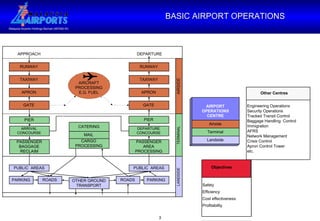
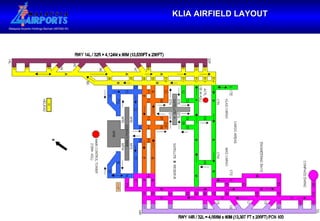
1. The document provides an overview of airside operations at airports, including the organization, key functions, objectives, and activities related to ensuring safety and efficiency.
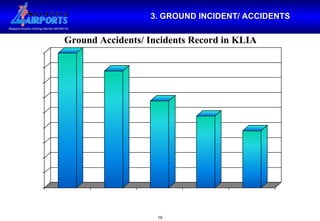
2. Maintaining safety on airport runways and aprons through inspection, permitting, incident investigation, and coordination with airport stakeholders are some of the main responsibilities of airside operations.
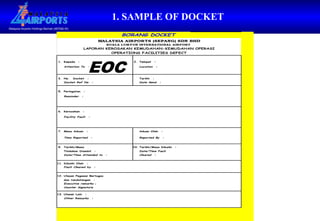
3. Notices to Airmen (NOTAMs) are used to communicate essential information about airport conditions or temporary changes and are issued according to standard formats and procedures.