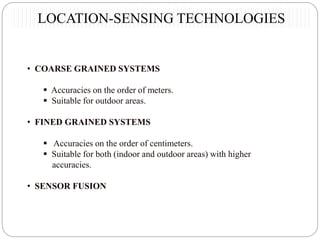
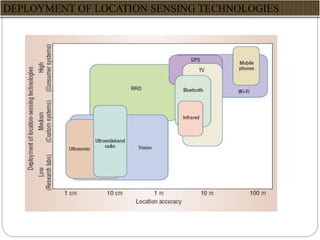
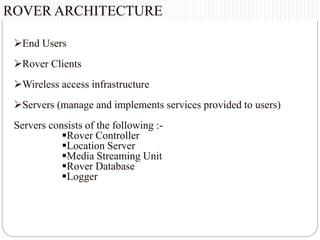
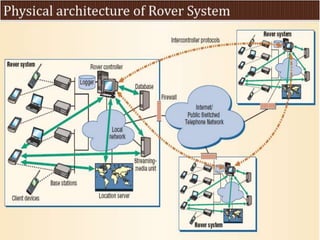
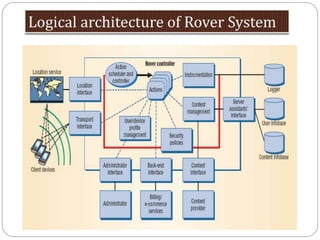
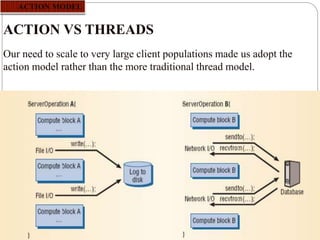
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on rover technology. It describes rover services like basic data, transactional, and map-based services. It explains the rover architecture including clients, controllers, databases and location servers. It discusses the action model for scheduling tasks and how rover clients, controllers and databases interact. It also outlines multi-rover systems for scaling to large user populations and provides conclusions and ideas for future work.