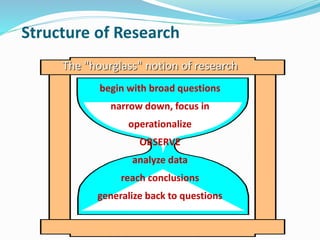
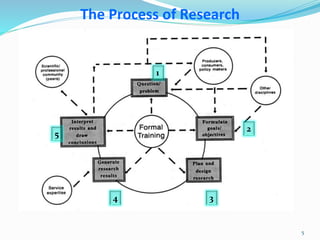
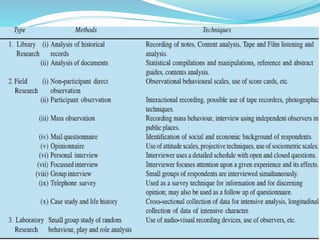
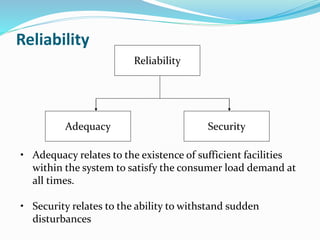
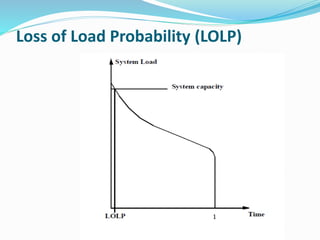
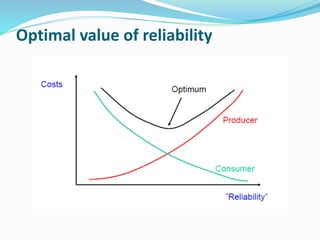
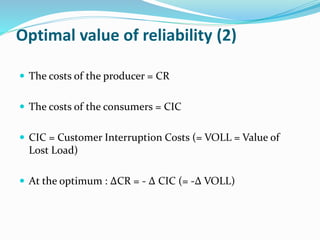
The document discusses research methodology and power system reliability. It introduces various research concepts like the research process, types of research, and the difference between research methods and methodology. It then covers power system reliability, including definitions, hierarchical analysis, reliability indices like LOLP, SAIFI and SAIDI, and the concept of optimal reliability value.