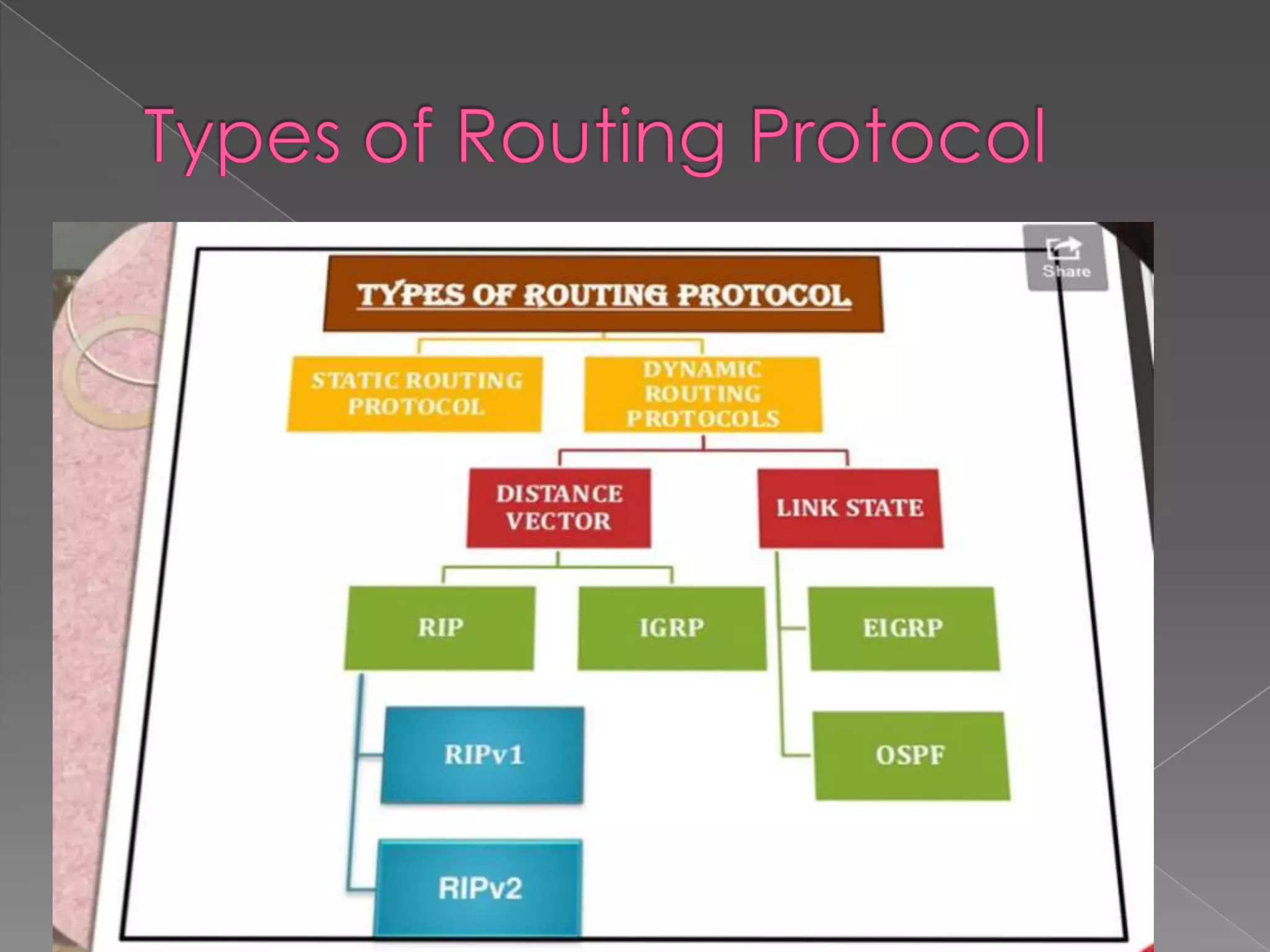
Routing protocols are used by routers to communicate and update routing tables with the best paths between sources and destinations. They use algorithms to evaluate metrics like number of hops, bandwidth, delay, load, and cost to determine optimal paths. Static routing is simple but cannot adapt to changes, while dynamic routing automatically detects changes and provides optimal and scalable routing. The four main interior gateway protocols are RIP, EIGRP, IS-IS, and OSPF, with OSPF and EIGRP being most widely used today.