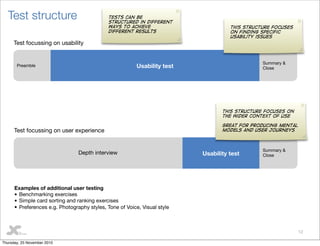
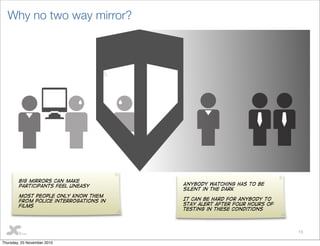
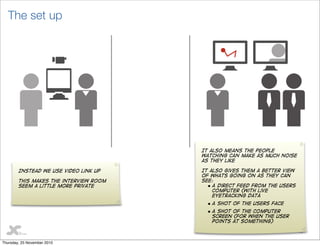
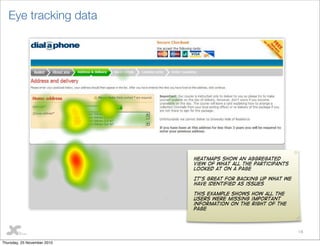
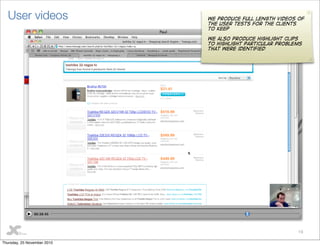
This document discusses user testing best practices. It recommends testing designs, wireframes, and HTML to catch issues early. Participants should include a mix of new and existing users. Two moderators are optimal - one leads interviews while the other takes notes. Stakeholders should observe. Tests follow a structure with pre- and post- interviews and usability tests. Recommendations prioritize improvements. Outputs include heatmaps, videos, and a visual report with quotes and actionable recommendations.