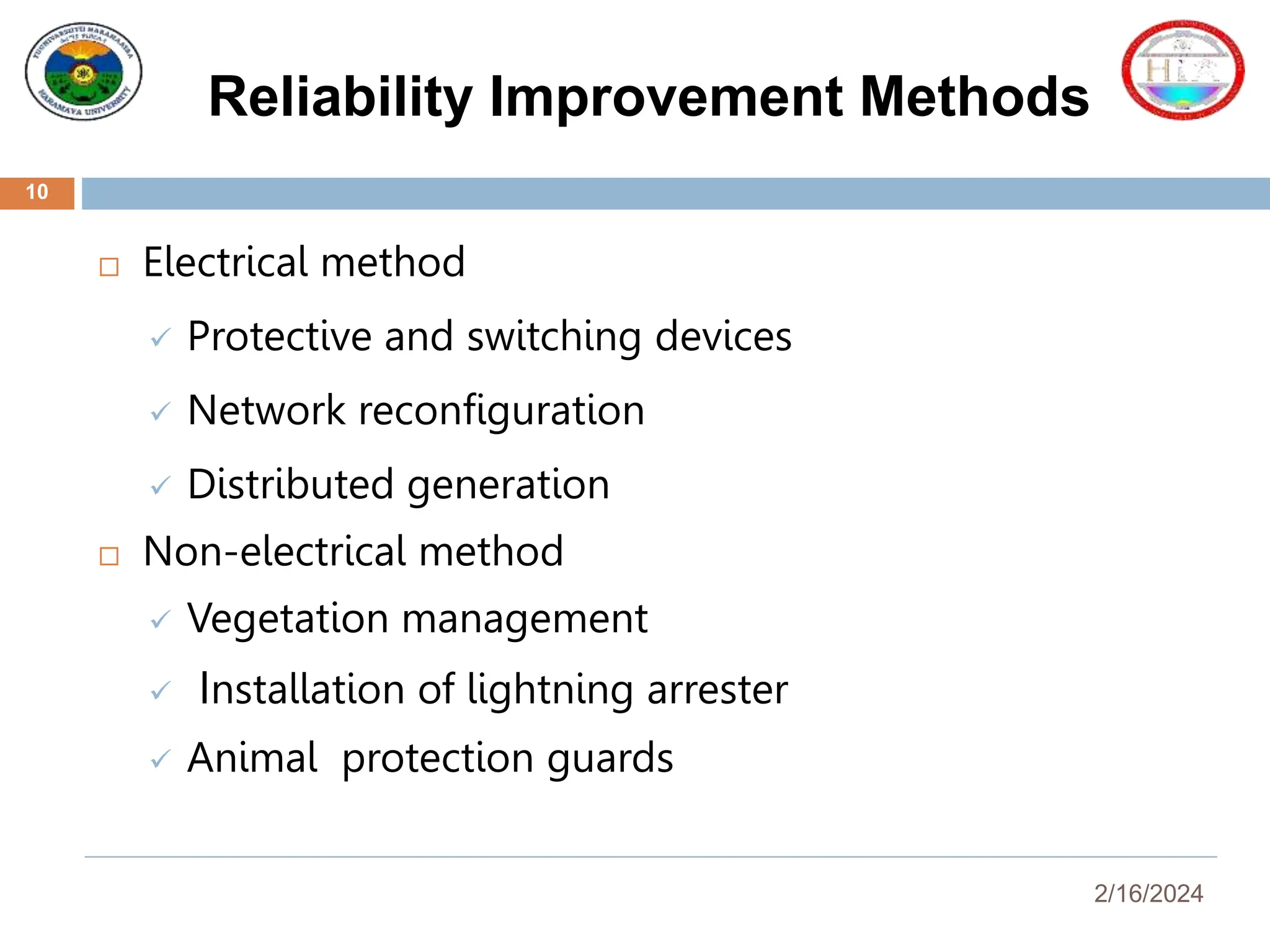
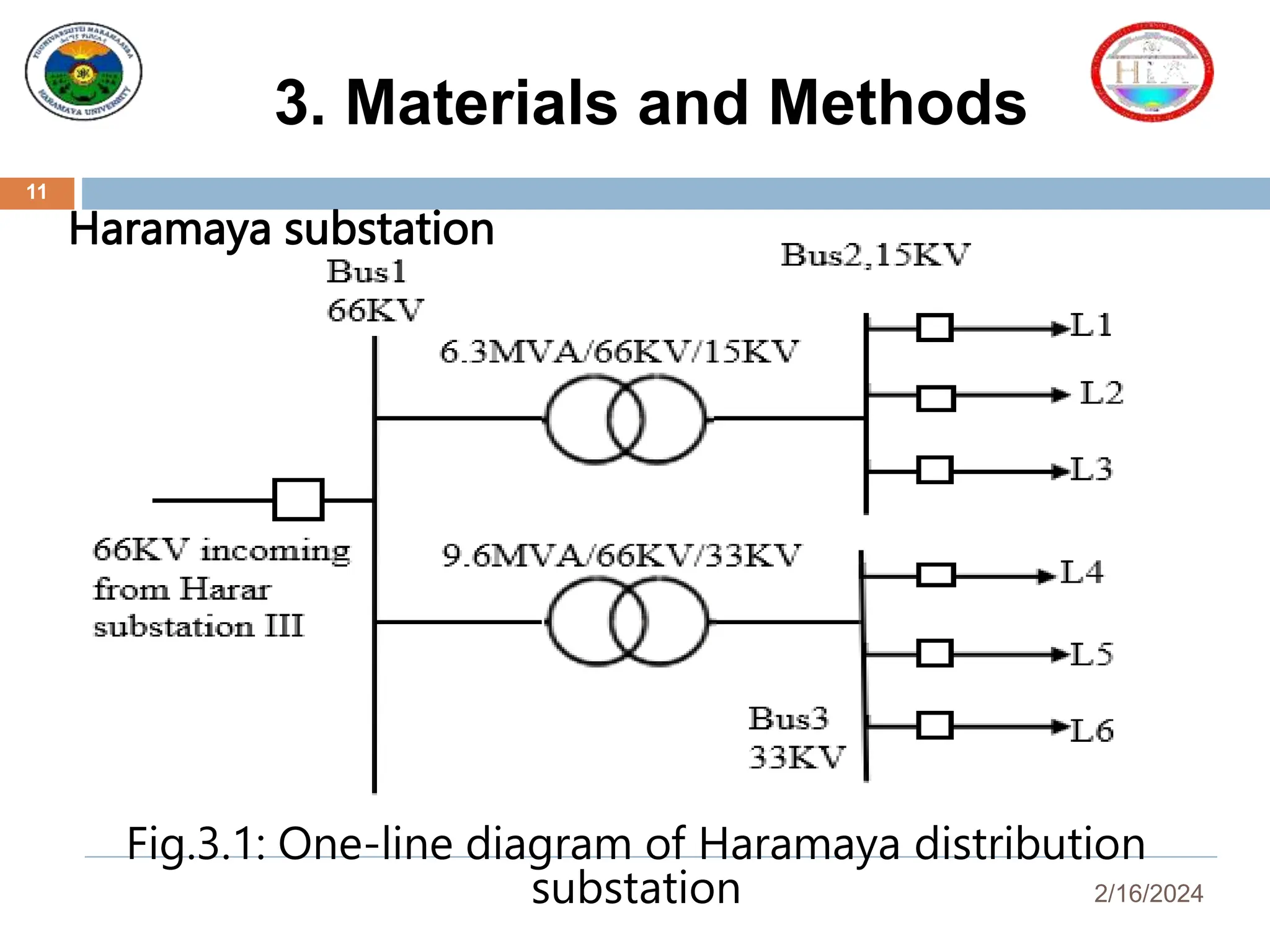
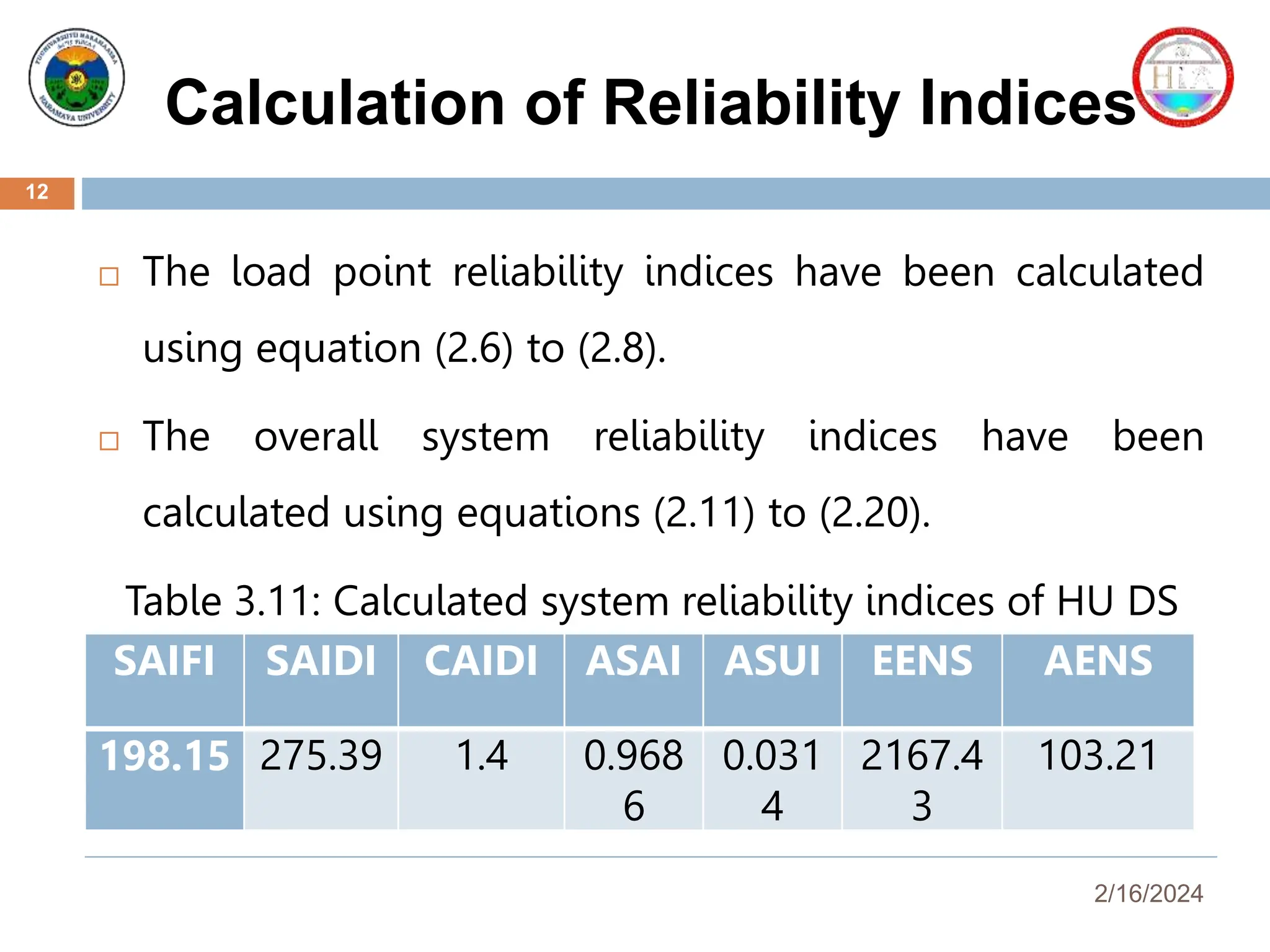
This document presents a reliability assessment of the Haramaya University distribution system, highlighting the critical issue of frequent power interruptions and their economic impact. It outlines the objectives, reliability metrics, methodologies, results, and cost analysis, concluding that implementing an underground ring distribution system could significantly improve reliability and result in substantial cost savings. Recommendations for future work and preventive maintenance are also provided to enhance system performance.