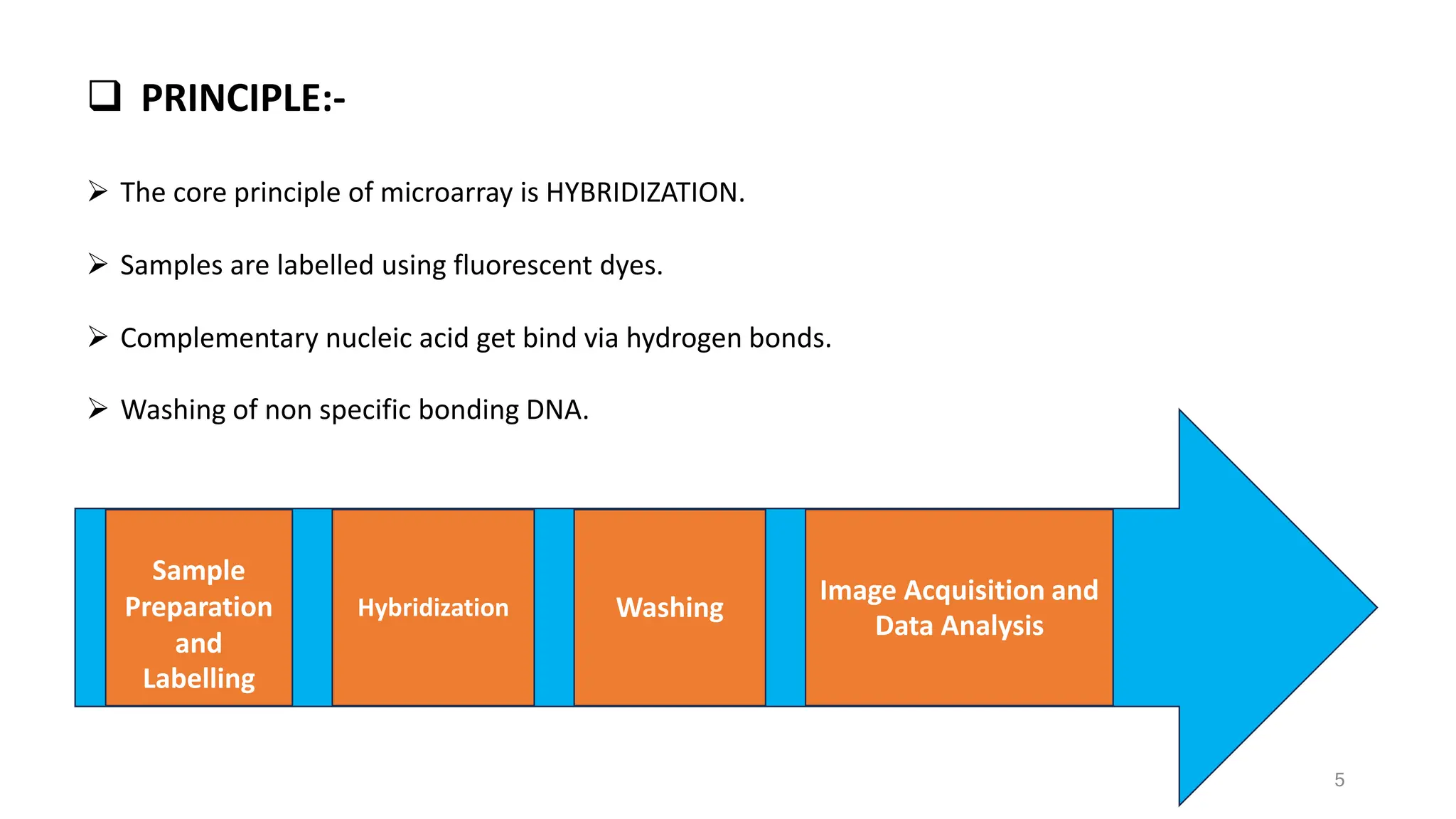
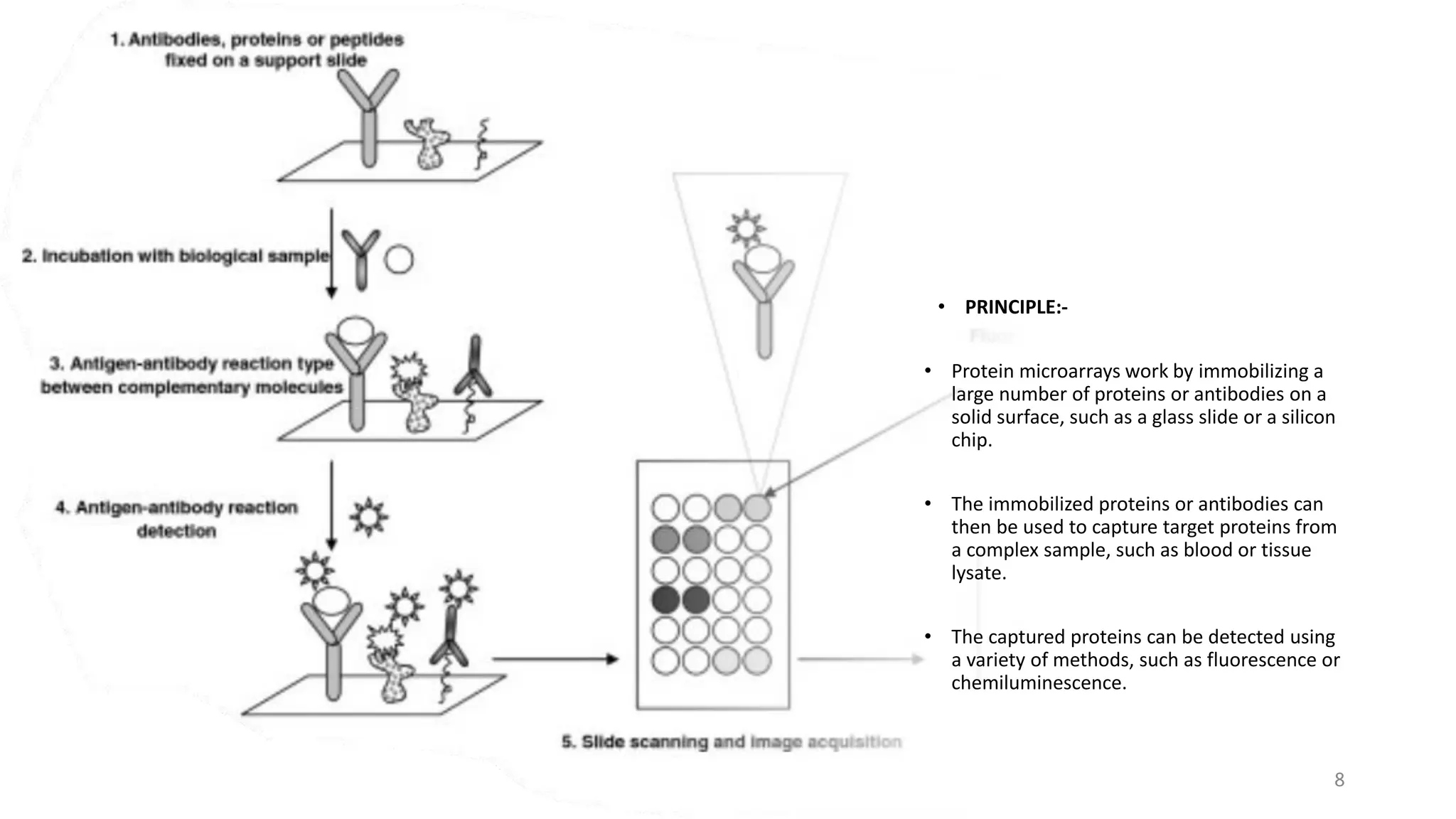
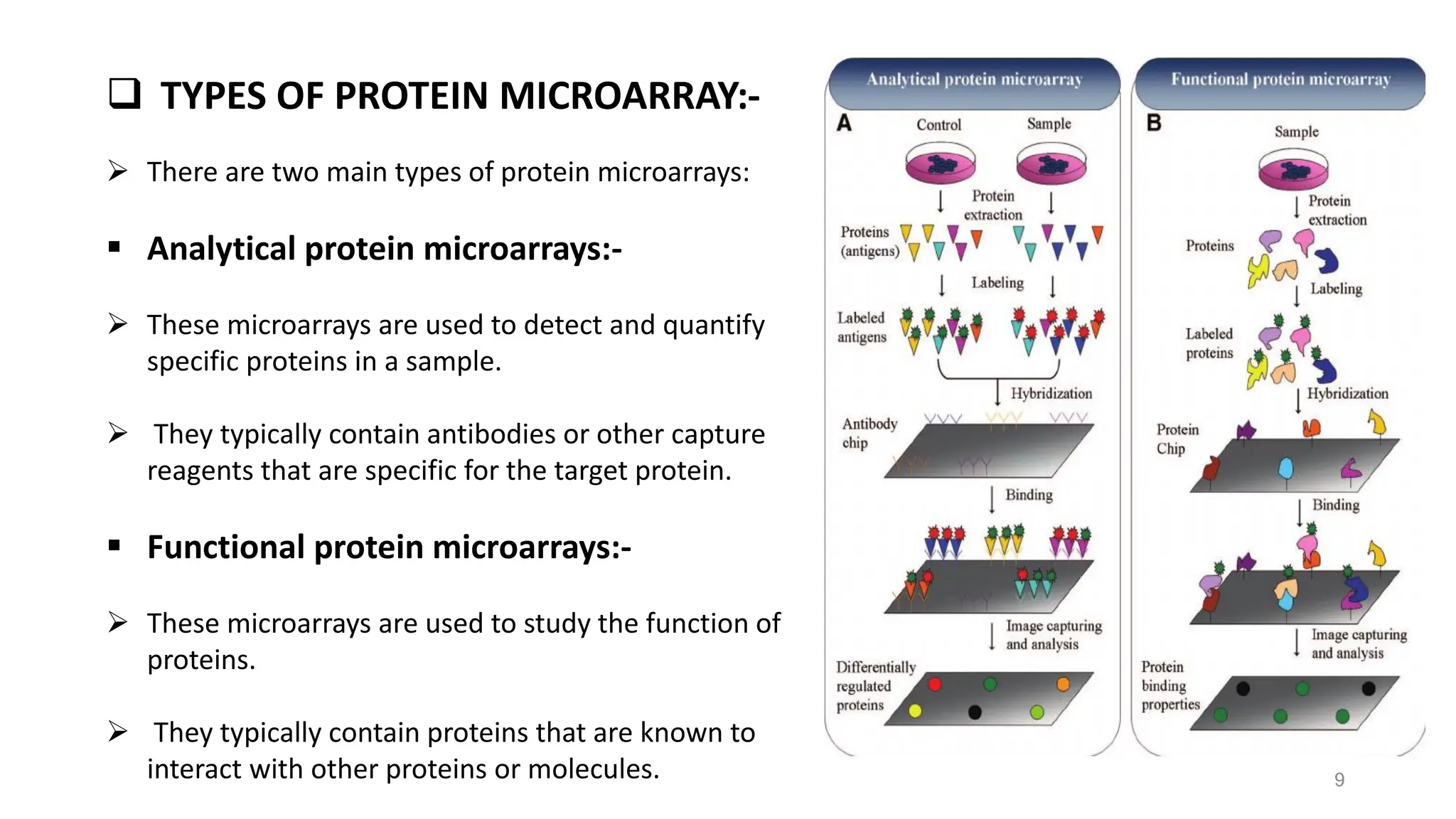
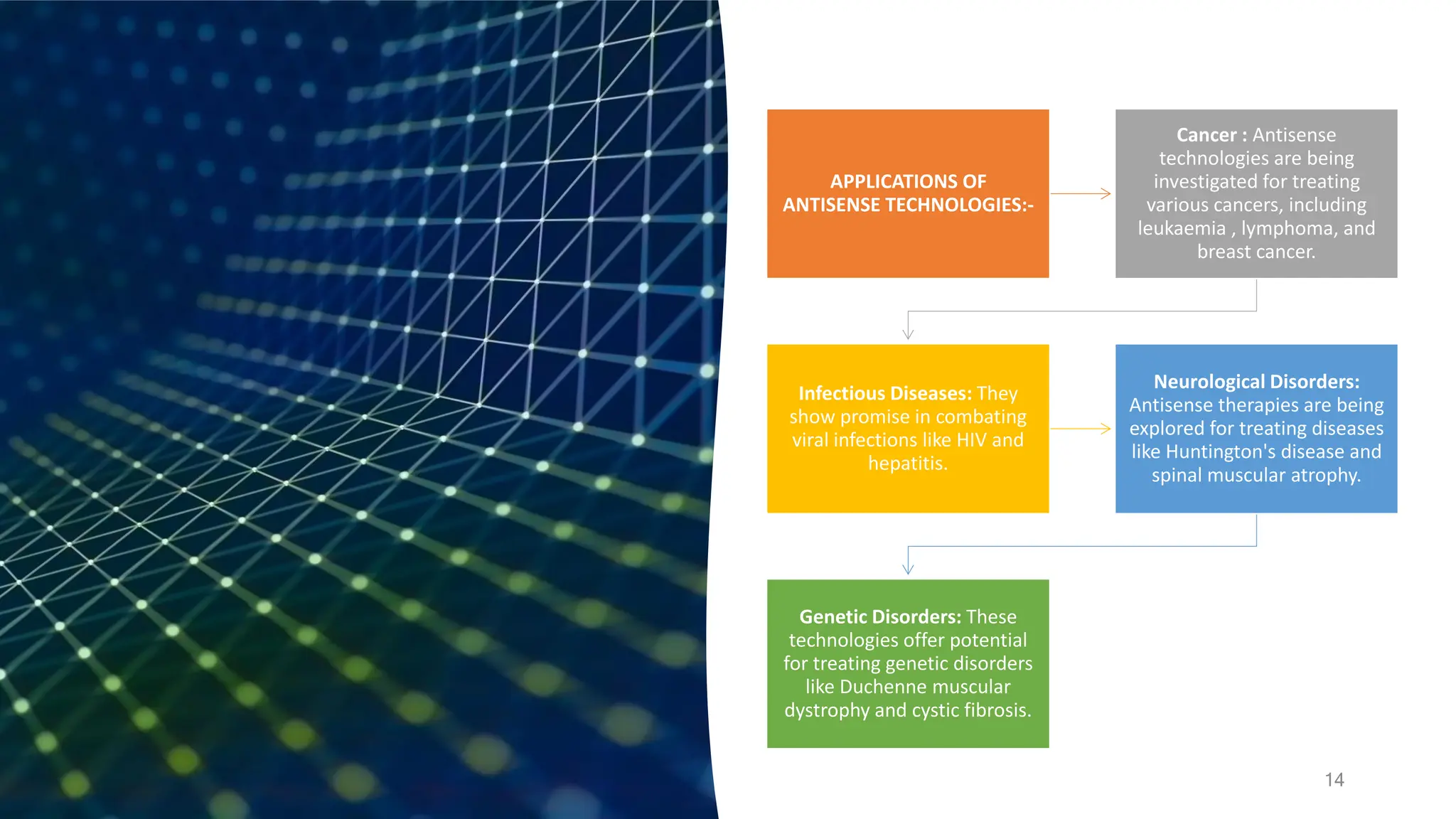
The document provides an overview of nucleic acid and protein microarrays, detailing their principles, types, and applications in fields such as disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and genomics. It also covers antisense technologies, explaining how they modulate gene expression through antisense oligonucleotides and their applications in treating various diseases. Additionally, the document distinguishes between different microarray types, such as DNA and protein microarrays, highlighting their significance in research and clinical diagnostics.