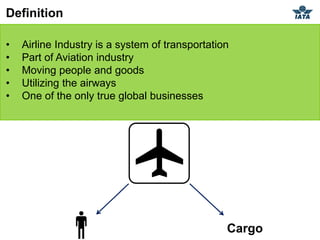
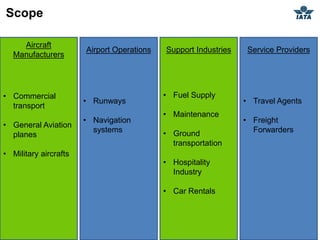
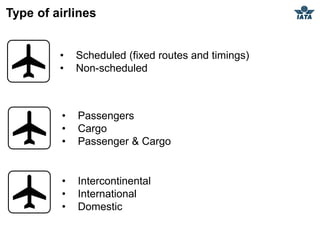
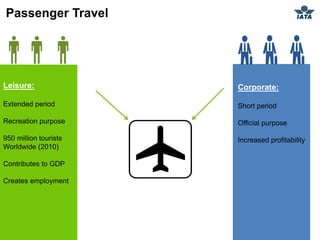
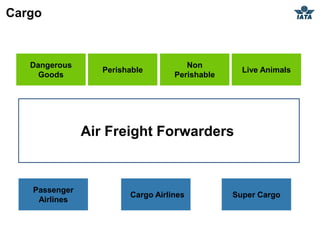
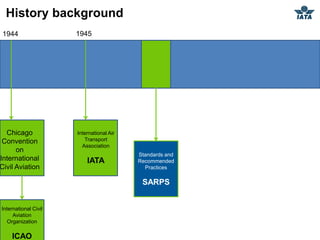
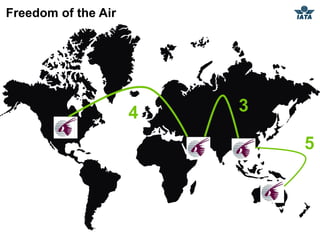
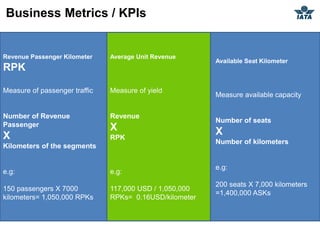
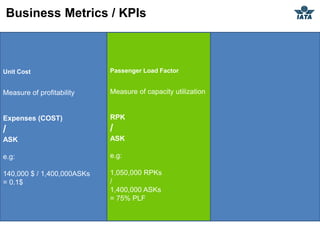
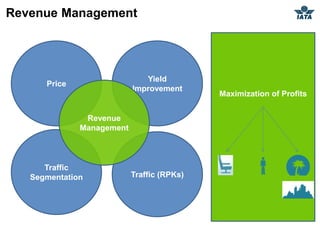
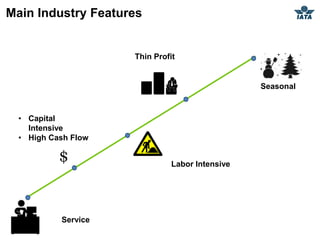
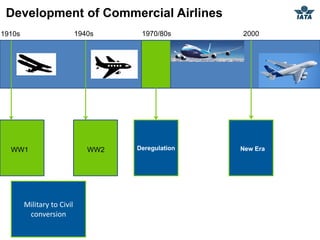
The airline industry involves transporting people and cargo by air on a global scale. It encompasses aircraft manufacturers, airports, airlines, cargo companies, travel agents, and other support industries. Major types include scheduled passenger carriers, cargo carriers, and general aviation. Key metrics used to evaluate airlines include revenue passenger kilometers (RPK), available seat kilometers (ASK), passenger load factor, unit cost, and average unit revenue. Major events were the 1944 Chicago Convention establishing international standards, and airline deregulation in the 1970s-80s allowing more competition. The industry is characterized as capital intensive, seasonal, thin profit margins, and labor intensive service-based.