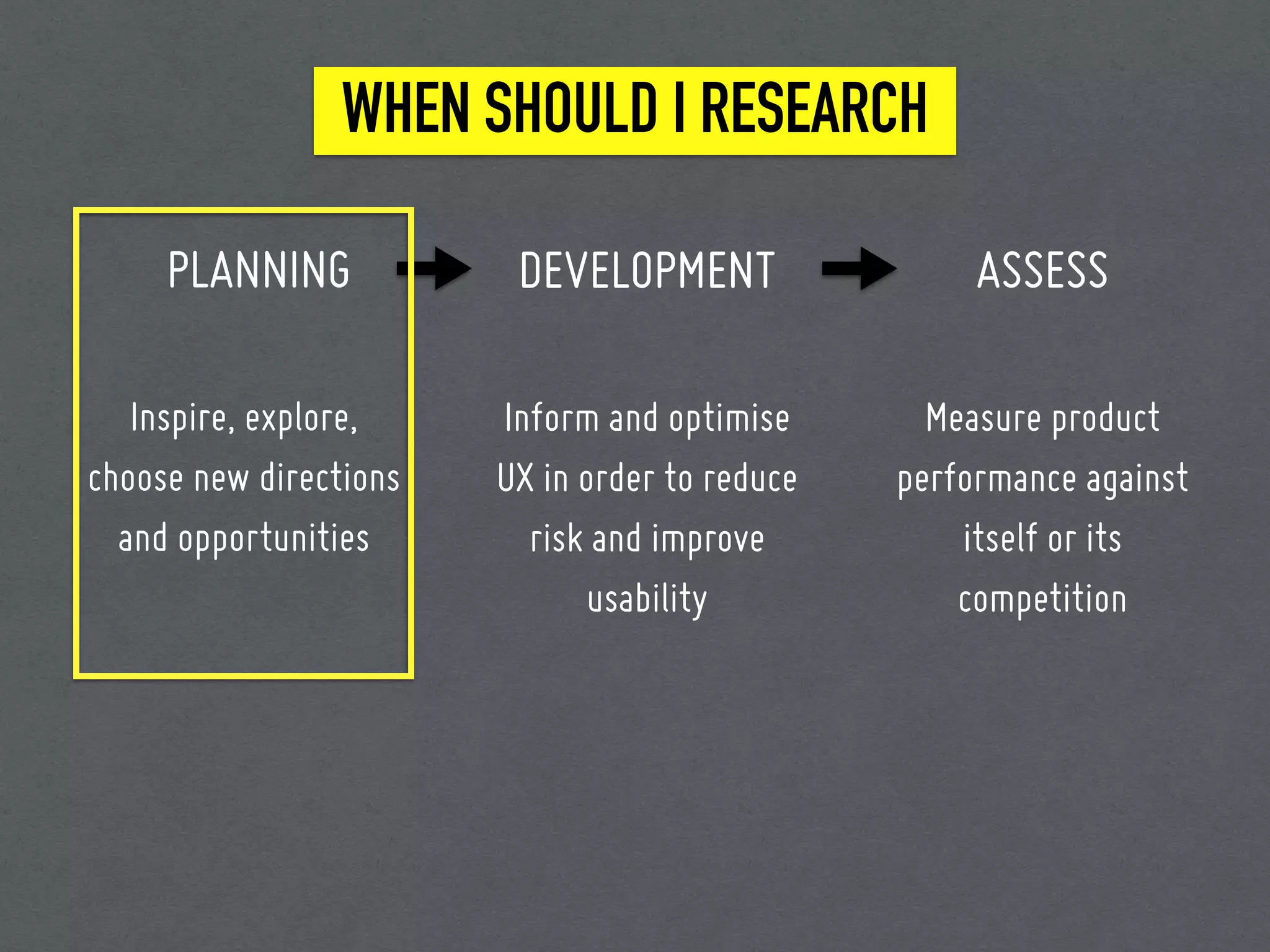
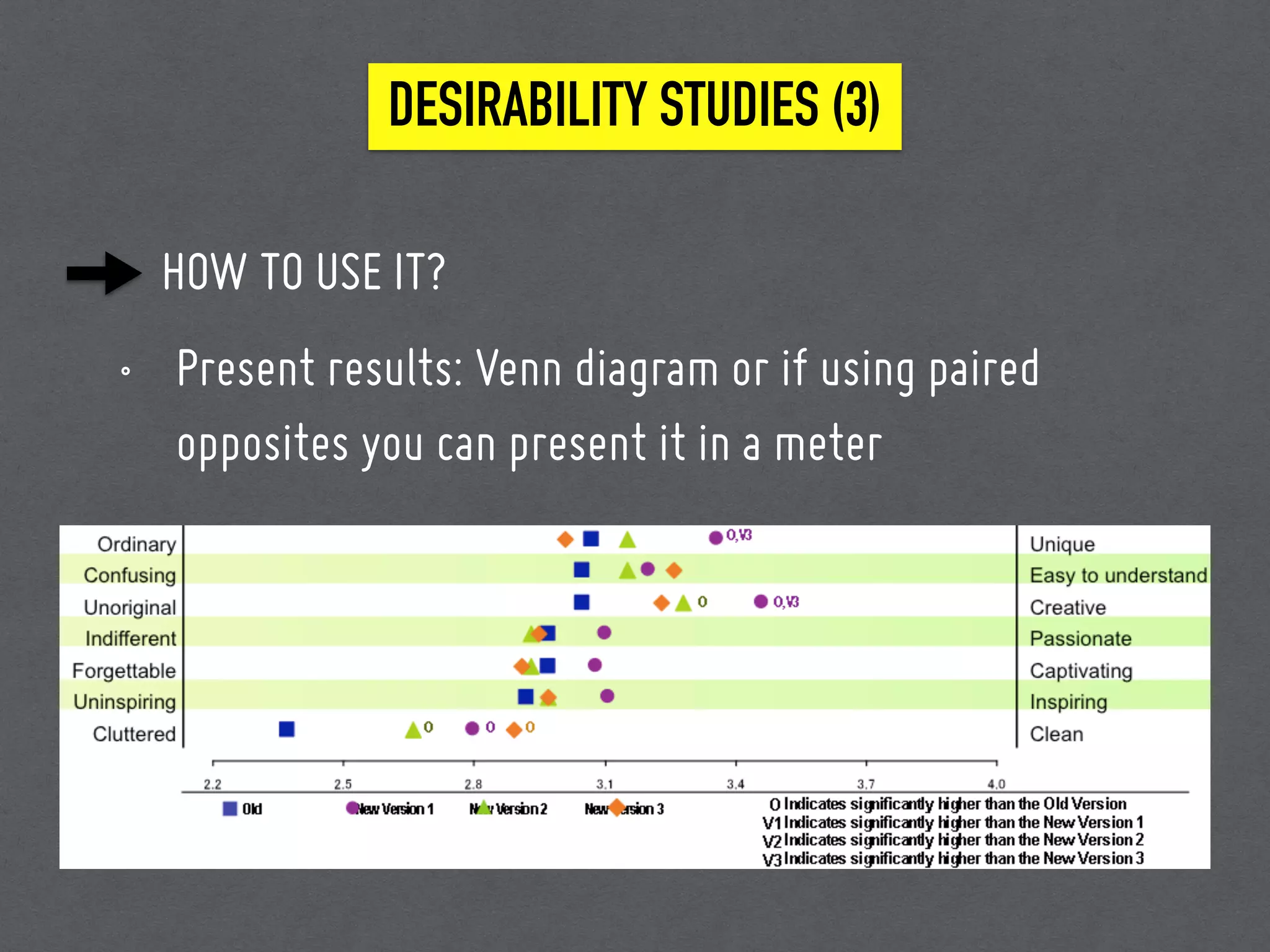
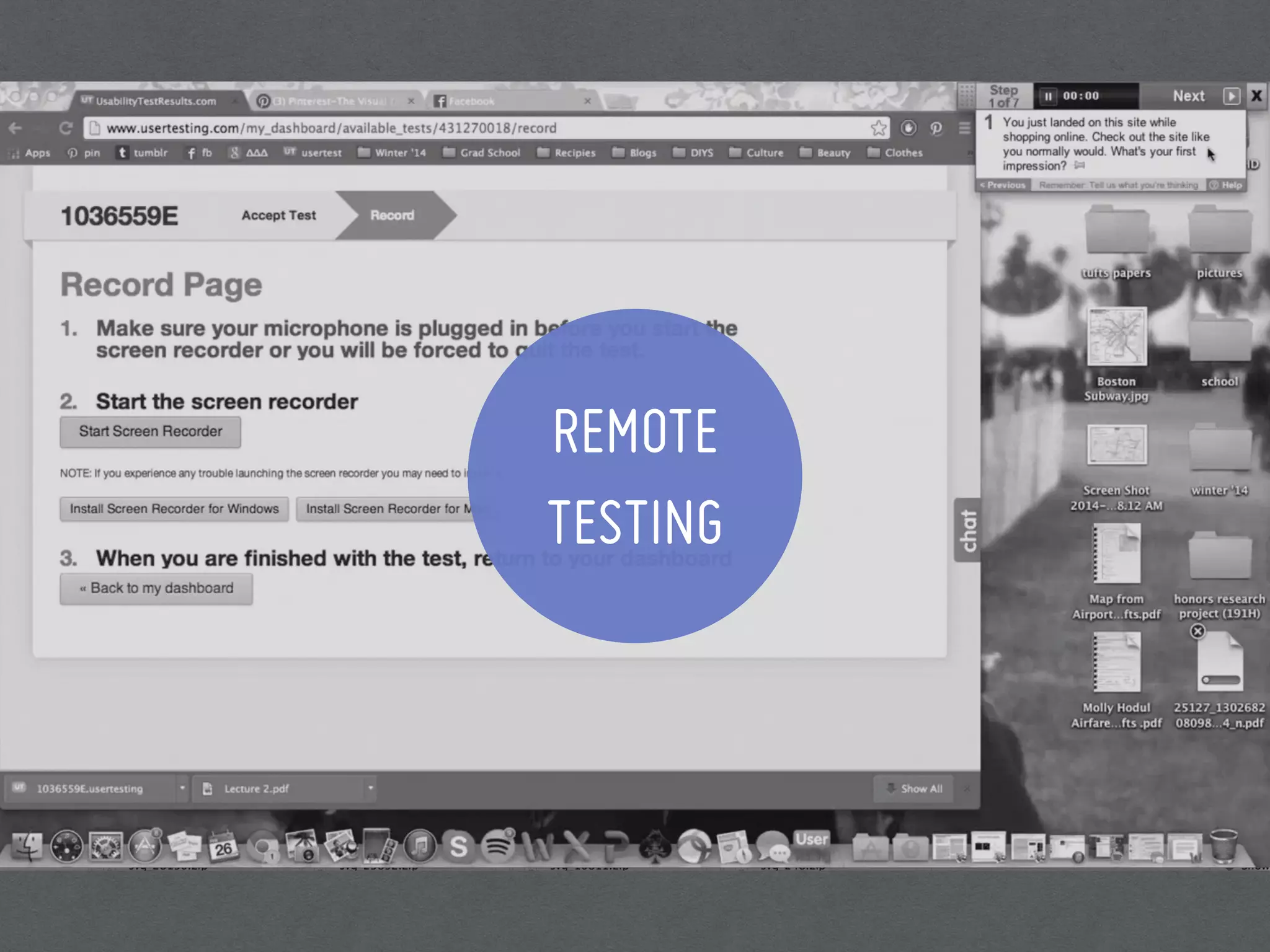
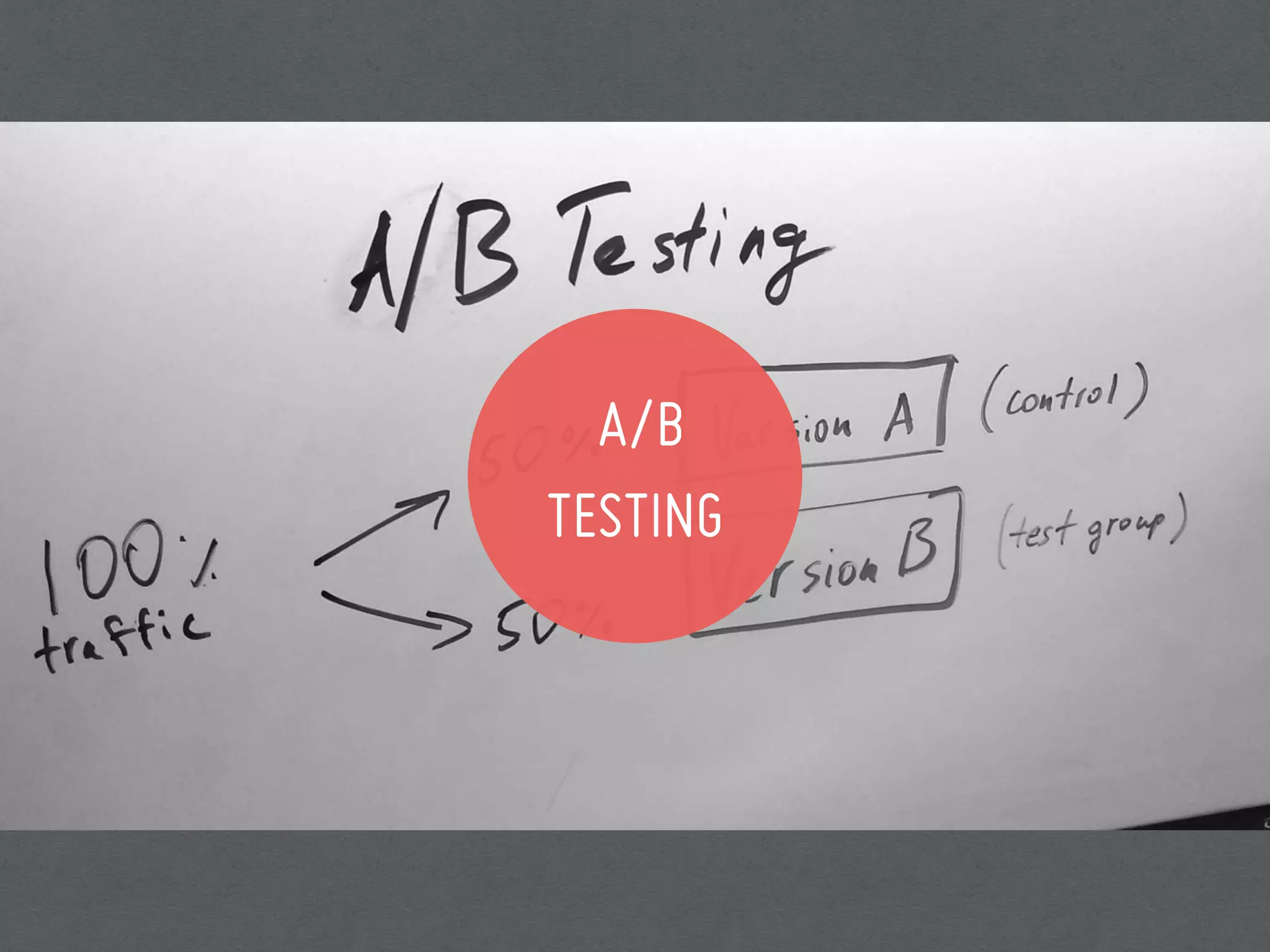
This document discusses 7 methods for conducting user research: field studies, desirability studies, surveys and polls, usability studies, remote testing, A/B testing, and researching without users. It provides an overview of when each method should be used, how to implement it, and tips/tools for each. The document emphasizes that user research is important because designers are not users, and it should be conducted at different stages of the product development process to inform, optimize, and assess the user experience.