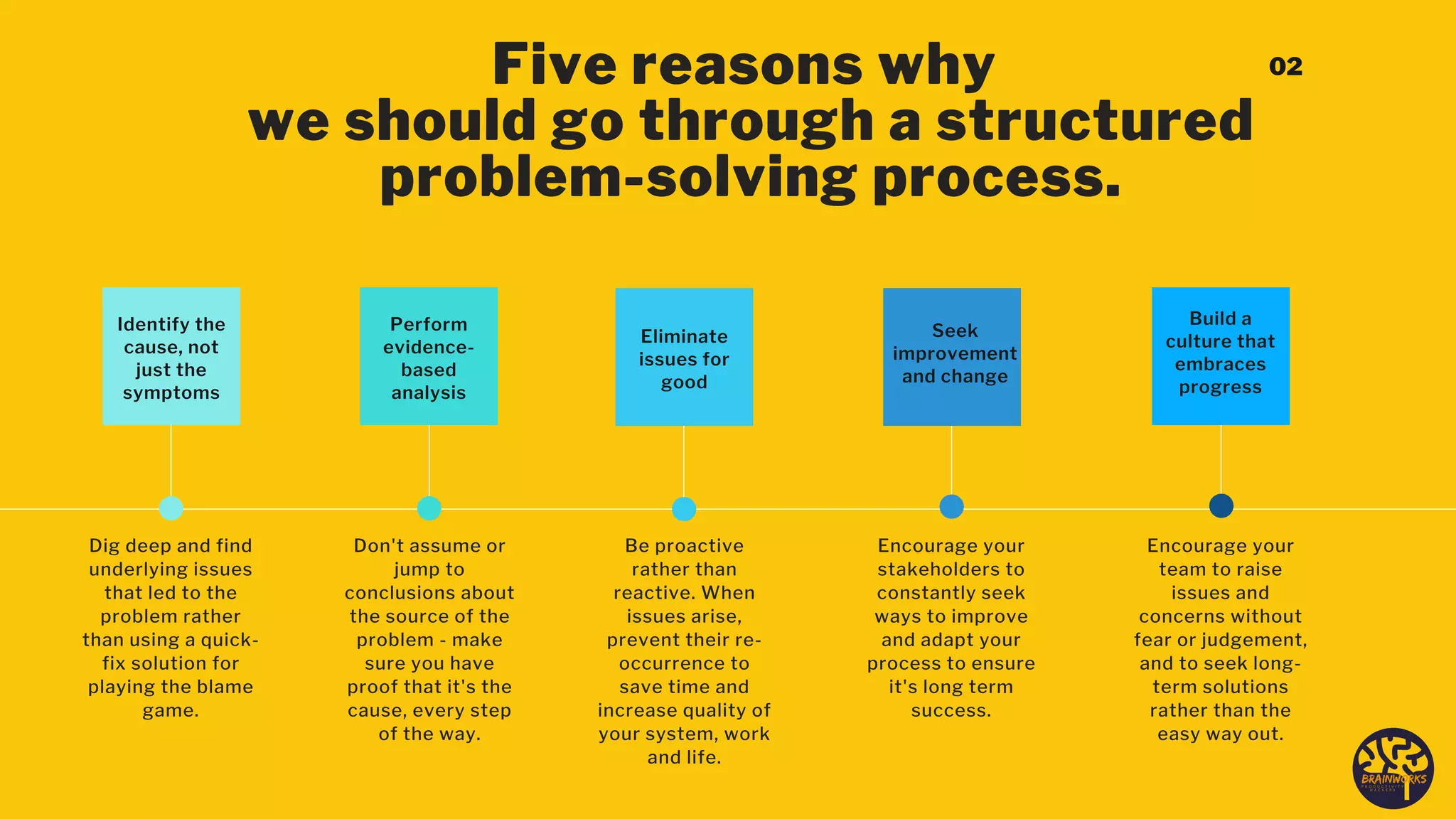
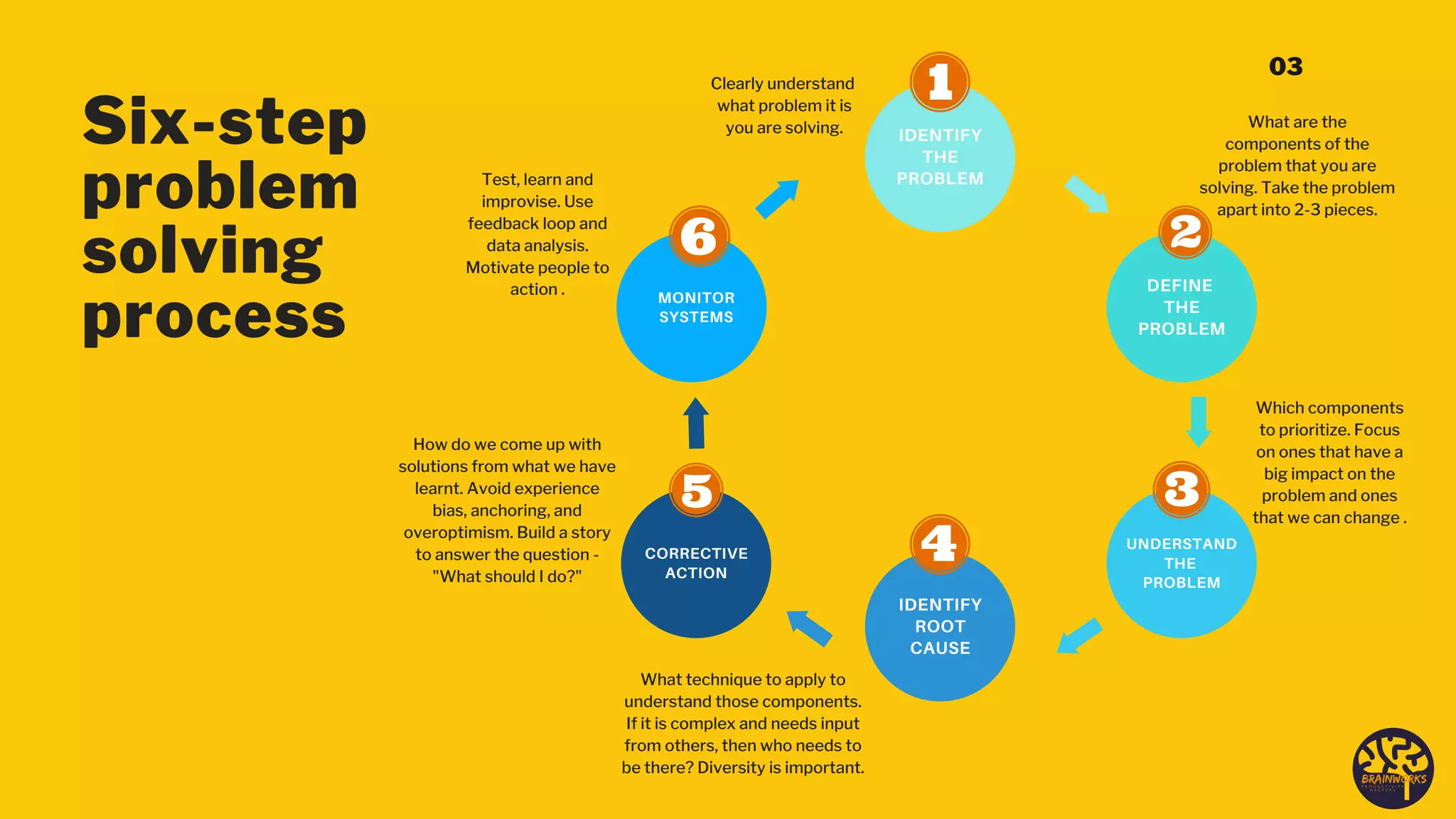
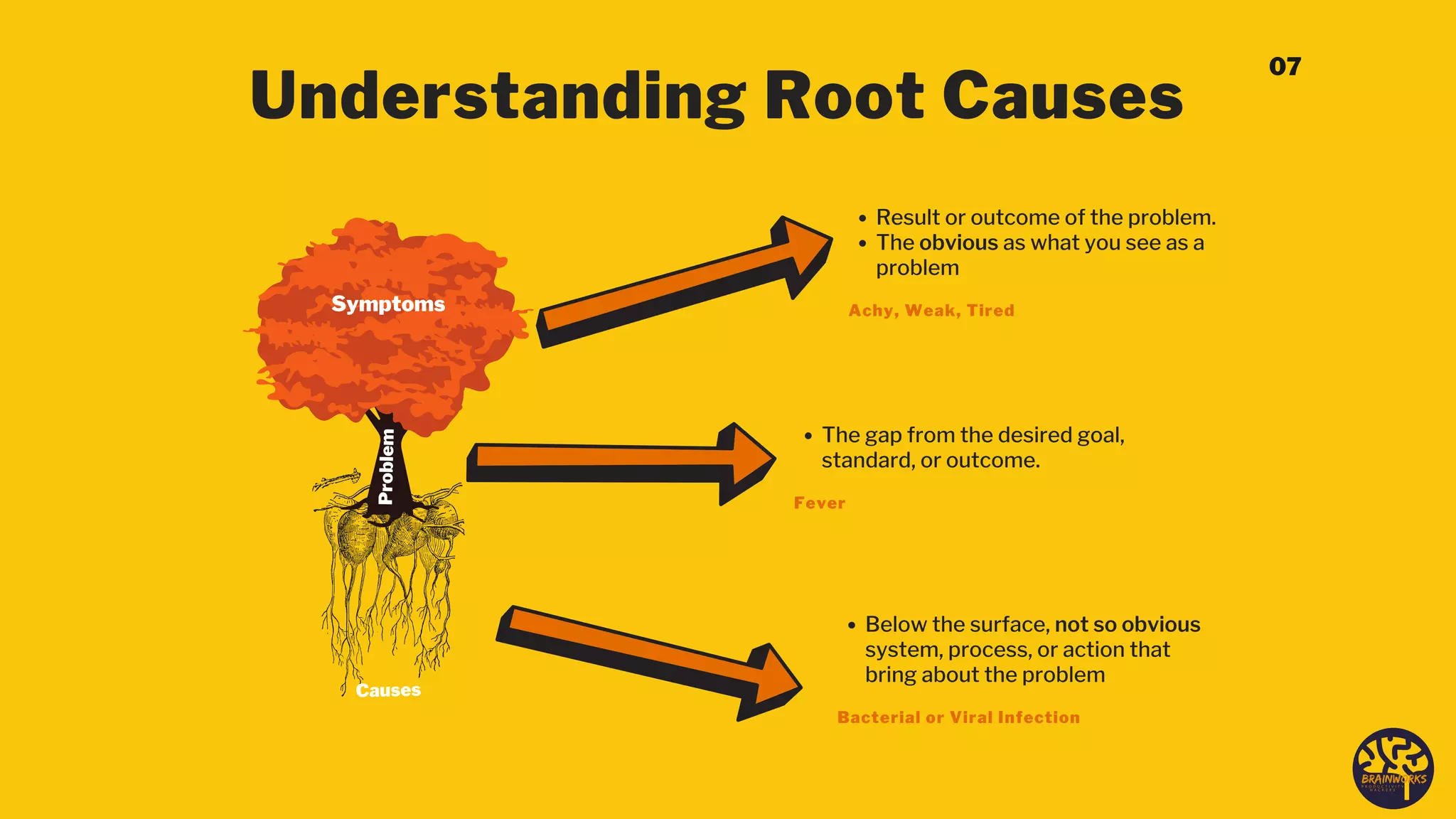
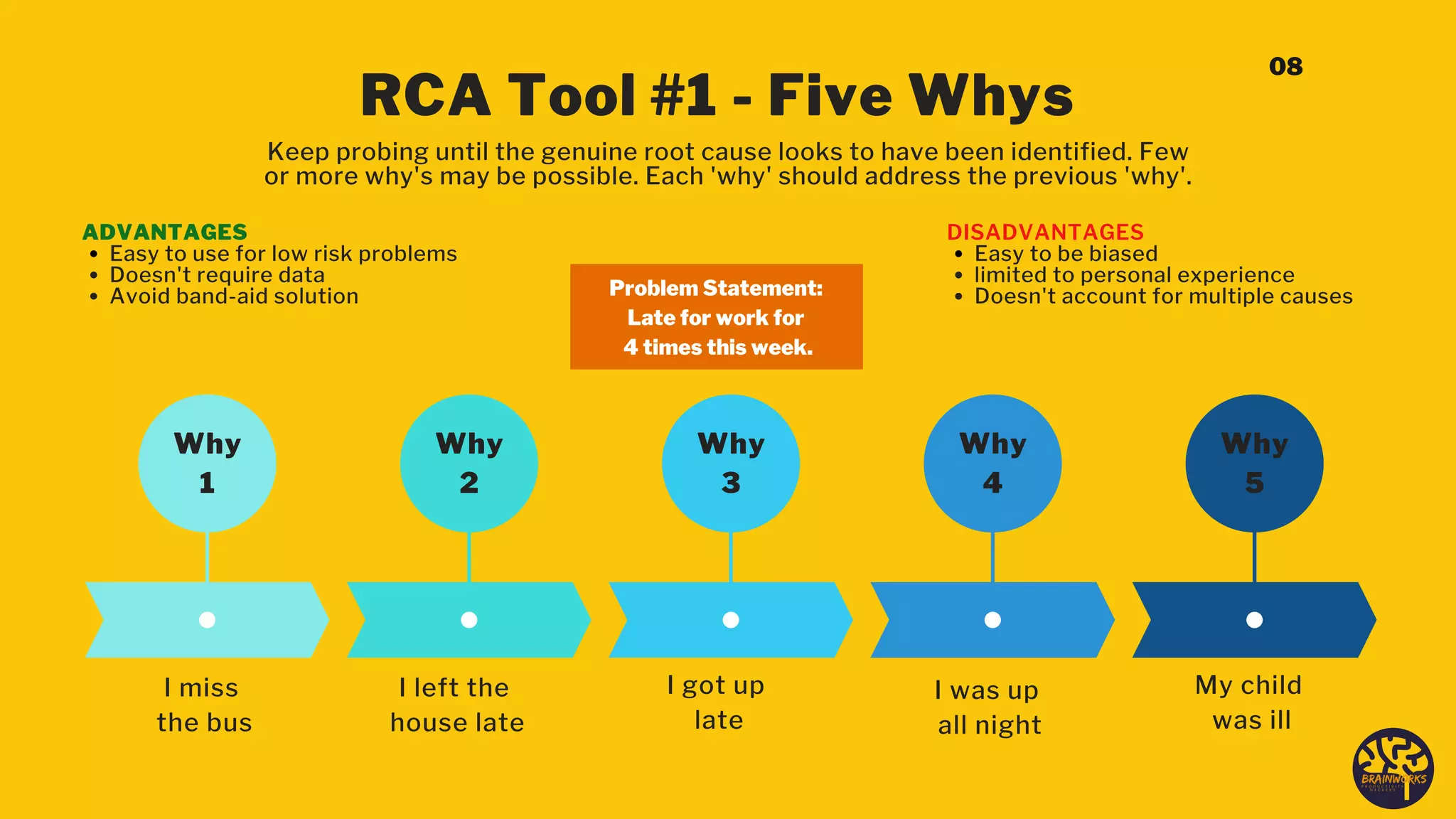
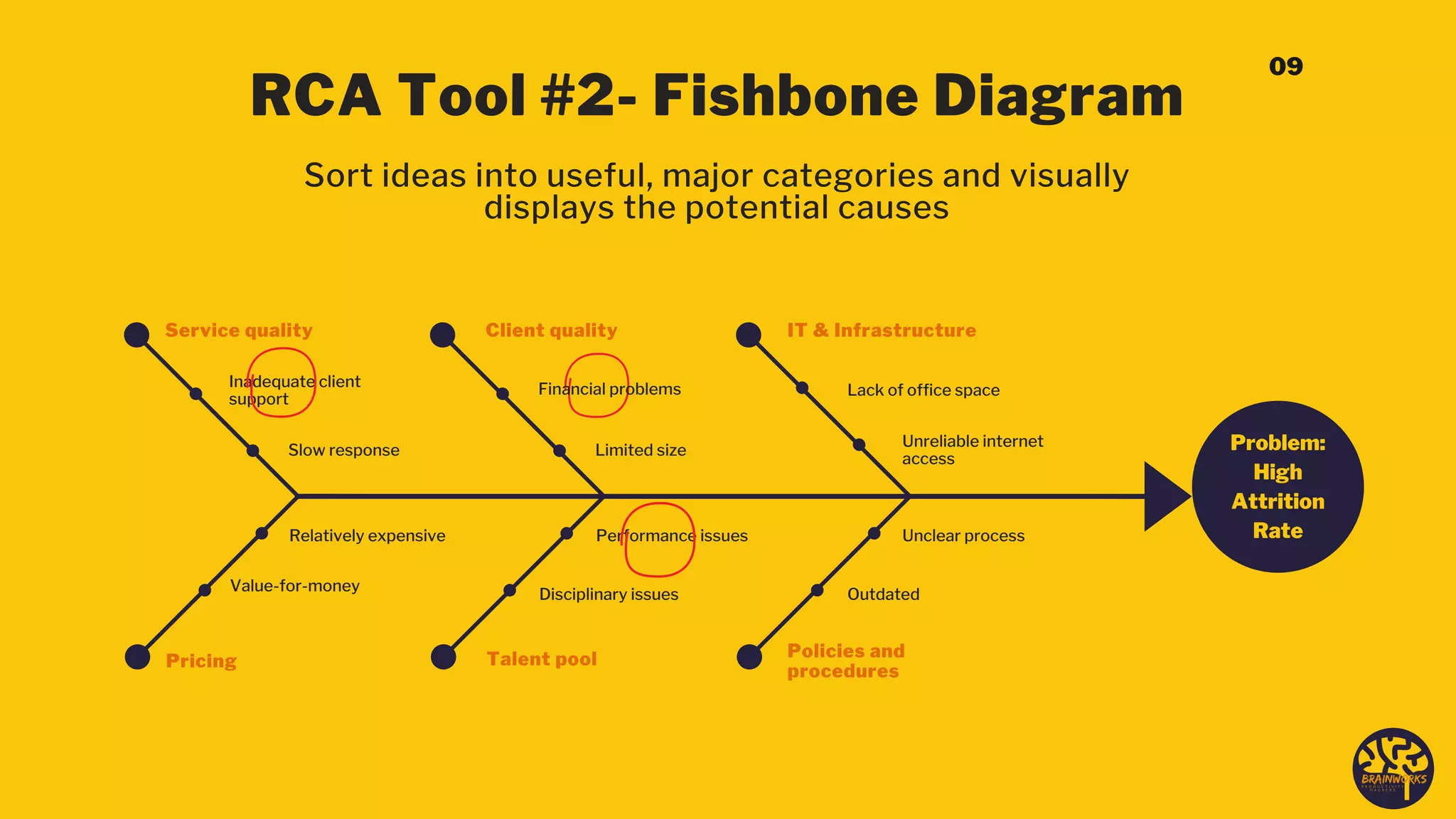
The document outlines a structured six-step problem-solving process that emphasizes understanding root causes through methods such as root cause analysis (RCA) and tools like the 'Five Whys' and 'Fishbone Diagram.' It encourages a proactive, evidence-based approach to addressing issues, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration among stakeholders. Ultimately, it highlights the importance of learning from mistakes and adapting processes to prevent future problems.