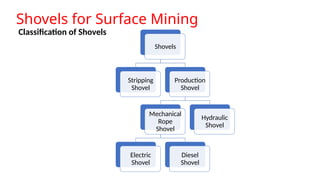
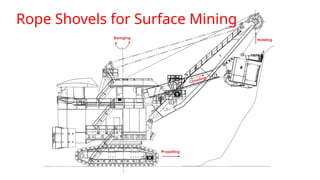
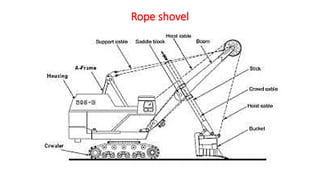
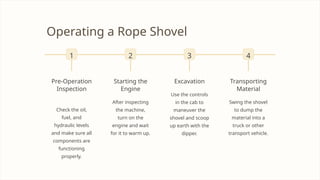
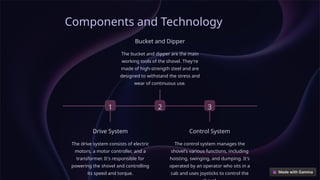
The document provides an in-depth overview of shovels used in surface mining, highlighting their historical development, various classifications, and technical components, such as rope and electric shovels. It discusses the advantages of these machines, including high productivity, precision, and lower operational costs, as well as modern advancements like automation and electric power sources. Additionally, case studies illustrate the successful implementation of electric shovels in mining operations, along with challenges related to infrastructure and maintenance.