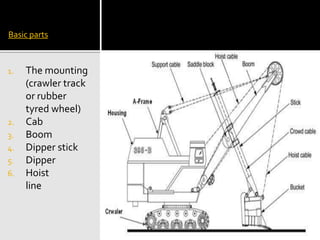
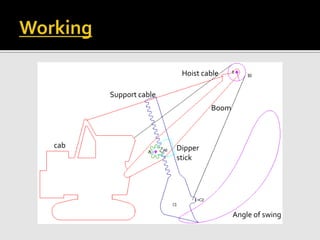
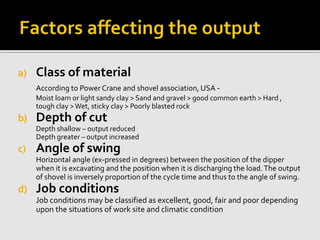
A power shovel is construction equipment designed to excavate and load earth into trucks, with types categorized by mounting (crawler or wheel-mounted). The size is indicated by dipper capacity, ranging from small (3/8 cubic meter) to large (80 cubic meters), and its operation involves key motions like hoisting, crowding, swinging, and propelling. Various factors, including job conditions, material type, and operator skill, affect the efficiency and selection of the appropriate power shovel for a given task.