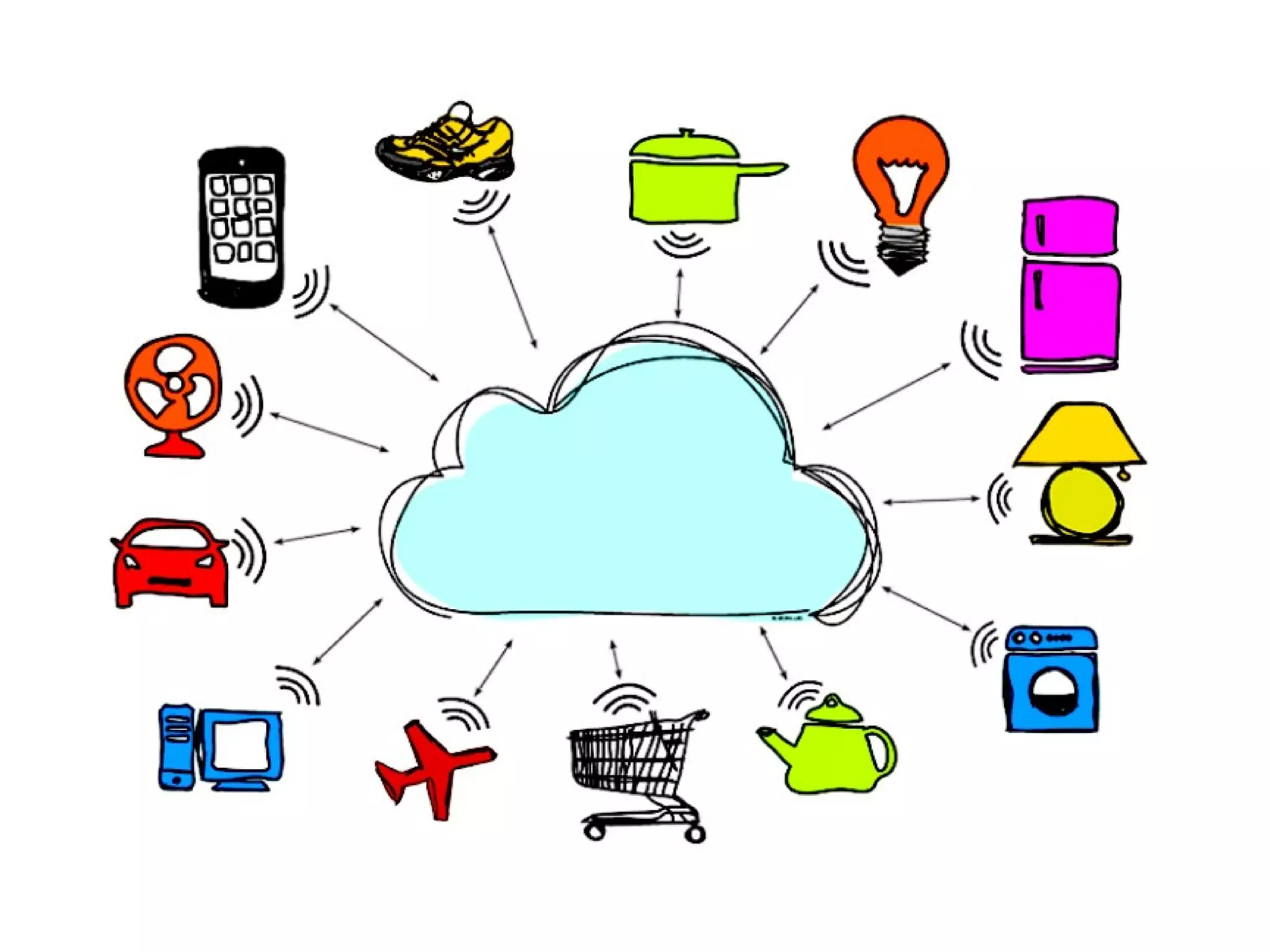
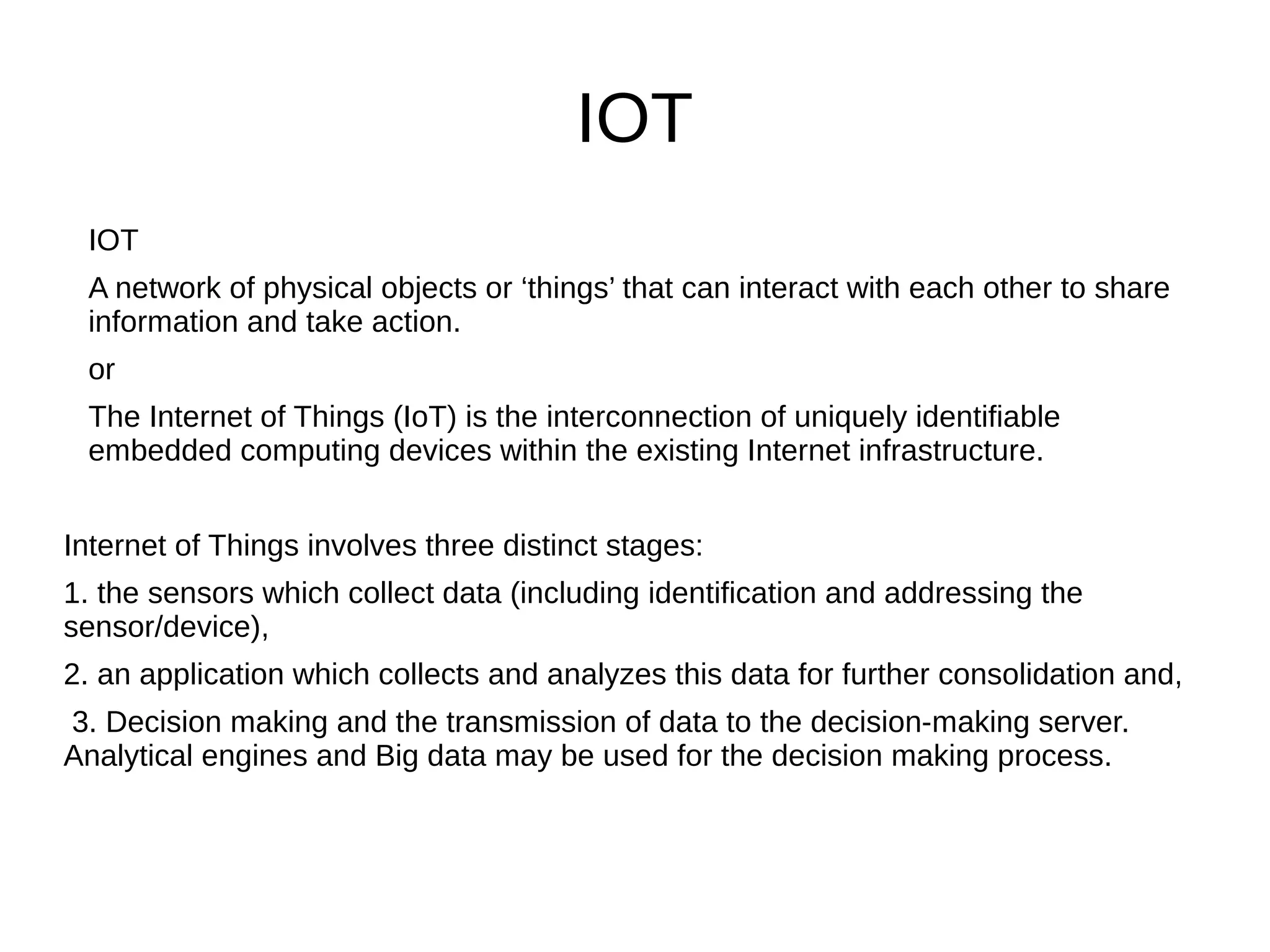
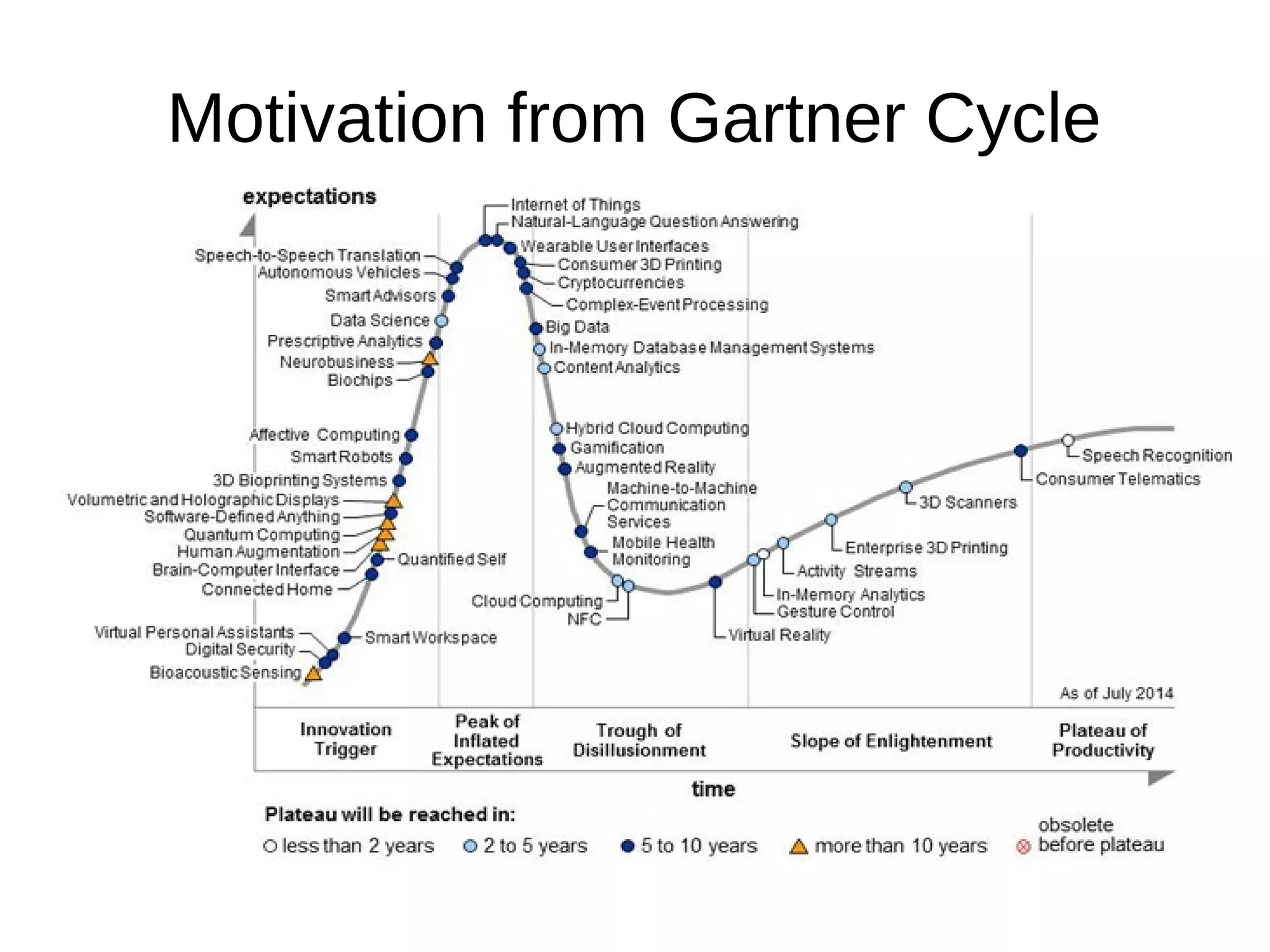
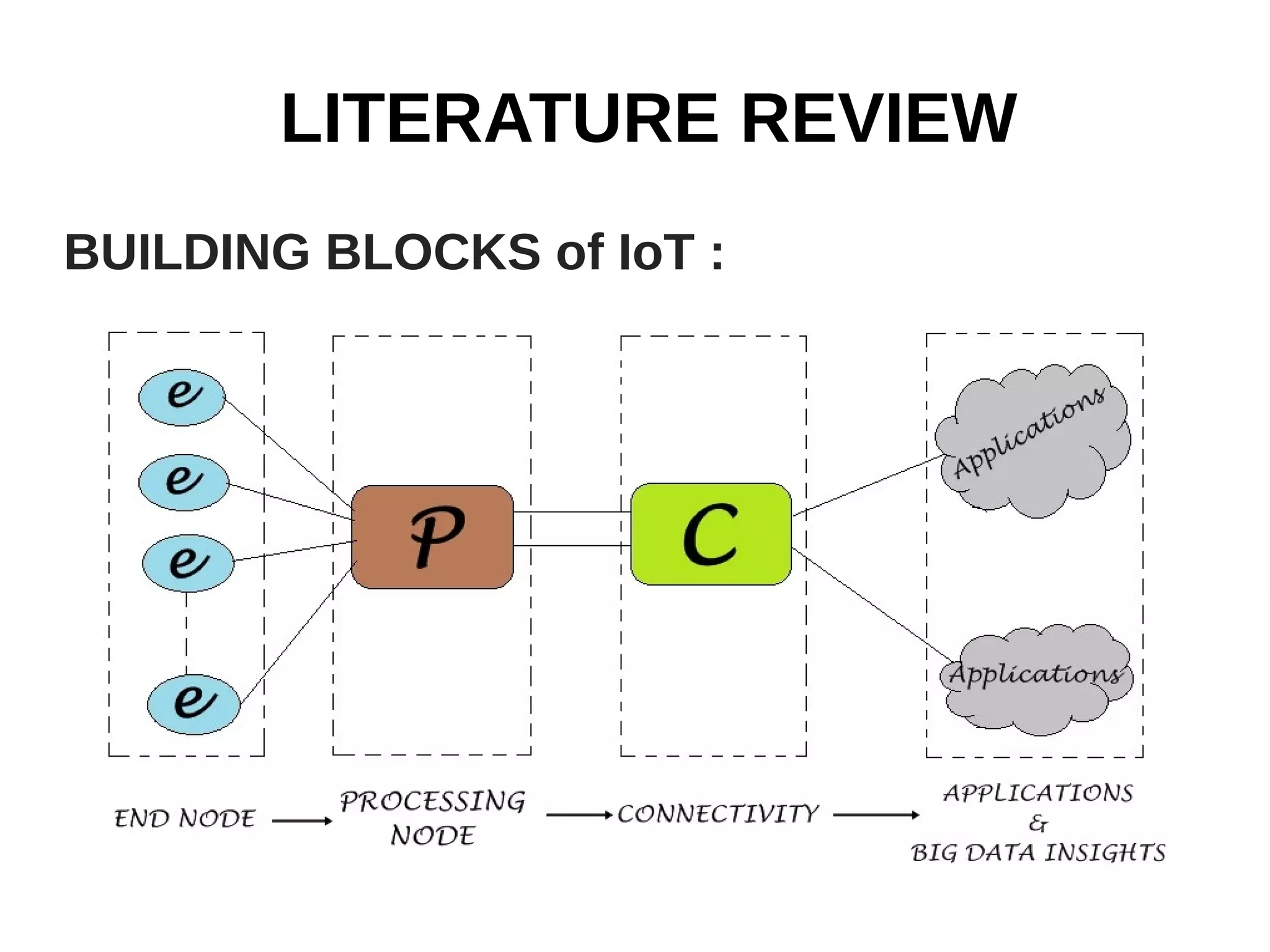
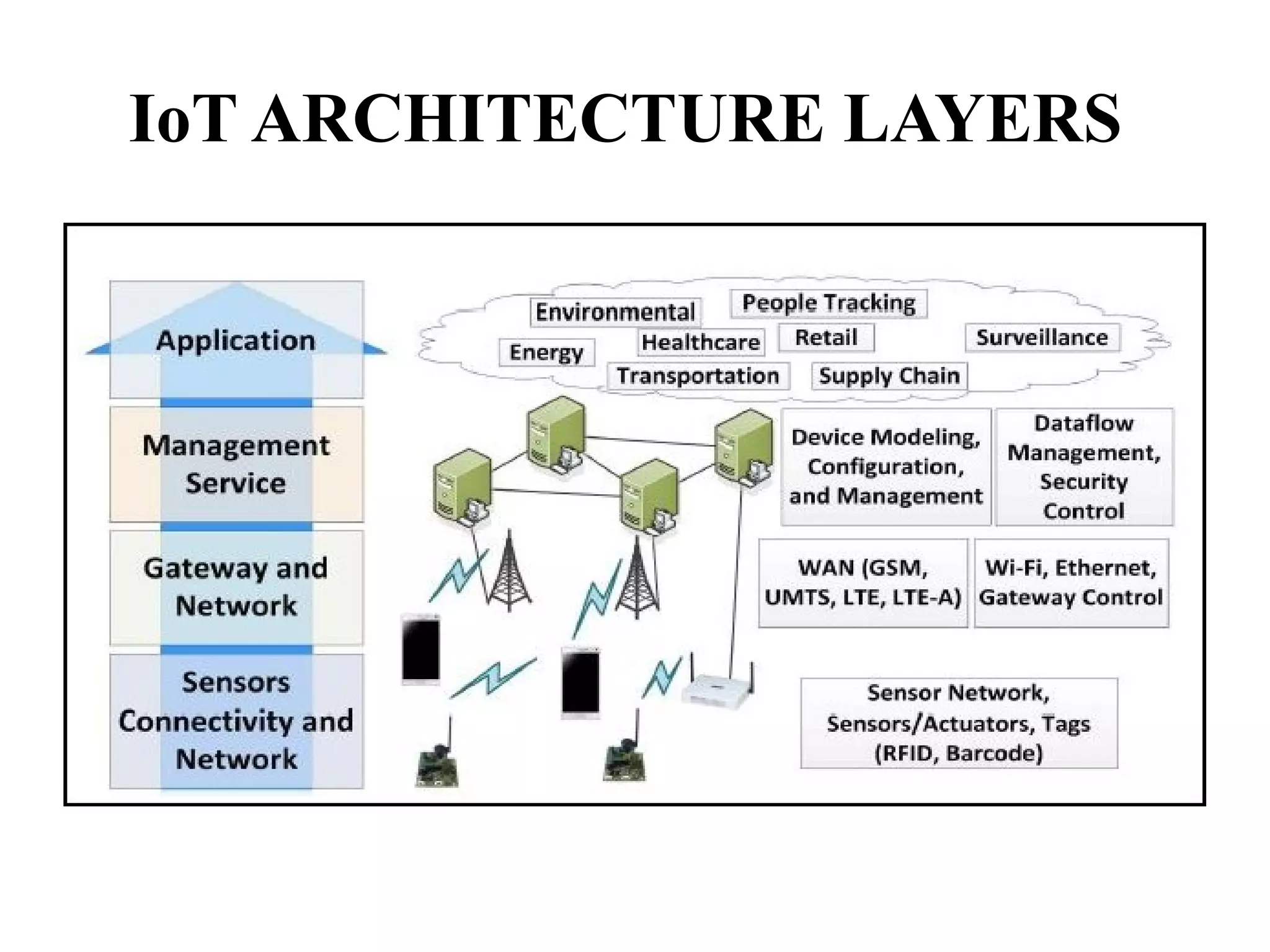
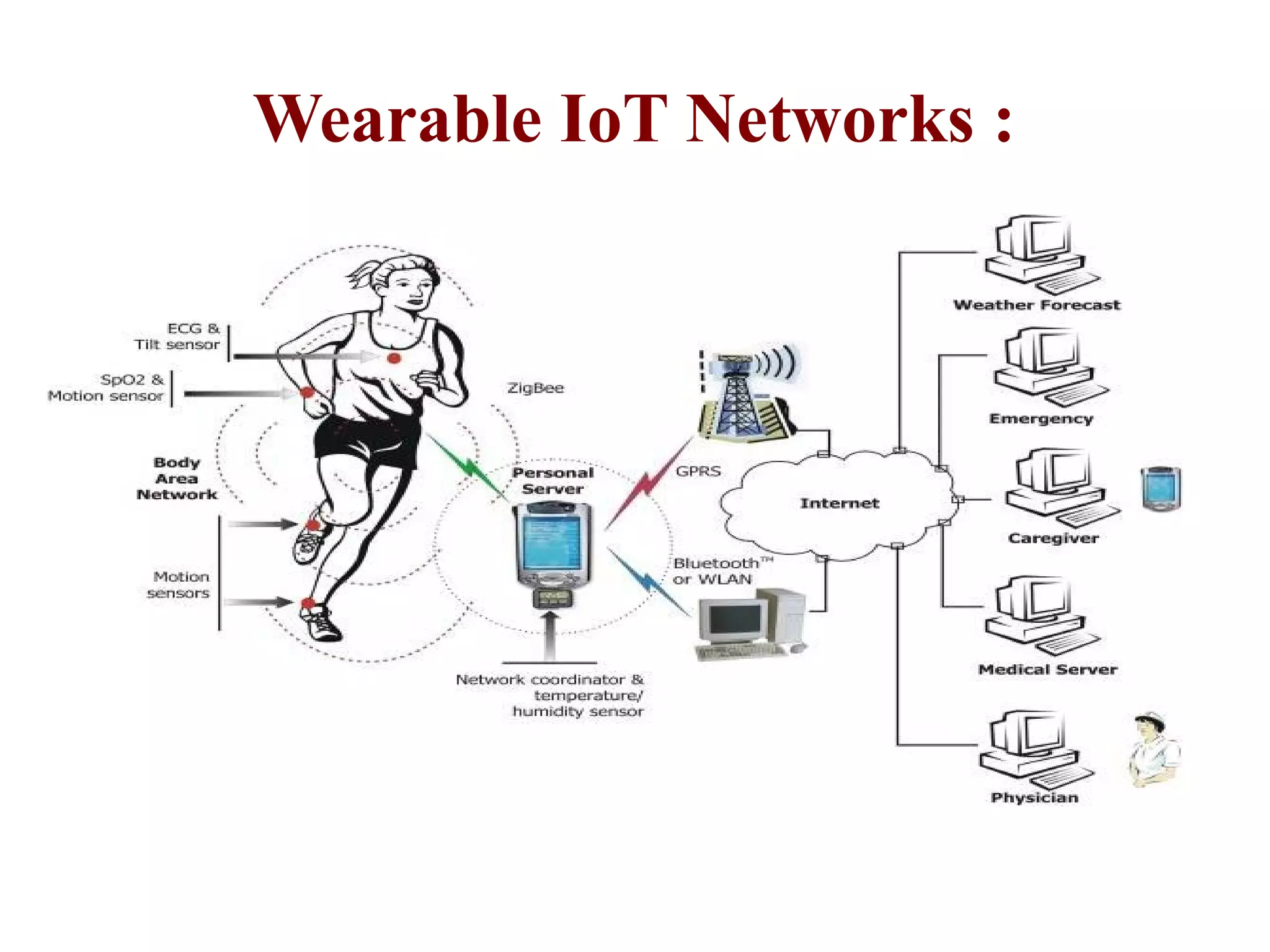
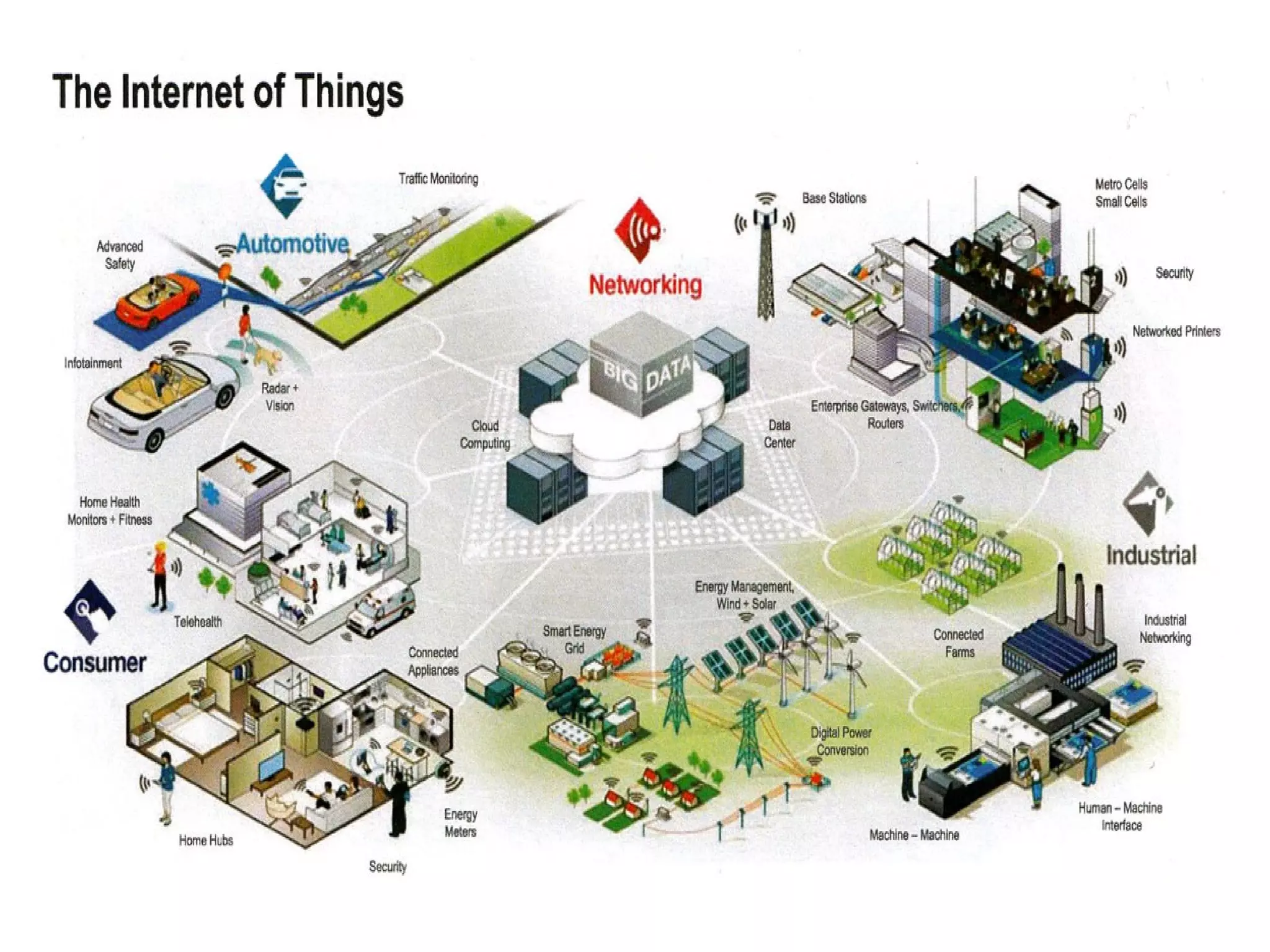
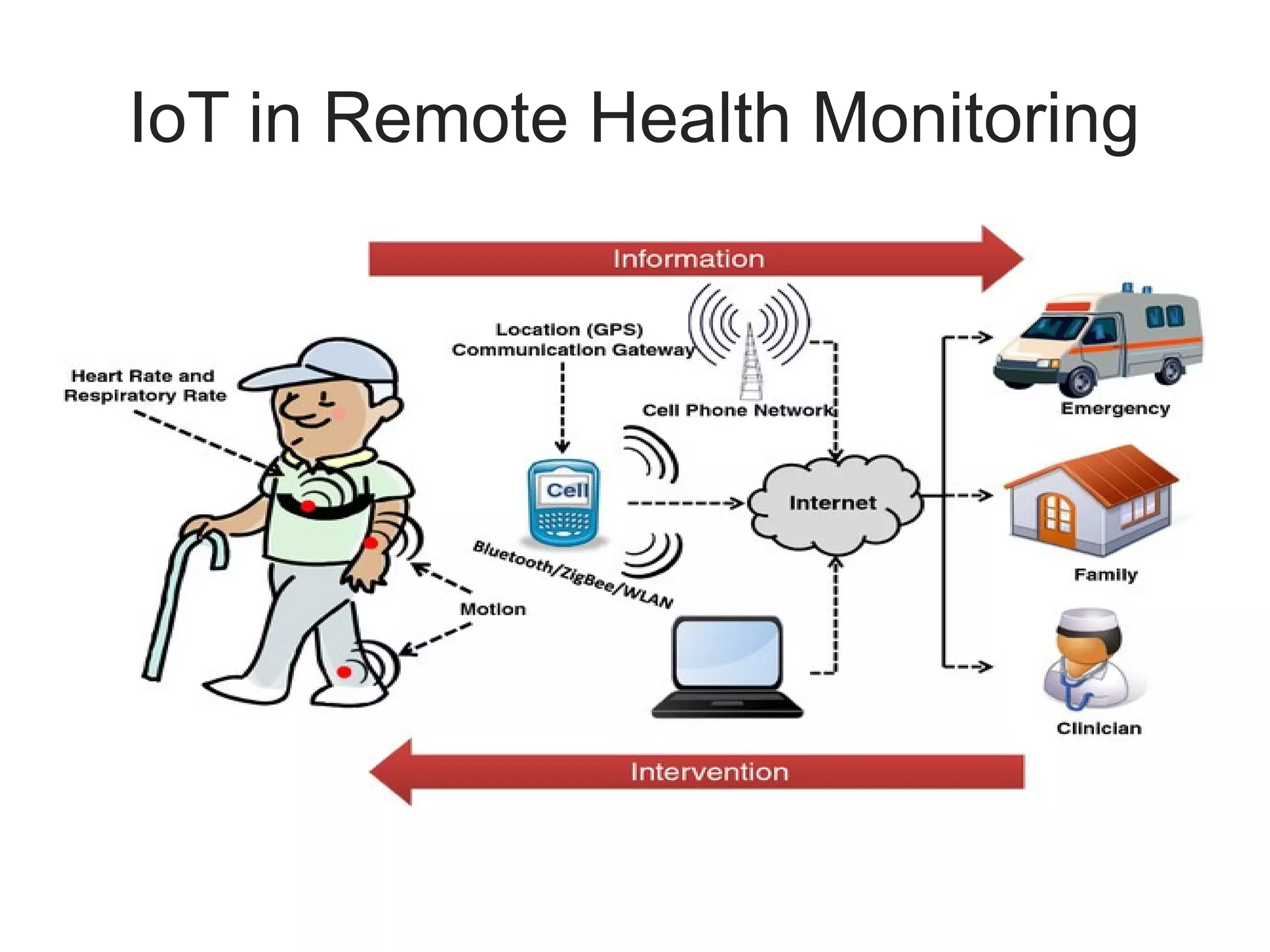
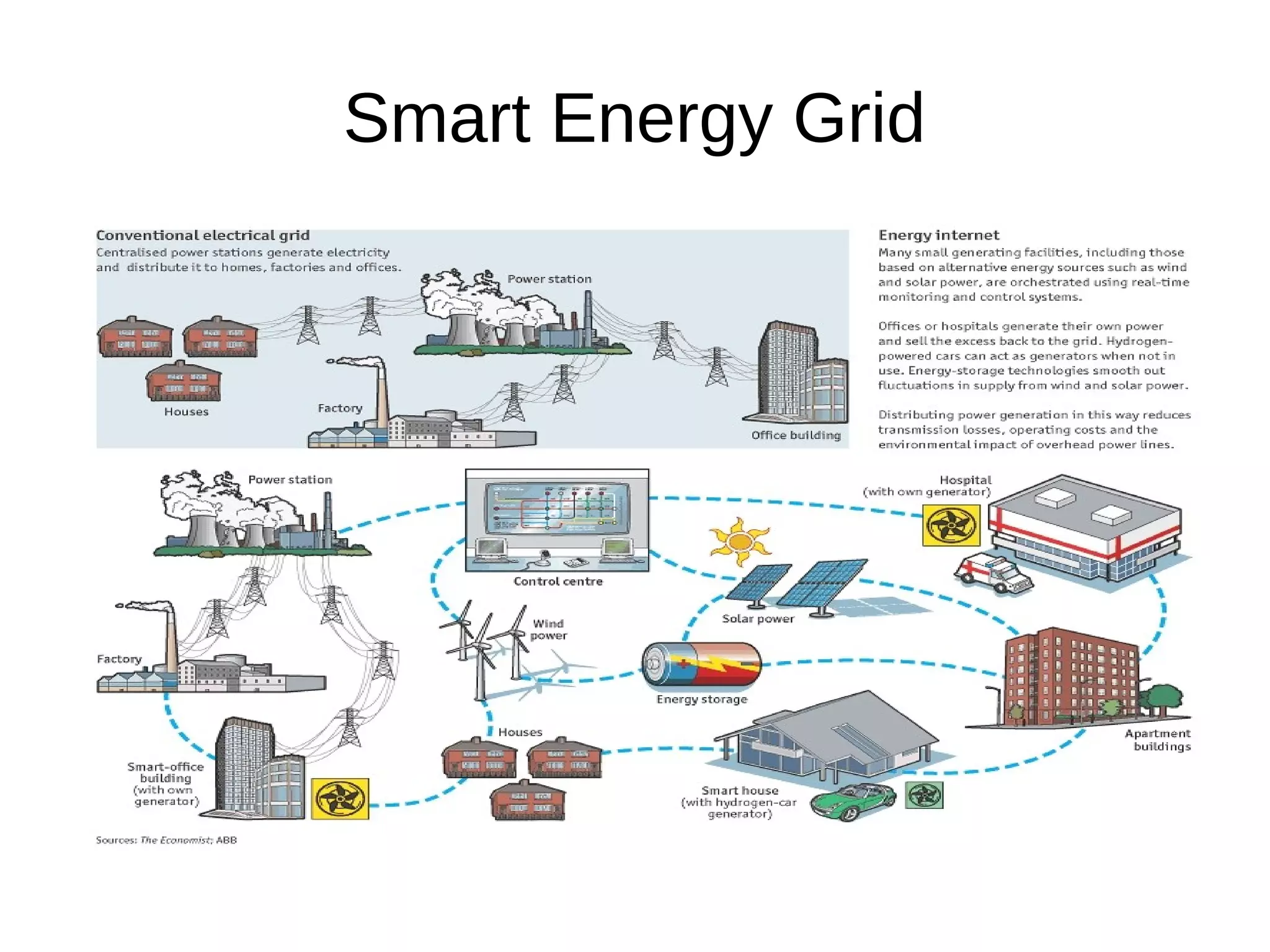
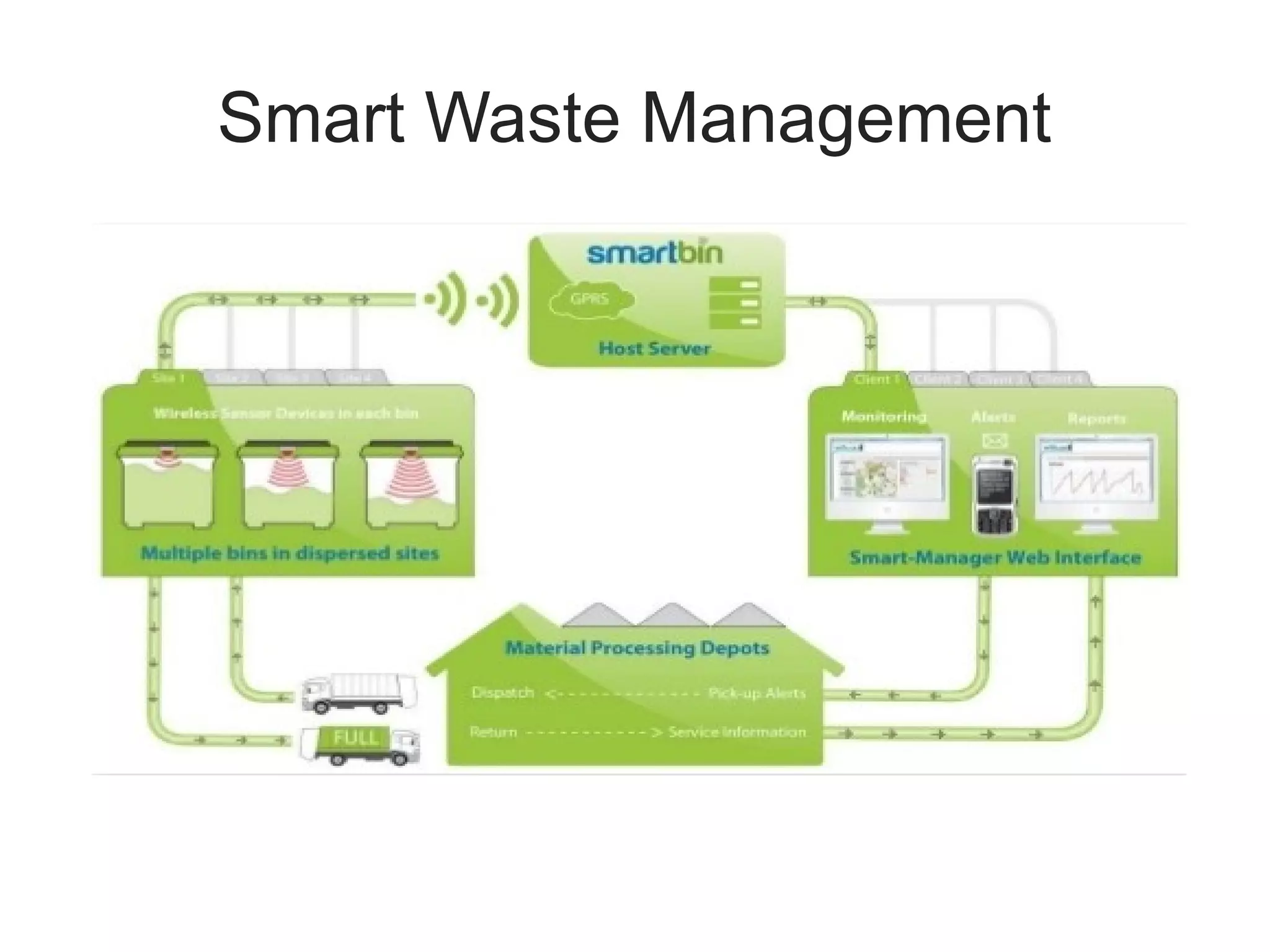
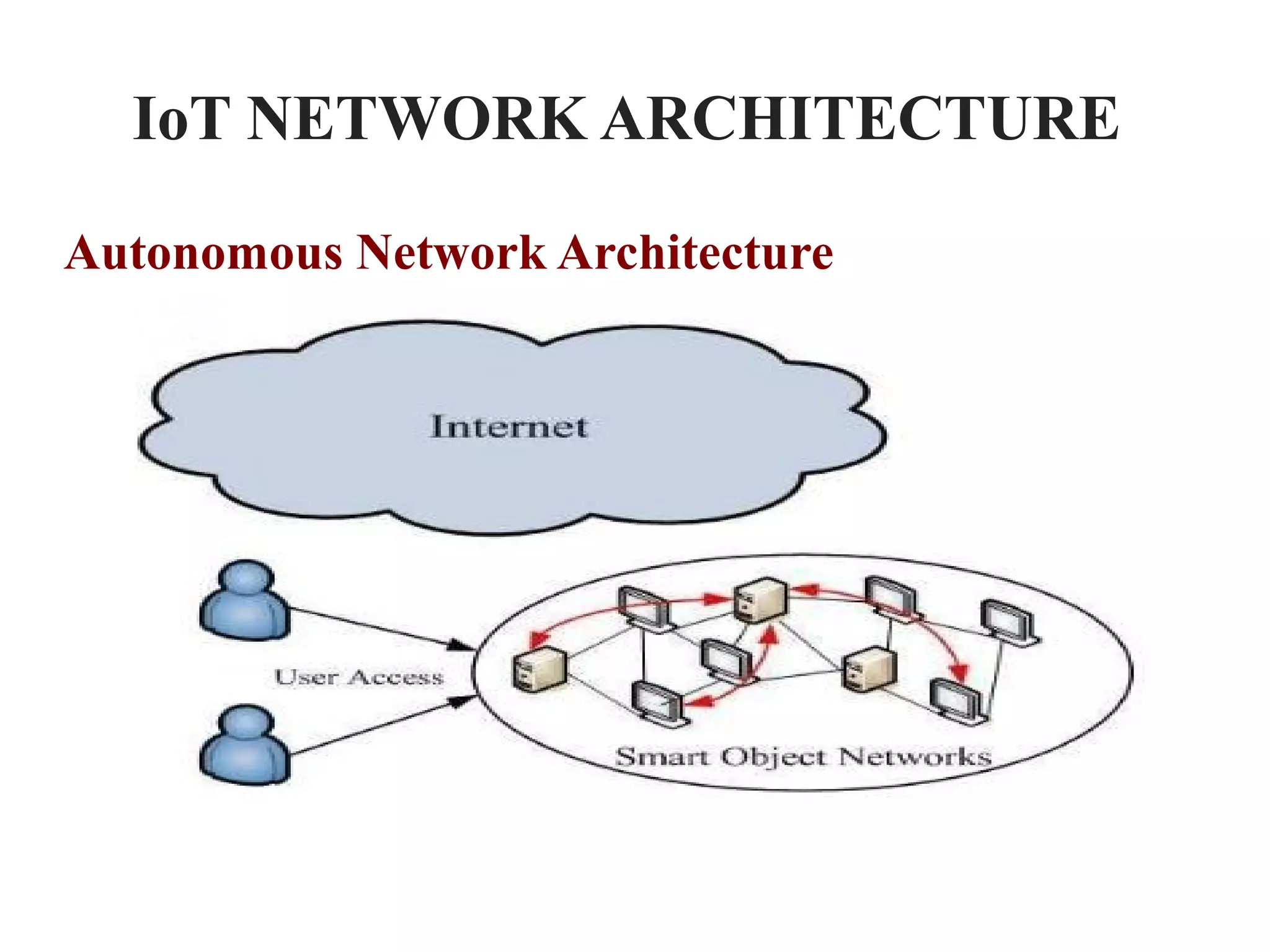
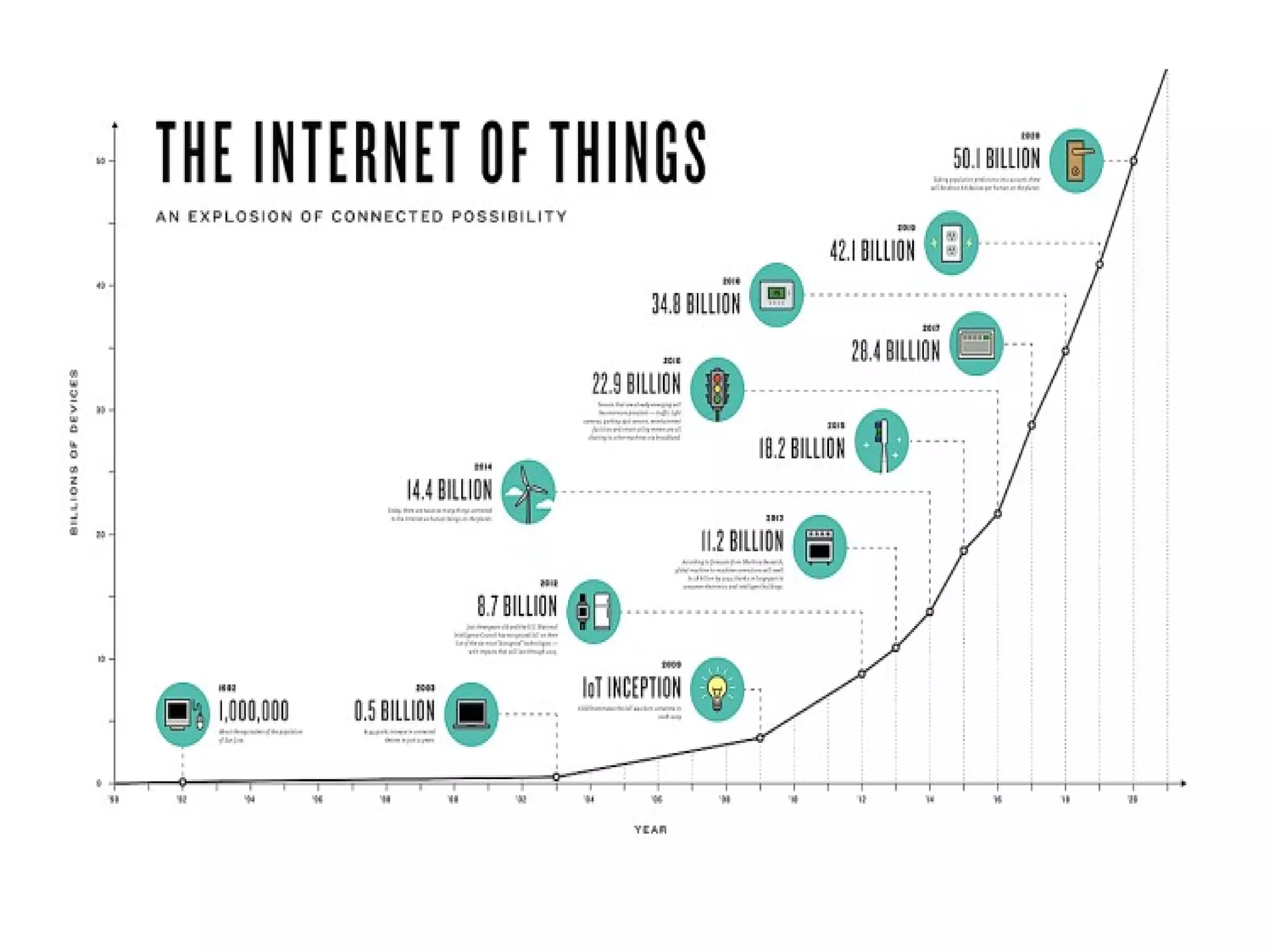
The document discusses the role of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and devices in developing smart cities. It defines key concepts like smart city and IoT. The objective is to study the capabilities of existing IoT devices and services to meet the needs of smart cities. The methodology examines popular IoT devices, technologies, networks and cloud services. It also outlines prototype projects and predictions about IoT growth and impact.