This document discusses different techniques for implementing subprograms (subroutines and functions) in programming languages. It covers:
- The general semantics of subprogram calls and returns, including saving execution context, passing parameters, and transferring control.
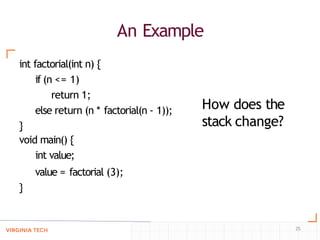
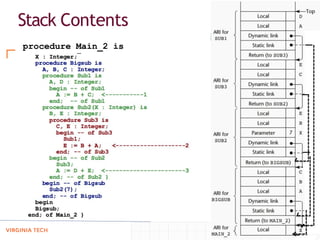
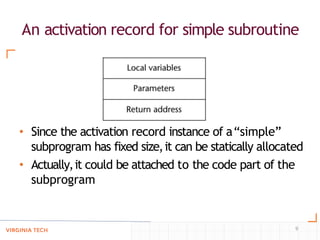
- Implementing "simple" subprograms where local variables are static and nesting is not allowed, using static allocation of code and activation records.
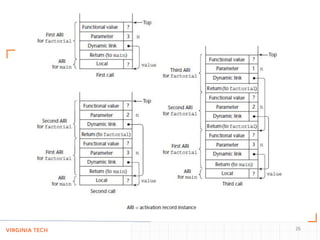
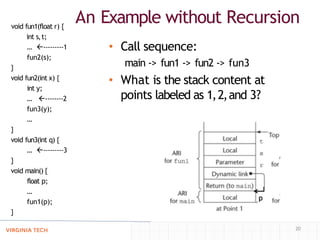
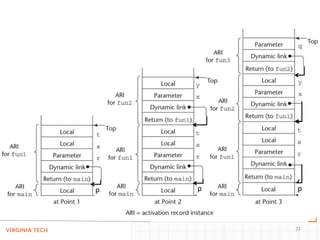
- Using a call stack to implement subprograms with stack-dynamic local variables, recursion, and nested subprograms, where activation records are dynamically allocated on the stack.
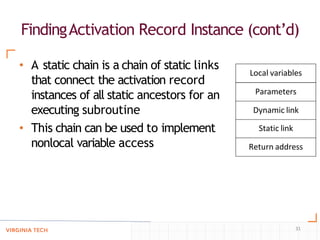
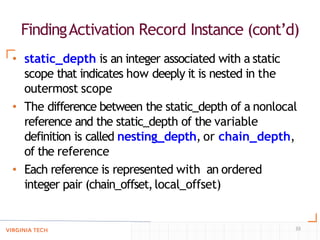
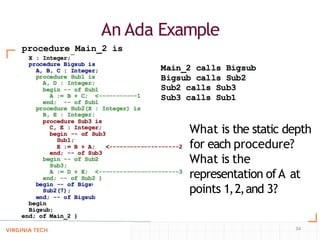
- Techniques like static chaining and static depths to allow accessing nonlocal variables in nested subprograms by finding the correct activation record on the stack.











![Call Stack
14
• Push(r1):
stack_pointer--;
M[stack_pointer] = r1;
• r1 = Pop();
r1 = M[stack_pointer];
stack_pointer++;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/implementsubprogram-1-240131052220-3ca3be99/85/ImplementSubprogram-theory-of-programming-14-320.jpg)




![An Example
23
void sub(float total,int part) {
int list[5];
float sum;
…
}
Local
Local
Local
Local
Local
Local
Parameter
Parameter
Dynamic link
Return address
part
total
list[0]
list[1]
list[2]
list[3]
list[4]
sum](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/implementsubprogram-1-240131052220-3ca3be99/85/ImplementSubprogram-theory-of-programming-23-320.jpg)