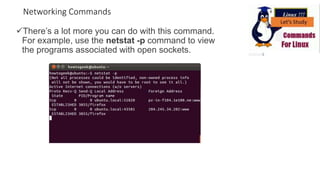
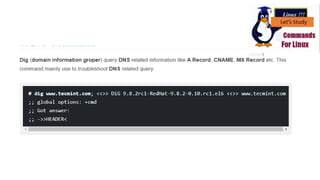
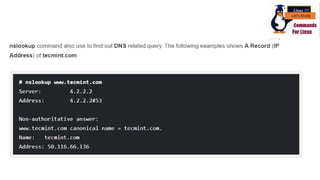
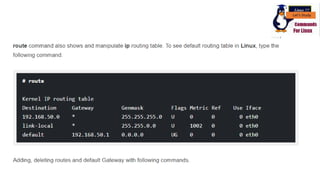
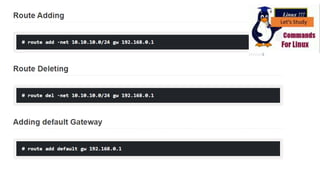
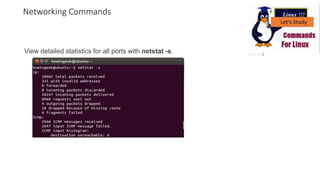
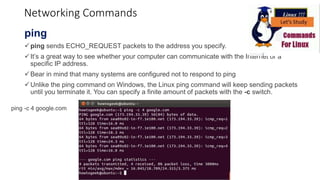
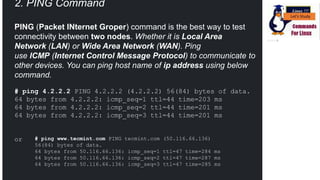
The document discusses various networking commands used in Linux systems. It provides descriptions and examples of commands like ping, traceroute, mtr, host, whois, ifconfig, dhclient, netstat and more. These commands are used to test and monitor network connectivity, view routing tables, lookup domain information, configure network interfaces and more. Maintaining system and network uptime is a key task for system and network administrators.




![Networking Commands
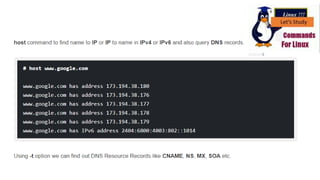
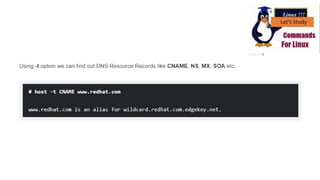
Host [install dnsutils]
The host command performs DNS lookups. Give it a domain name and
you’ll see the associated IP address. Give it an IP address and you’ll see
the associated domain name.
host howtogeek.com
host 208.43.115.82](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13thweeksystemad-210311021534/85/Linux-Commands-8-320.jpg)