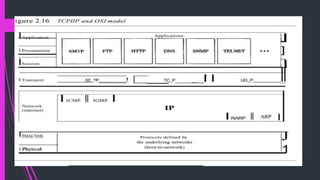
This document provides an overview of TCP/IP protocols. It describes the key layers of the TCP/IP model including the application layer, transport layer, network layer, and physical/data link layers. The transport layer contains TCP and UDP which handle transmission reliability and error detection. The network layer deals with packet delivery between networks using IP. Some advantages of TCP/IP are that it is nonproprietary, compatible with all operating systems and hardware. Disadvantages include its large size which can impact small networks and slower speeds due to running multiple layers.