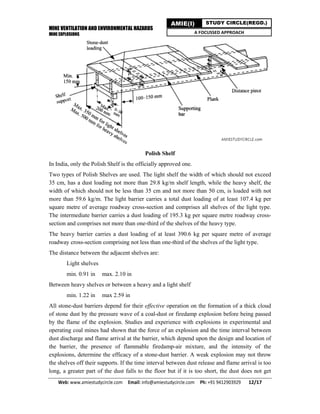
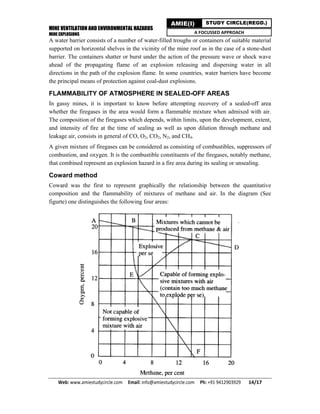
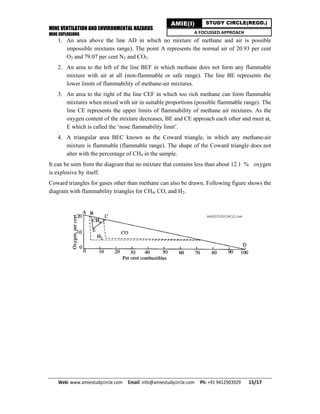
Methane gas is released from coal seams during mining, posing an explosion hazard if allowed to accumulate between its lower (5%) and upper (15%) explosive limits in air. Proper mine ventilation is needed to dilute methane concentrations and prevent explosions from sparks or flames. When methane burns or explodes, it produces carbon dioxide, water vapor and heat. Preventive measures include adequate ventilation, prohibiting smoking and open flames, monitoring methane levels, maintaining electrical equipment, and controlling methane emissions from abandoned areas and coal faces.