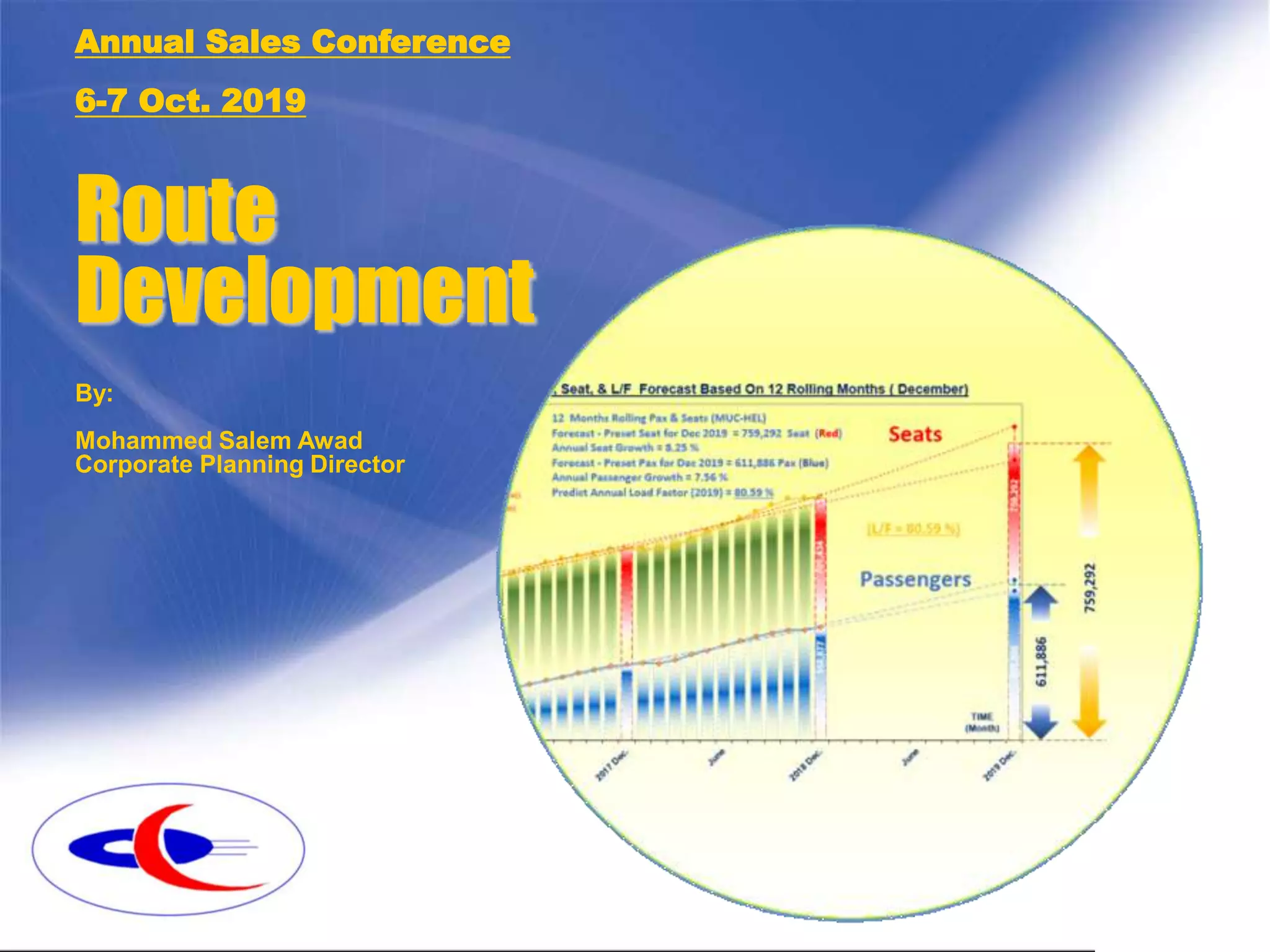
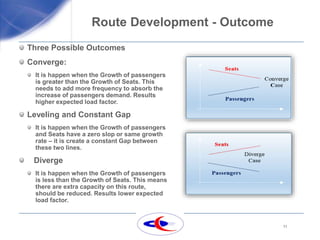
This document discusses route development strategies for airlines. It outlines analyzing supply (available seats) and demand (passengers) trends on routes to forecast performance. Three outcomes are possible: converge, where passenger growth exceeds seat growth; leveling, where growth is equal; and diverge, where passenger growth lags. Monthly seasonality patterns identify peak periods. The goal is adjusting flight frequencies, aircraft size, or other factors to achieve the annual load factor target based on supply-demand analyses. Examples of route analyses between various city pairs are also presented.