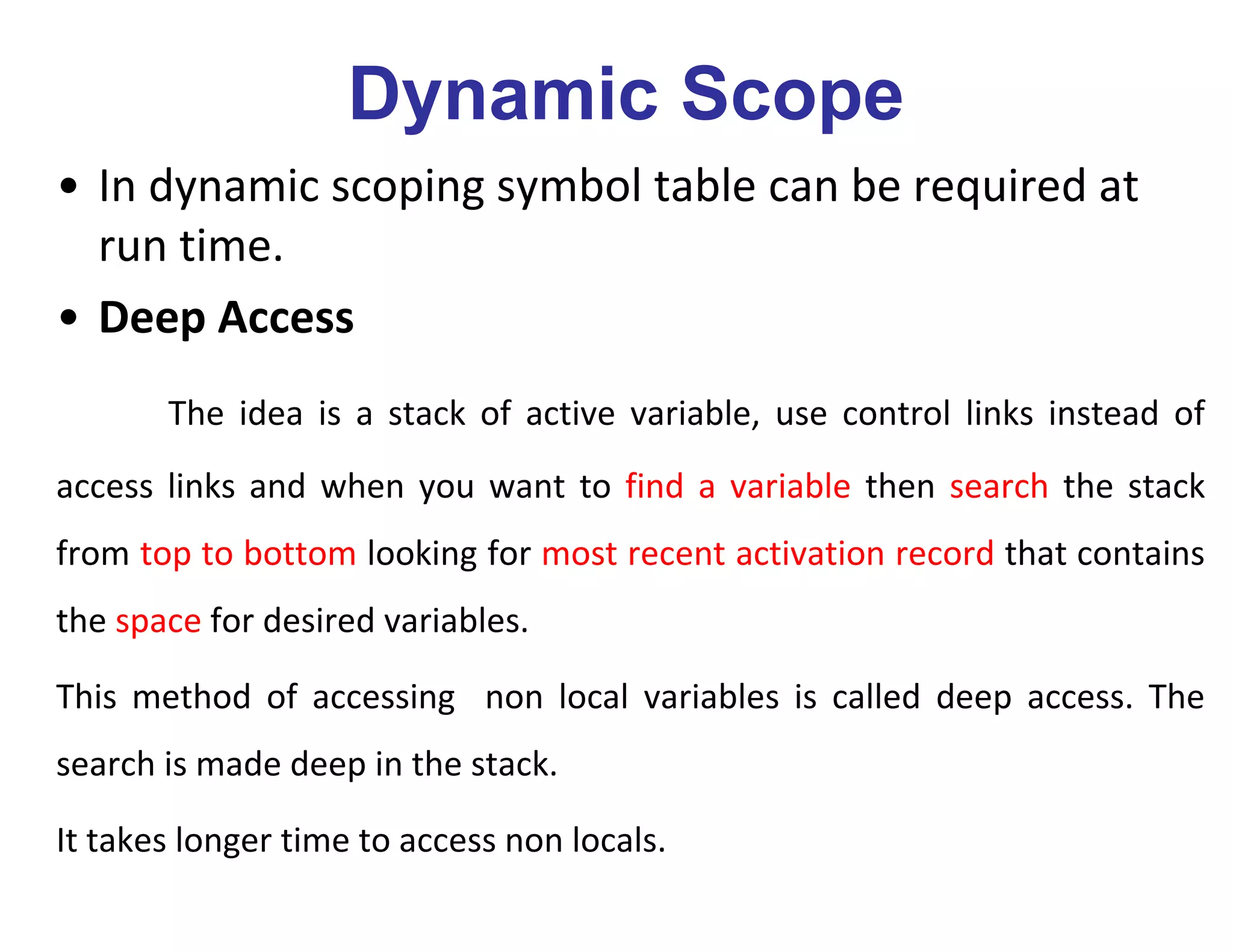
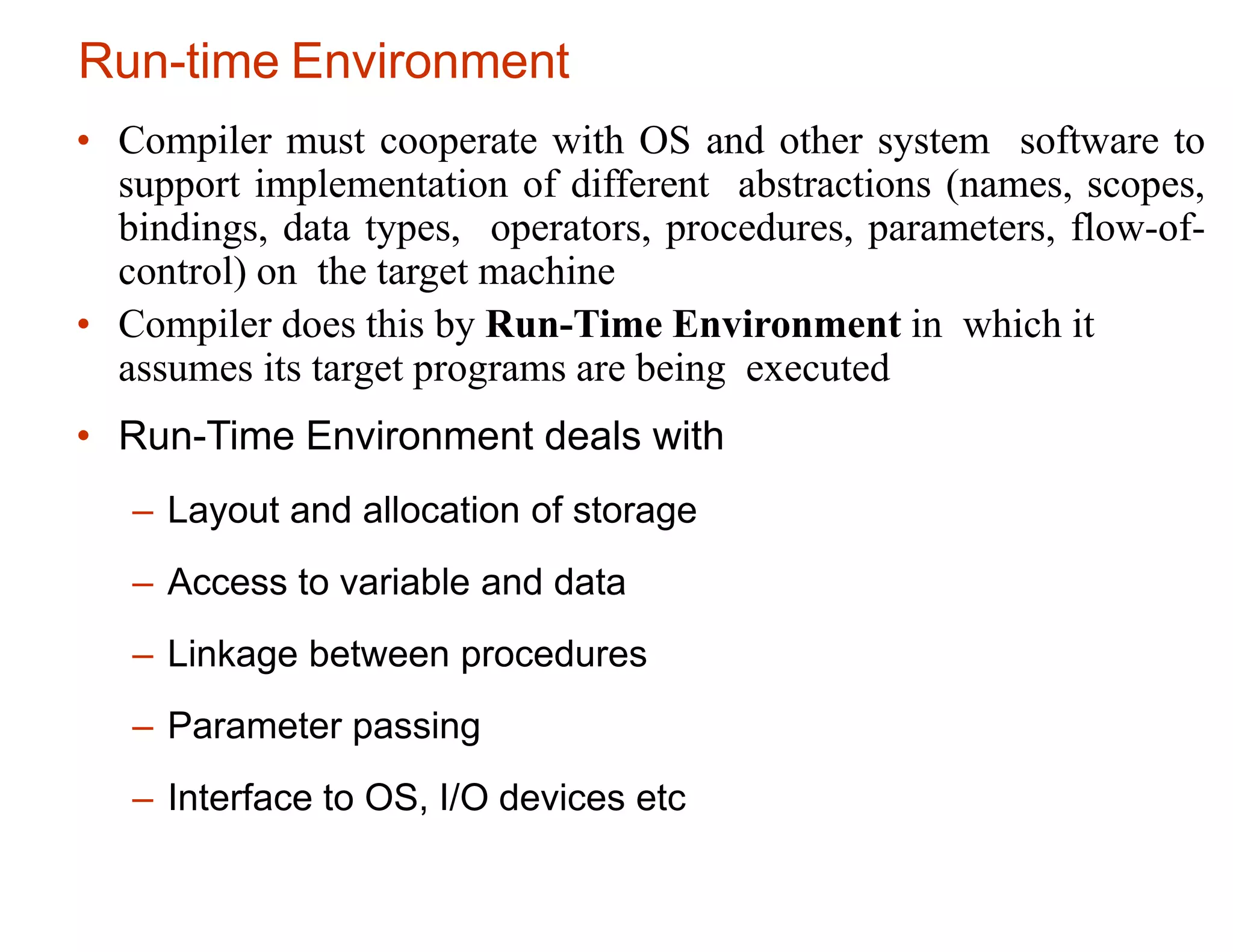
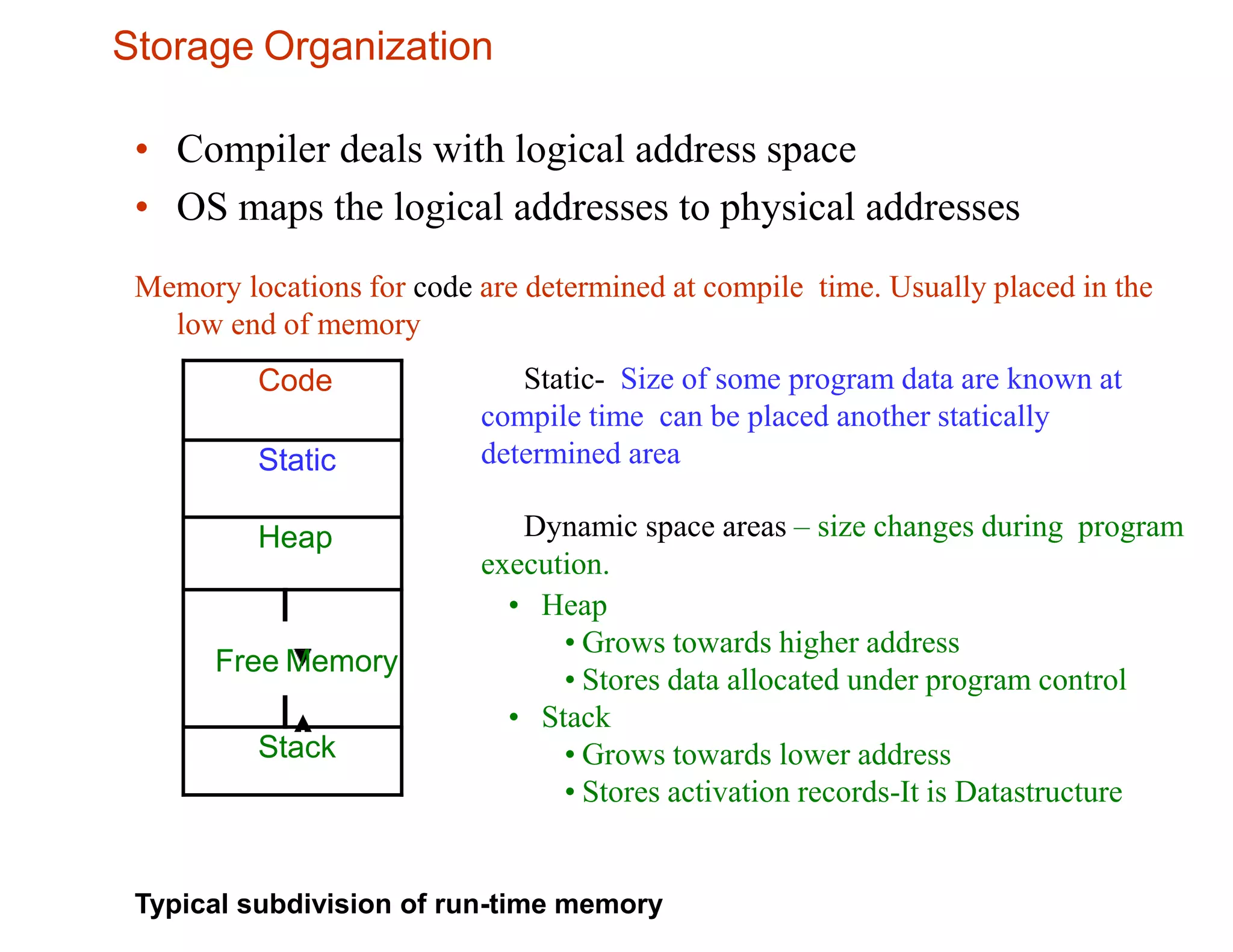
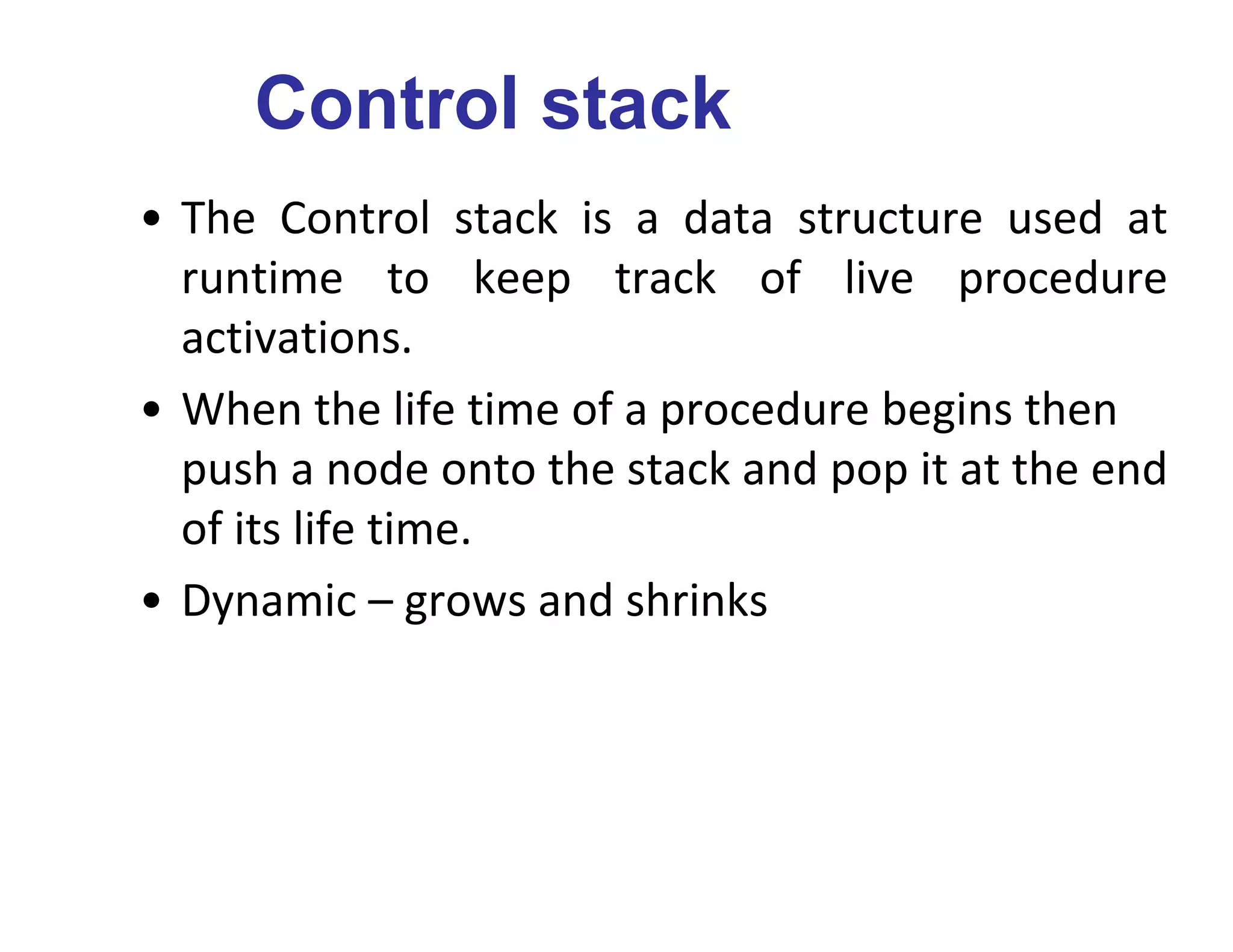
The runtime environment handles the implementation of programming language abstractions on the target machine. It allocates storage for code and data and handles access to variables, procedure linkage and parameter passing. Storage is typically divided into code, static, heap and stack areas. The compiler generates code that maps logical addresses to physical addresses. The stack grows downward and stores activation records for procedures, while the heap grows upward and dynamically allocates memory. Procedure activations are represented by activation records on the call stack. The runtime environment implements variable scoping and access to non-local data using techniques like static scopes, access links and displays.





























![Example
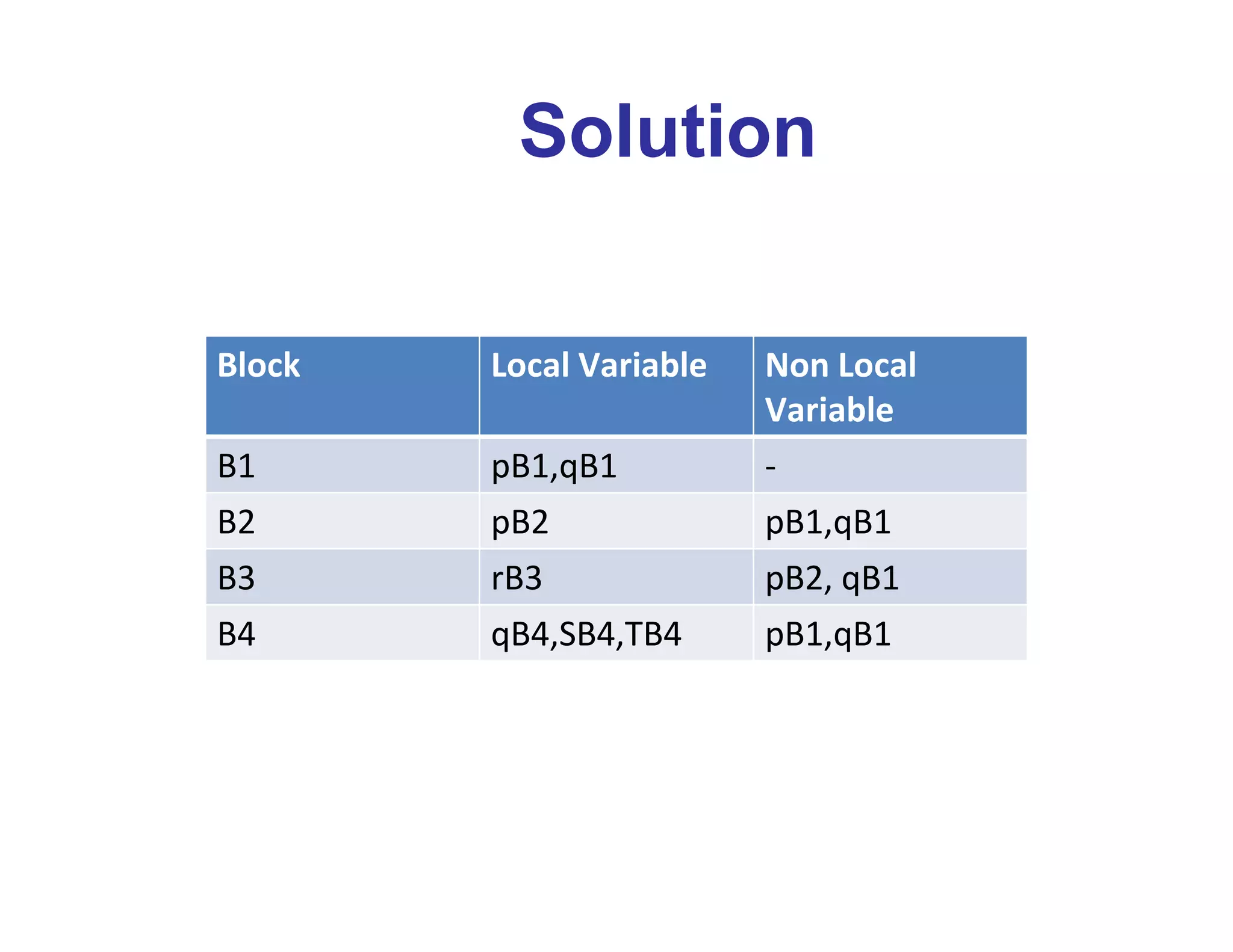
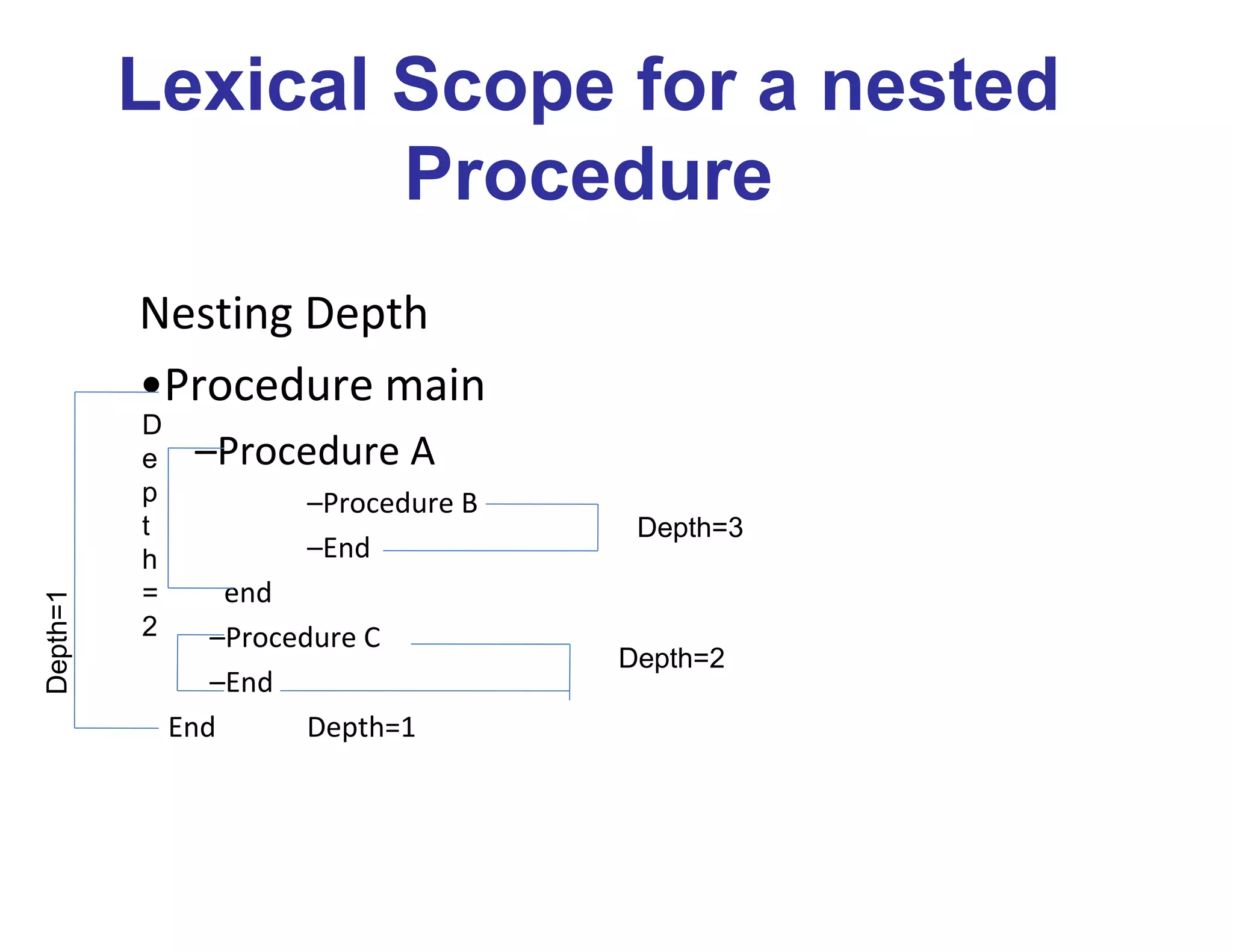
Consider the scope of procedure as shown below
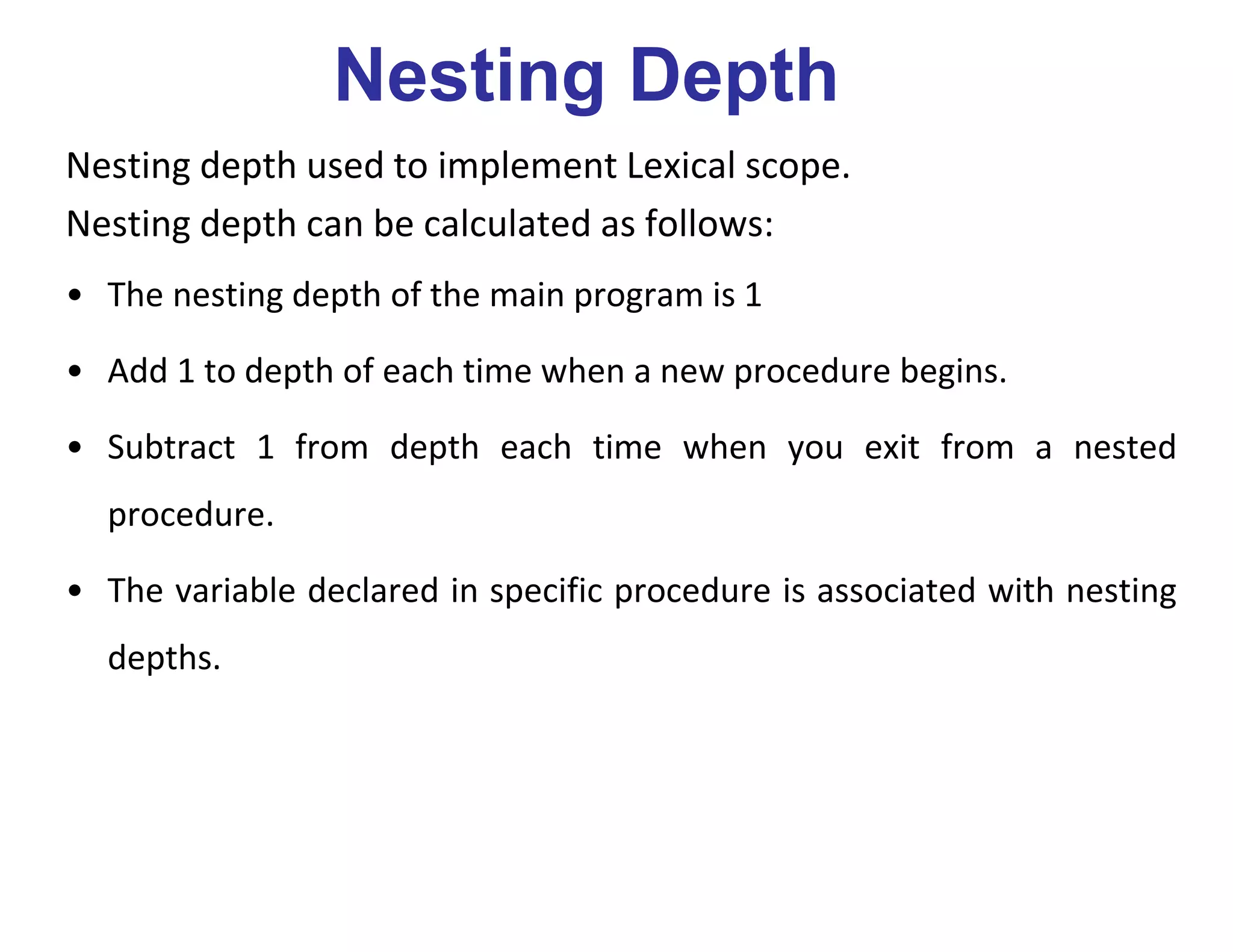
Nesting depth y calls a procedure at depth x then
i)y<x then x=y+1 and the called procedure is nested within caller. Then by
keeping first y elements of display array as it is we can set display[x] to the
new activation record.
ii)y>=x then first x-1 elements will be kept as it is in display array but
display[x] points to new activation record.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runtimeenvironment-200312101513/75/Runtimeenvironment-37-2048.jpg)