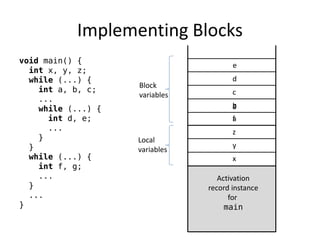
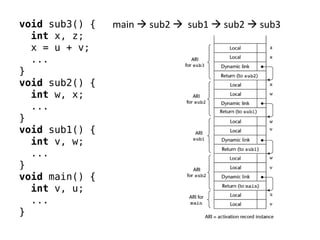
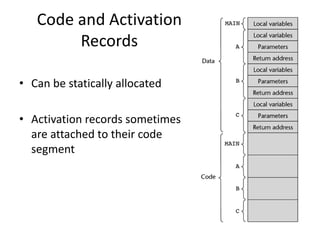
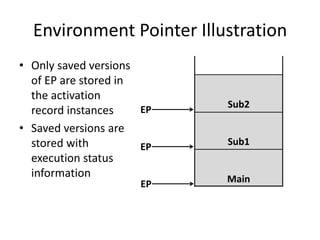
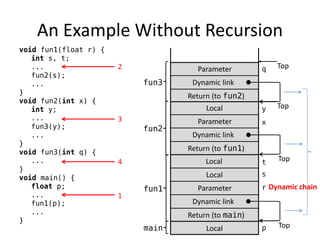
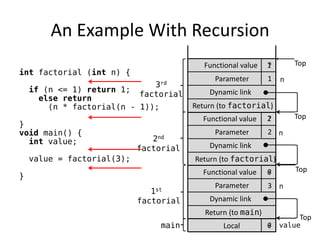
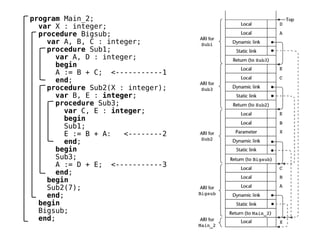
Implementing subprograms requires saving execution context, allocating activation records, and maintaining dynamic or static chains. Activation records contain parameters, local variables, return addresses, and dynamic/static links. Nested subprograms are supported through static chains that connect activation records. Dynamic scoping searches the dynamic chain for non-local variables, while shallow access uses a central variable table. Blocks are implemented as parameterless subprograms to allocate separate activation records for block variables.










![An Example: C Function
void sub(float total, int part)
{
int list[4];
float sum;
. . .
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-implementingsubprograms-141110164719-conversion-gate02/85/09-implementing-subprograms-12-320.jpg)






![Blocks
•Blocks are user-specified local scopes for variables
•C:
{ int temp;
temp = list[upper];
list[upper] = list[lower];
list[lower] = temp;
}
•The lifetime of temp in the above example begins when control enters the block and ends when exits
•An advantage of using a local variable is that it cannot interfere with any other variable with the same name](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-implementingsubprograms-141110164719-conversion-gate02/85/09-implementing-subprograms-23-320.jpg)