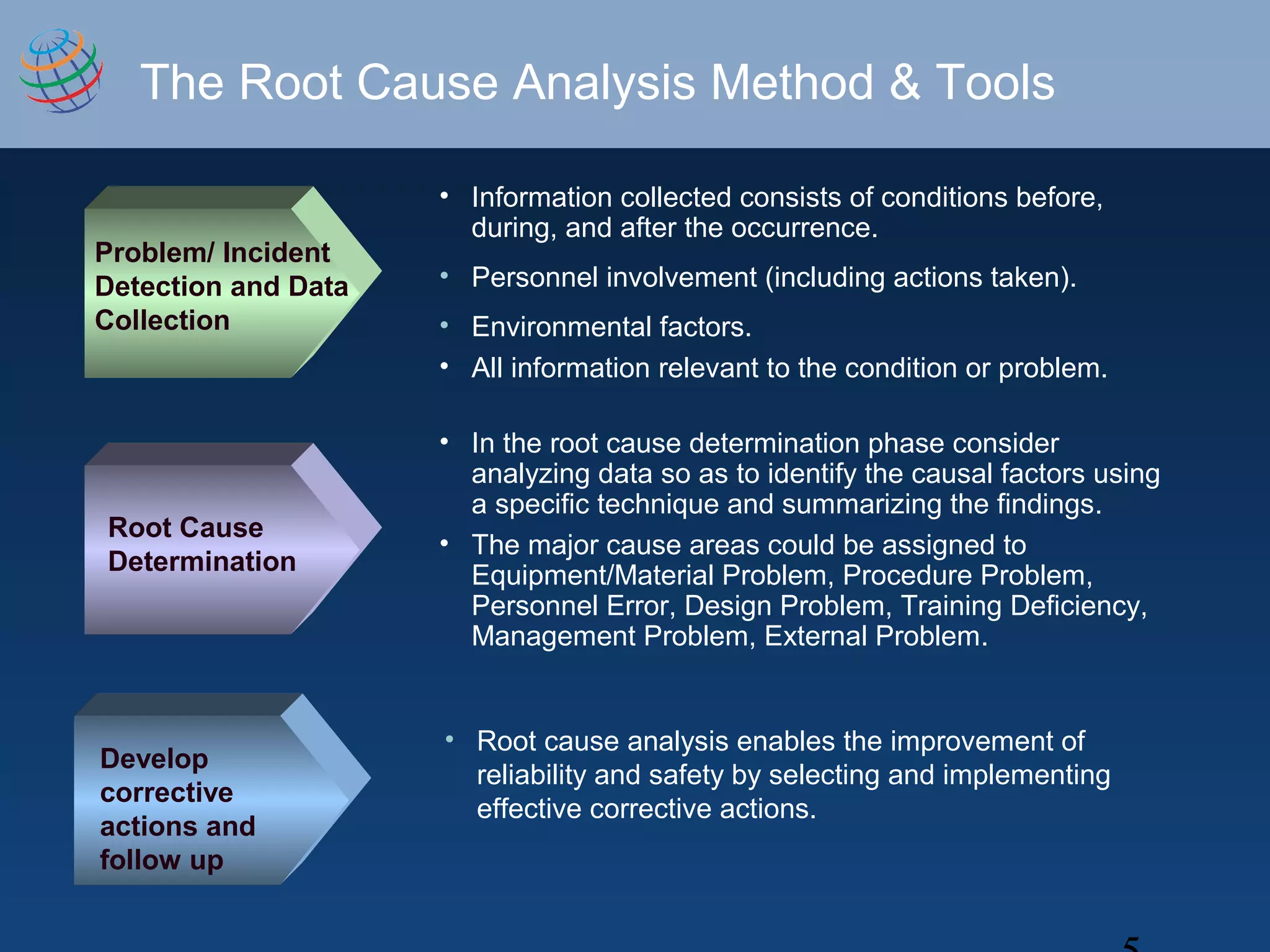
Root Cause Analysis is a process to determine the underlying cause of problems. It involves defining the problem, collecting data, analyzing the data to identify causal factors, and developing corrective actions. The key steps are problem detection, root cause determination, and developing solutions. Root cause analysis should be performed for significant issues like outages, nonconformances, or chronic problems. It involves asking "why" repeatedly until reaching the deepest underlying cause. Root cause analysis is important for improving processes and preventing future issues.