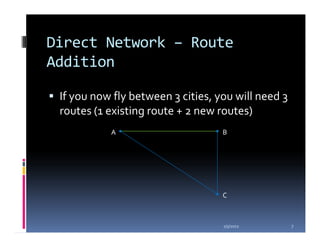
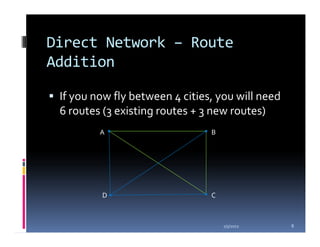
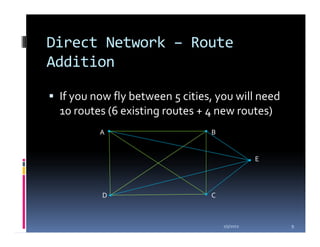
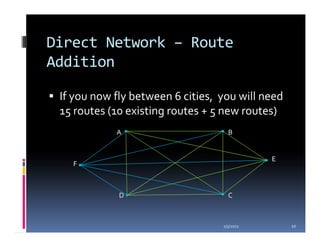
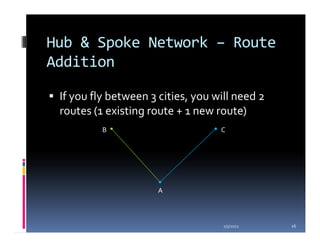
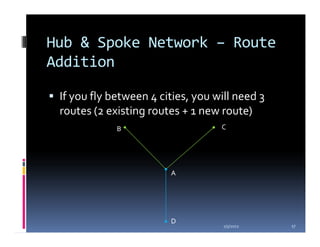
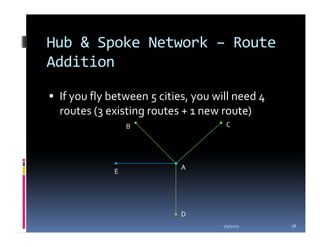
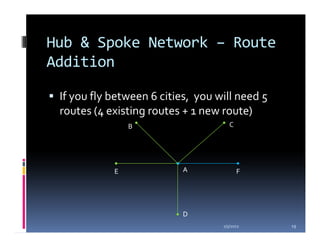
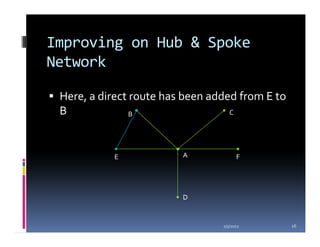
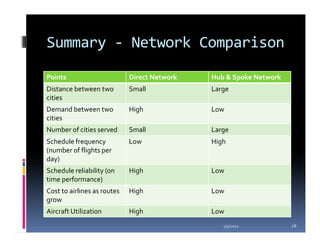
This document compares the direct network and hub & spoke network structures in the airline industry, detailing their respective advantages and disadvantages. The direct network offers high schedule reliability and aircraft utilization but is challenged by low schedule frequency and rapid route expansion as the number of cities increases. In contrast, the hub & spoke network provides higher schedule frequency and lower costs but suffers from lower reliability and aircraft utilization due to interdependencies on connected flights.