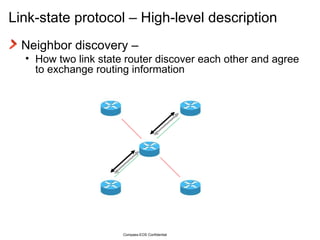
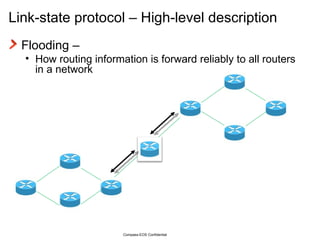
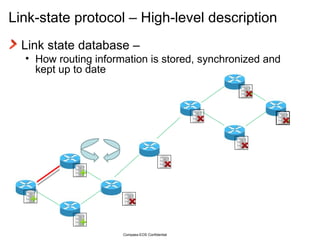
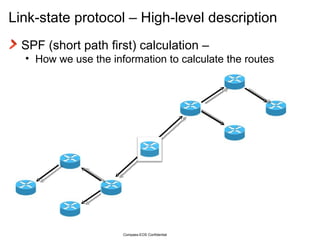
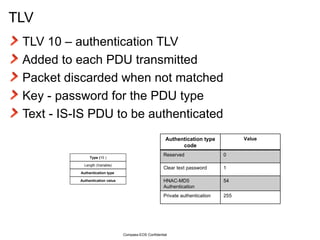
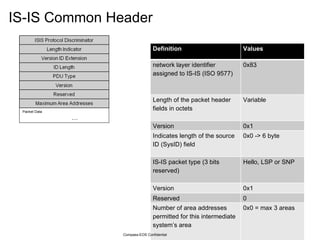
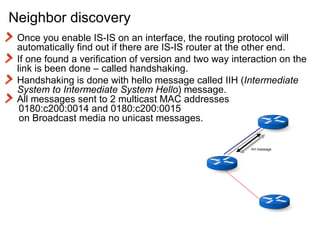
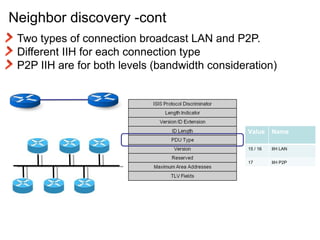
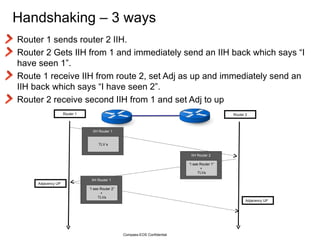
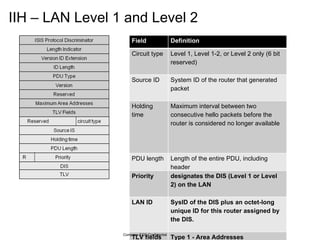
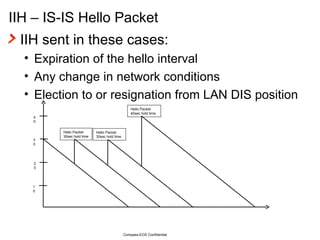
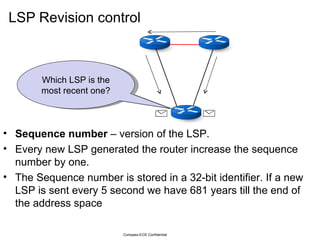
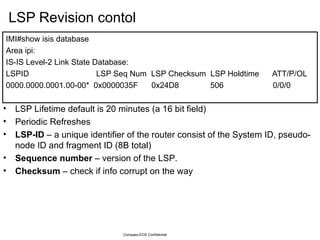
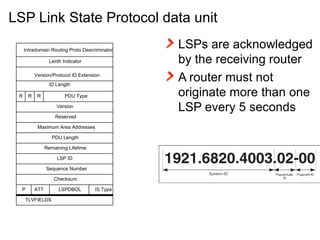
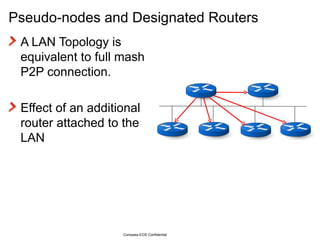
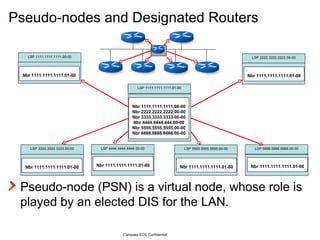
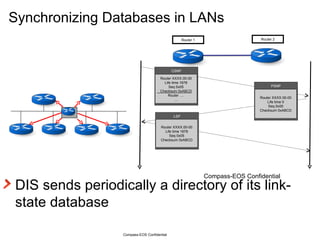
The document provides an overview of the Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) routing protocol. It describes key IS-IS concepts like neighbor discovery using hello messages, flooding of link state packets (LSPs) to share routing information, synchronization of the link state database, and running shortest path first (SPF) calculations to determine optimal routes. Pseudo-nodes and designated routers are used on broadcast networks to represent the entire network topology. Sequence numbers, checksums, and hold timers ensure freshness and accuracy of routing data.