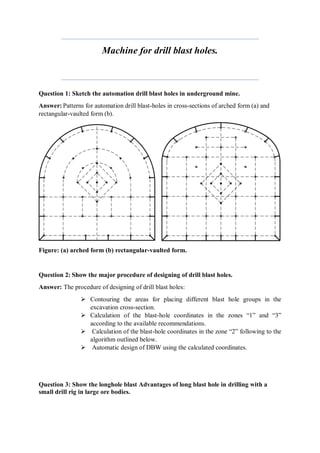
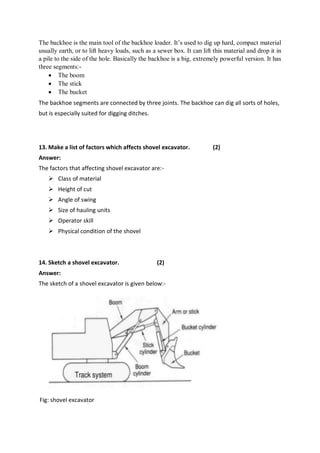
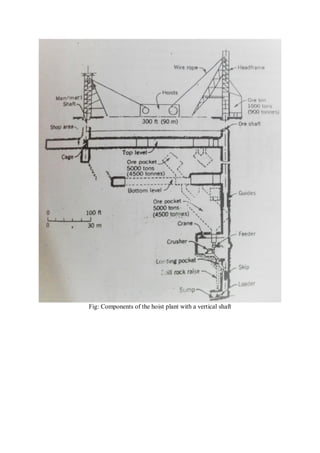
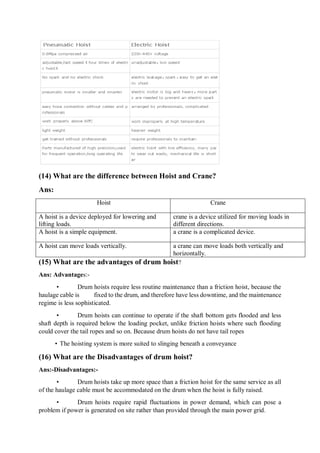
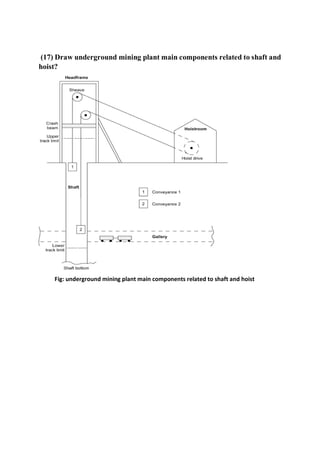
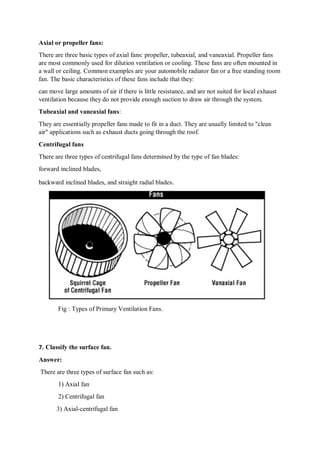
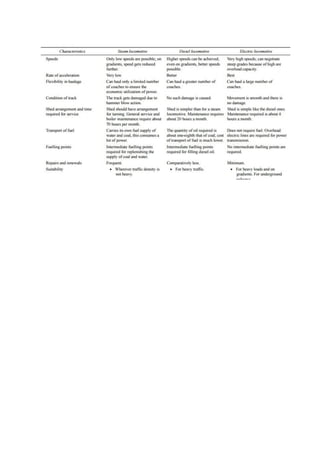
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or geological materials from the earth, with various methods including underground, surface, placer, and in-situ mining. The document describes different types of mining equipment, such as excavators, drills, roof bolters, shuttle cars, draglines, continuous miners, and rock dusters, as well as drilling techniques like rotary and percussion drilling. Additional operations, safety measures, and advantages and disadvantages of various drilling methods and equipment are also discussed.



![4. List of components of oil drilling rings with sketch.
List of Items
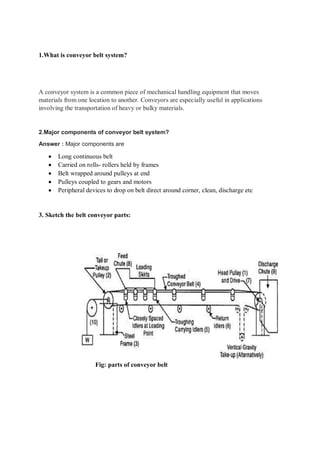
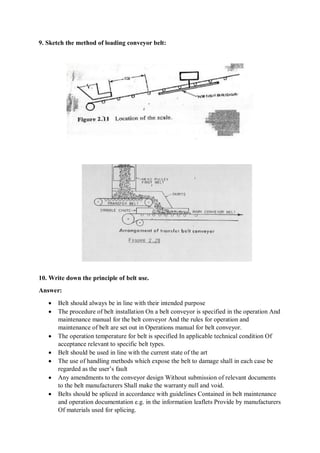
1. Mud tank
2. Shale shakers
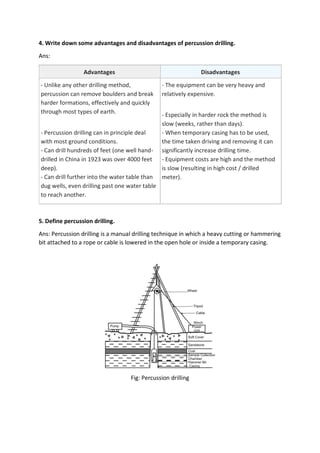
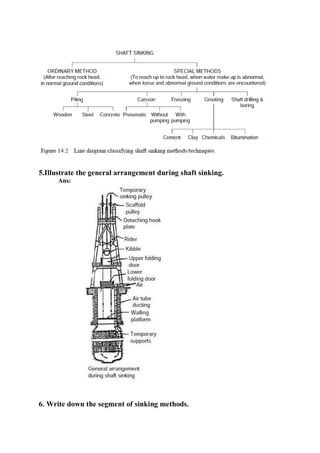
3. Suction line
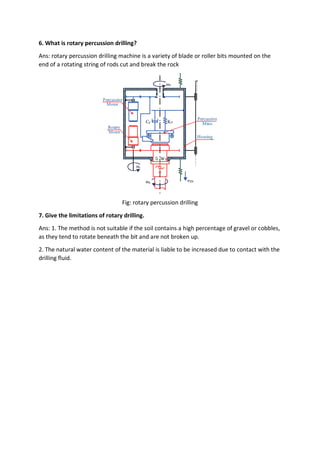
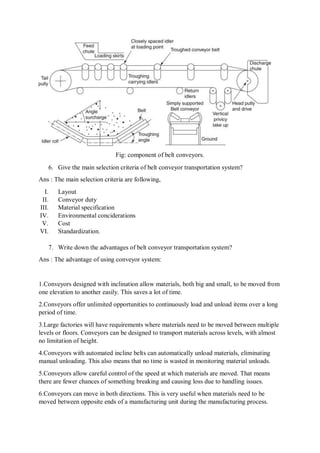
4. mud pump
5. Motor or power source
6. Hose
7. Draw works
8. Standpipe
9. Kelly hose
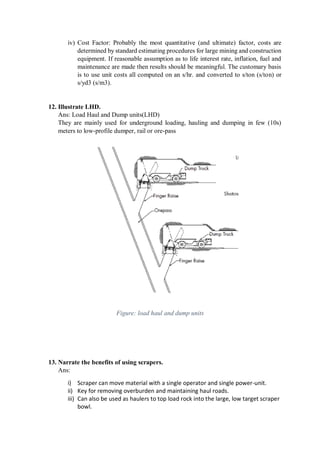
10. Goose neck
11. Traveling block
12. Drill line
13. Crown block
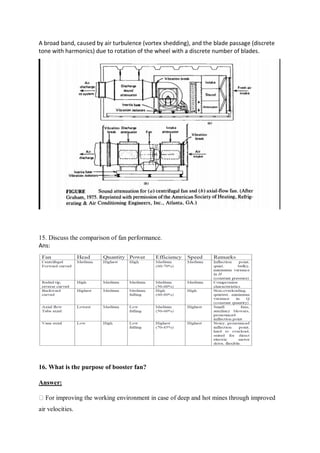
14. Derrick
15. Racking board
16. Stand of drill pipe
17. Setback (floor)
18. Swivel
19. Kelly drive
20. Rotary table
21. Drill floor
22. Bell nipple
23. Blowout preventer annular type
24. Blowout preventer pipe ram & blind ram
25. Drill string
26. Drill bit
27. Casing head or wellhead
28. Flow line
5. Define Auger drilling. How deep can an auger drill?
An auger is a drilling device, or drill bit, used for making holes in wood or in the ground.[1]
It
usually includes a rotating helical screw blade called a 'flighting' to act as a screw conveyor to
remove the drilled out material. The rotation of the blade causes the material to move out of
the hole being drilled.
Most augers dig about 3 ft. deep, but for deeper holes, ask for an extension rod, usually for no
extra fee. Deeper holes are typically required for footings for decks or other structures attached
to houses located in very cold climates where frost depths exceed 3 ft.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machineriesandmaintenance-210830194547/85/Machineries-and-Maintenance-Question-Patterns-for-Mining-students-4-320.jpg)