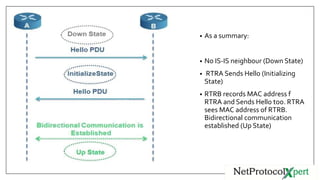
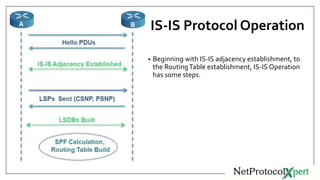
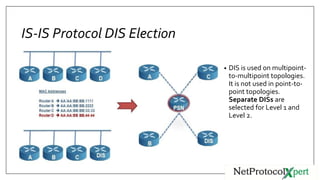
IS-IS uses three types of adjacencies - L1, L2, and L1/2. Adjacencies are established through a three-way handshake and can be in one of three states: down, initializing, or up. Key IS-IS operations include routers discovering neighbors through hello messages, establishing adjacencies, building LSPs, flooding LSPs to neighbors, running SPF to build routing tables. DIS is elected to reduce the mesh in broadcast networks and is chosen based on priority and MAC address.