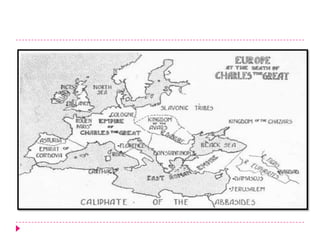
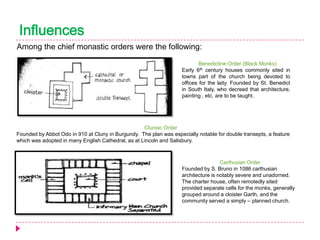
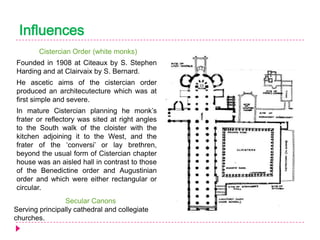
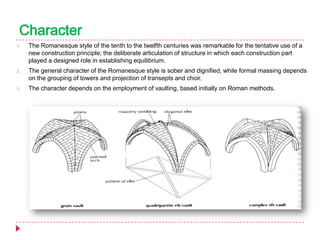
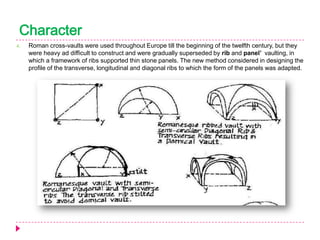
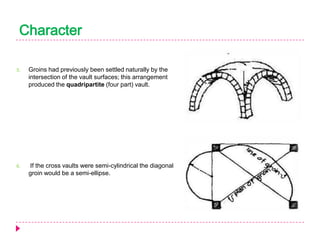
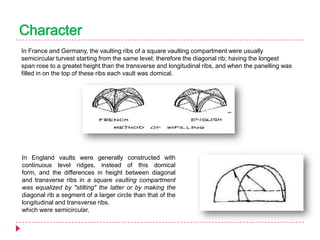
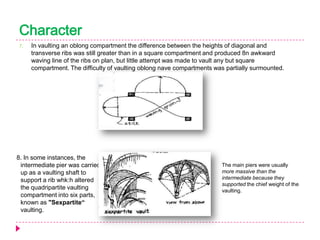
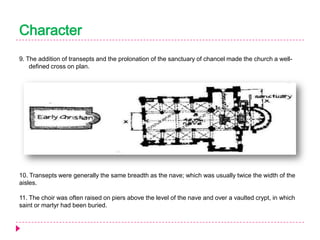
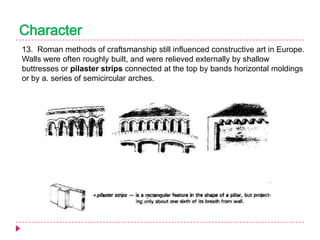
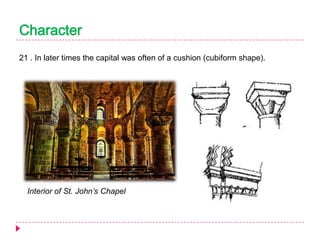
Romanesque architecture developed throughout Western Europe between the 10th and 12th centuries. It was influenced by a variety of geographical, geological, climatic, religious, social, political, and historical factors. The style is characterized by its sober and dignified formal massing, with an emphasis on towers, transepts, and vaulted construction methods derived from Roman precedents. Rib and panel vaulting became widespread, allowing for more complex vault configurations. Door and window openings featured receding concentric moldings and arches. Ornamentation included carved vegetable and animal motifs. Major Romanesque architectural works include cathedrals, abbeys, and their associated structures across Europe.