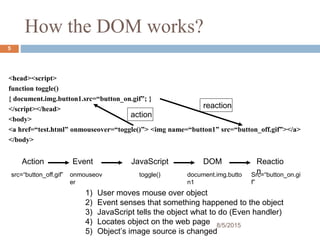
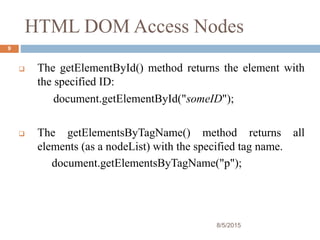
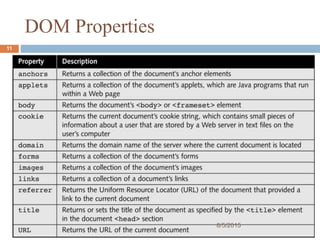
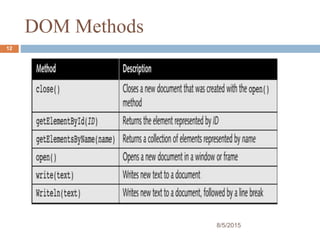
The presentation provides an introduction to the Document Object Model (DOM) and how it allows JavaScript to access and modify HTML documents. It discusses how the DOM presents an HTML document as a tree structure, and how JavaScript can then restructure the document by adding, removing, or changing elements. It also gives examples of how DOM properties and methods allow accessing and manipulating specific nodes, such as changing the background color of the document body.