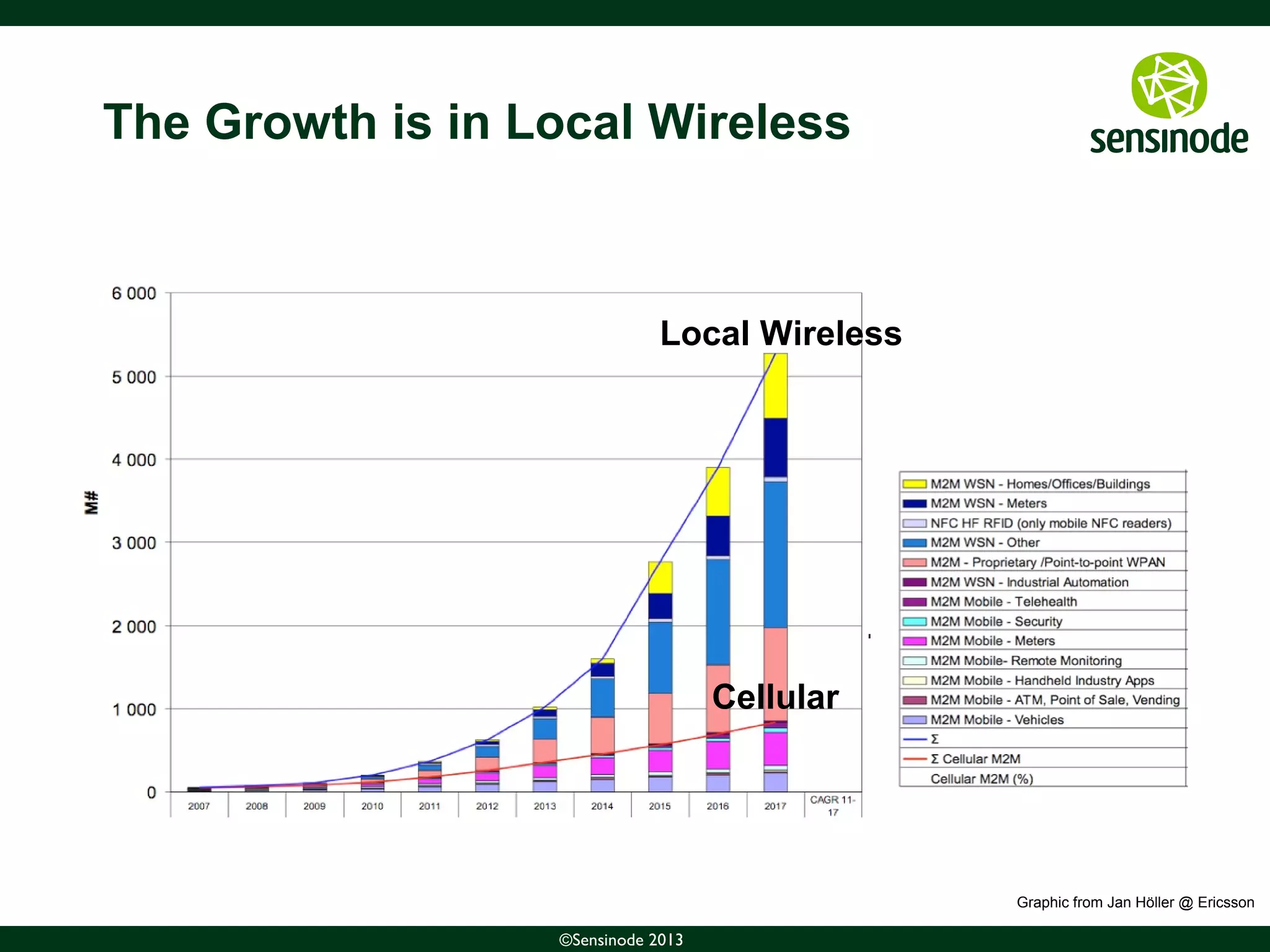
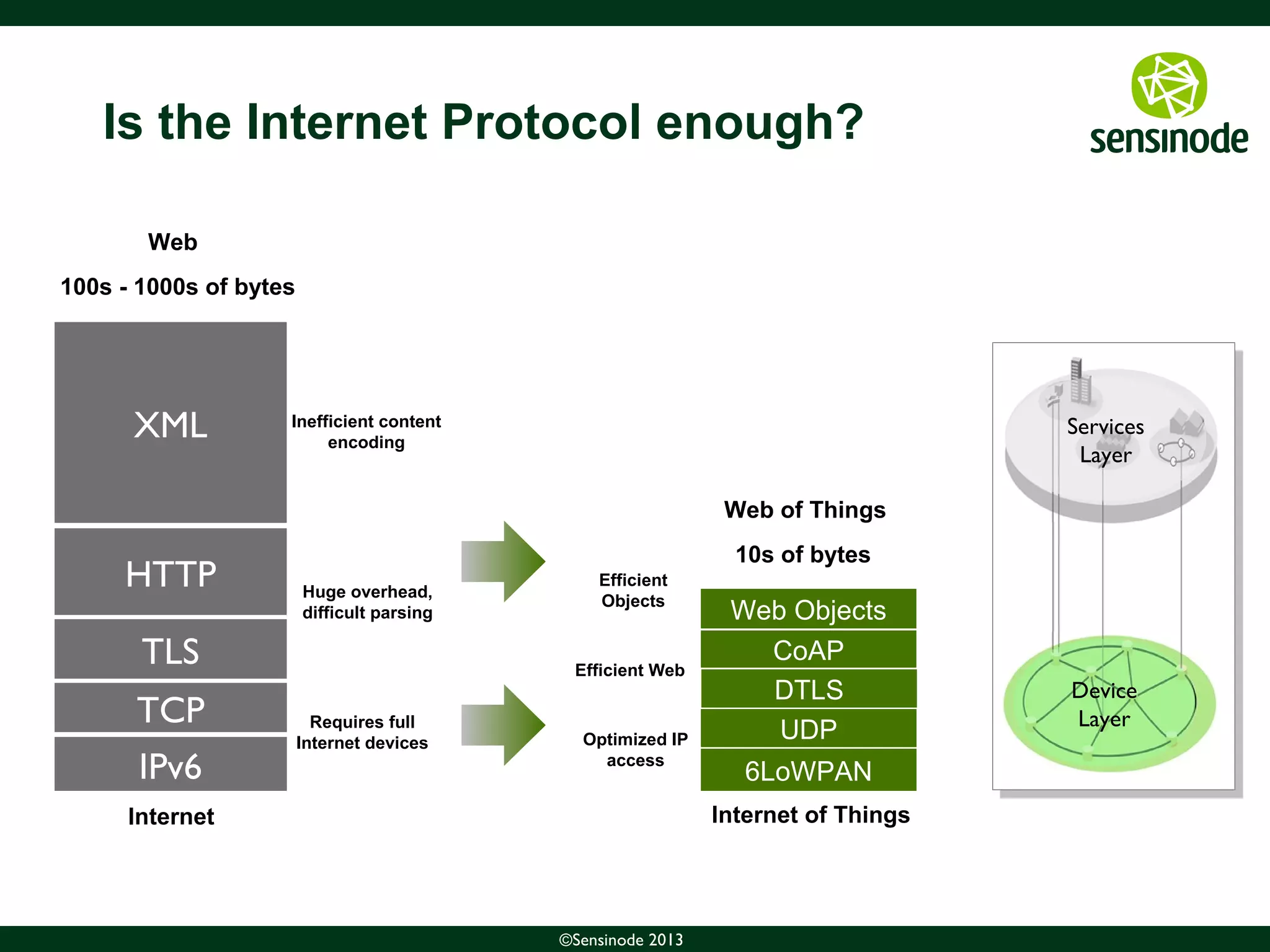
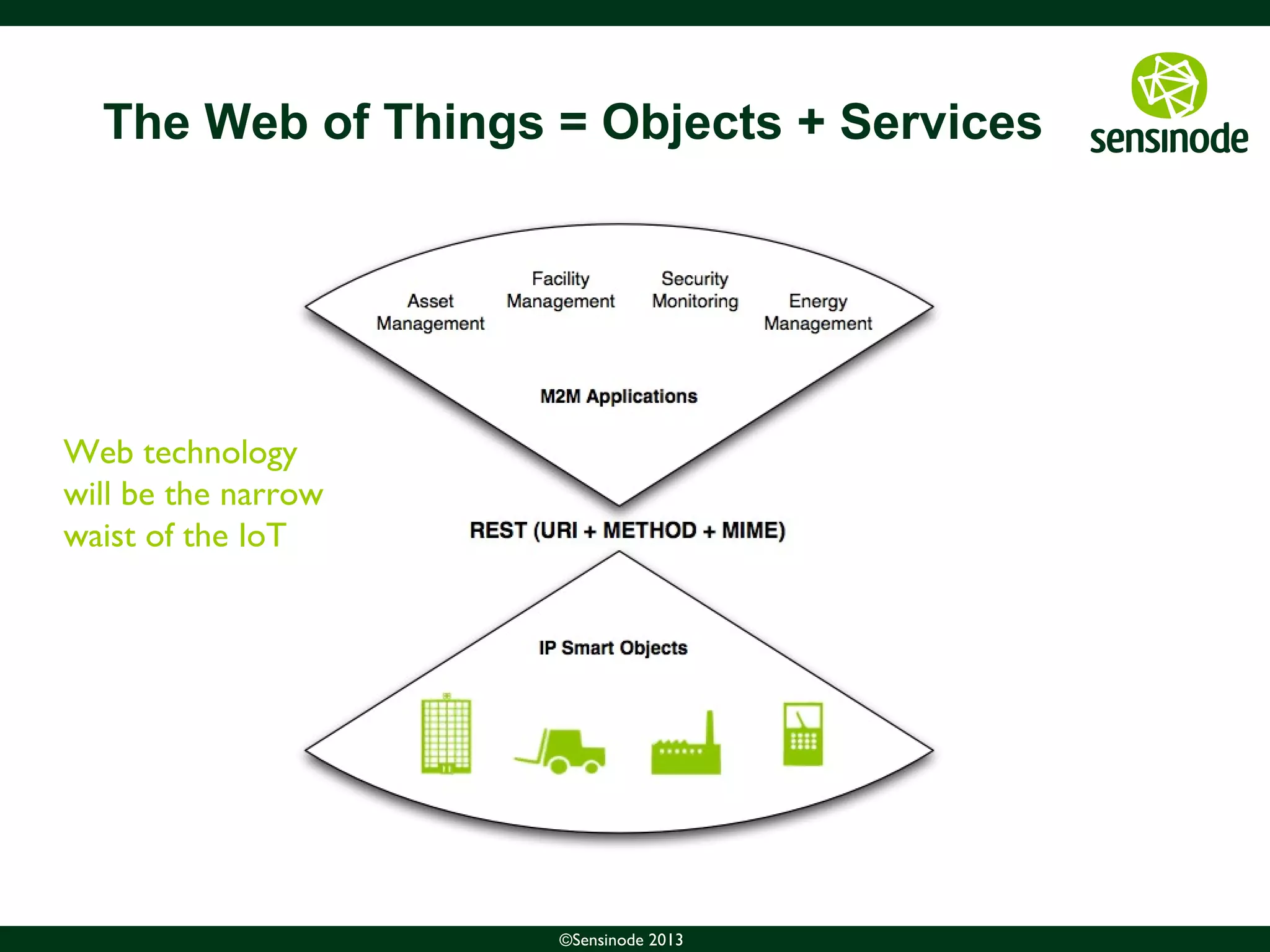
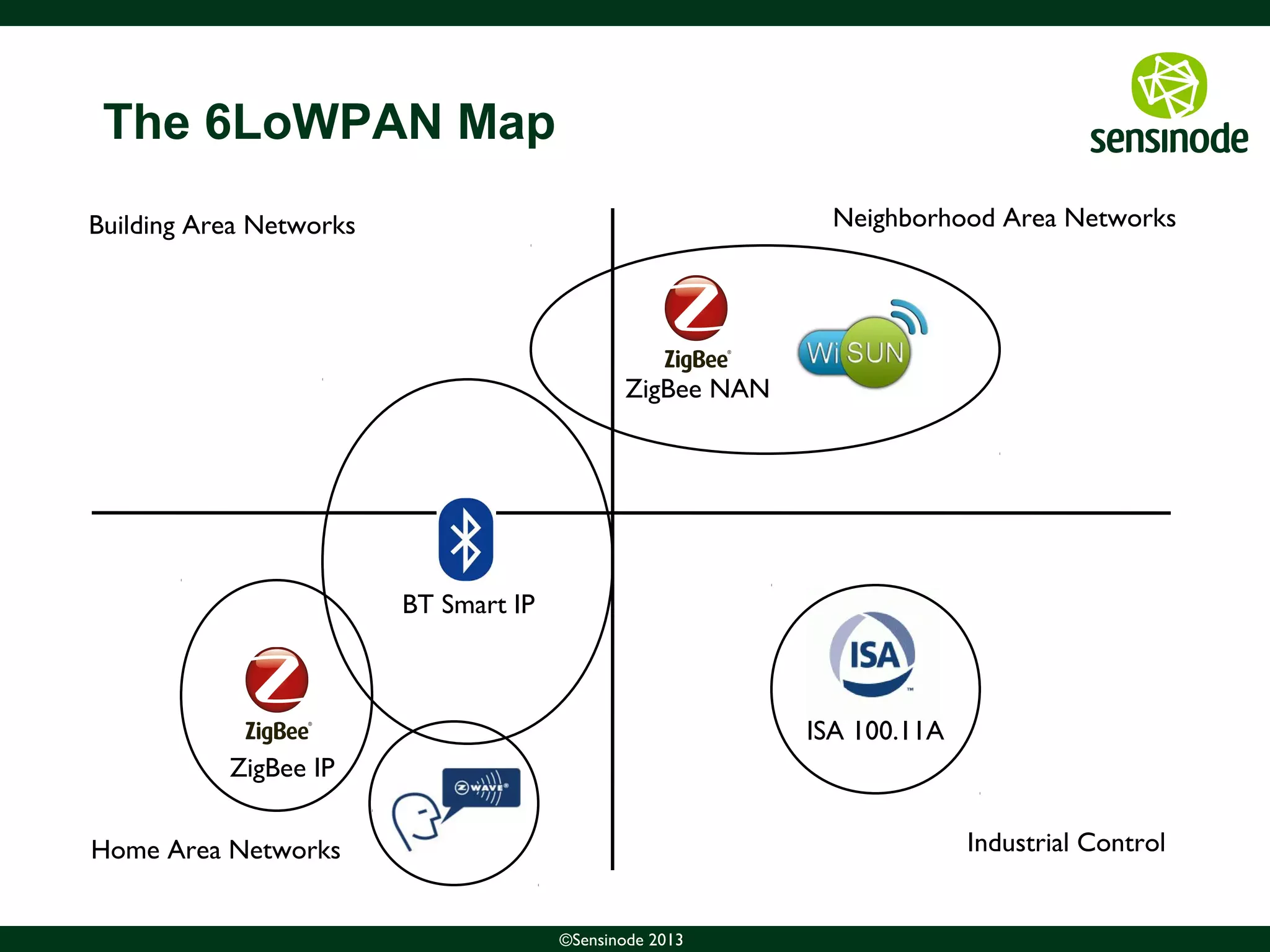
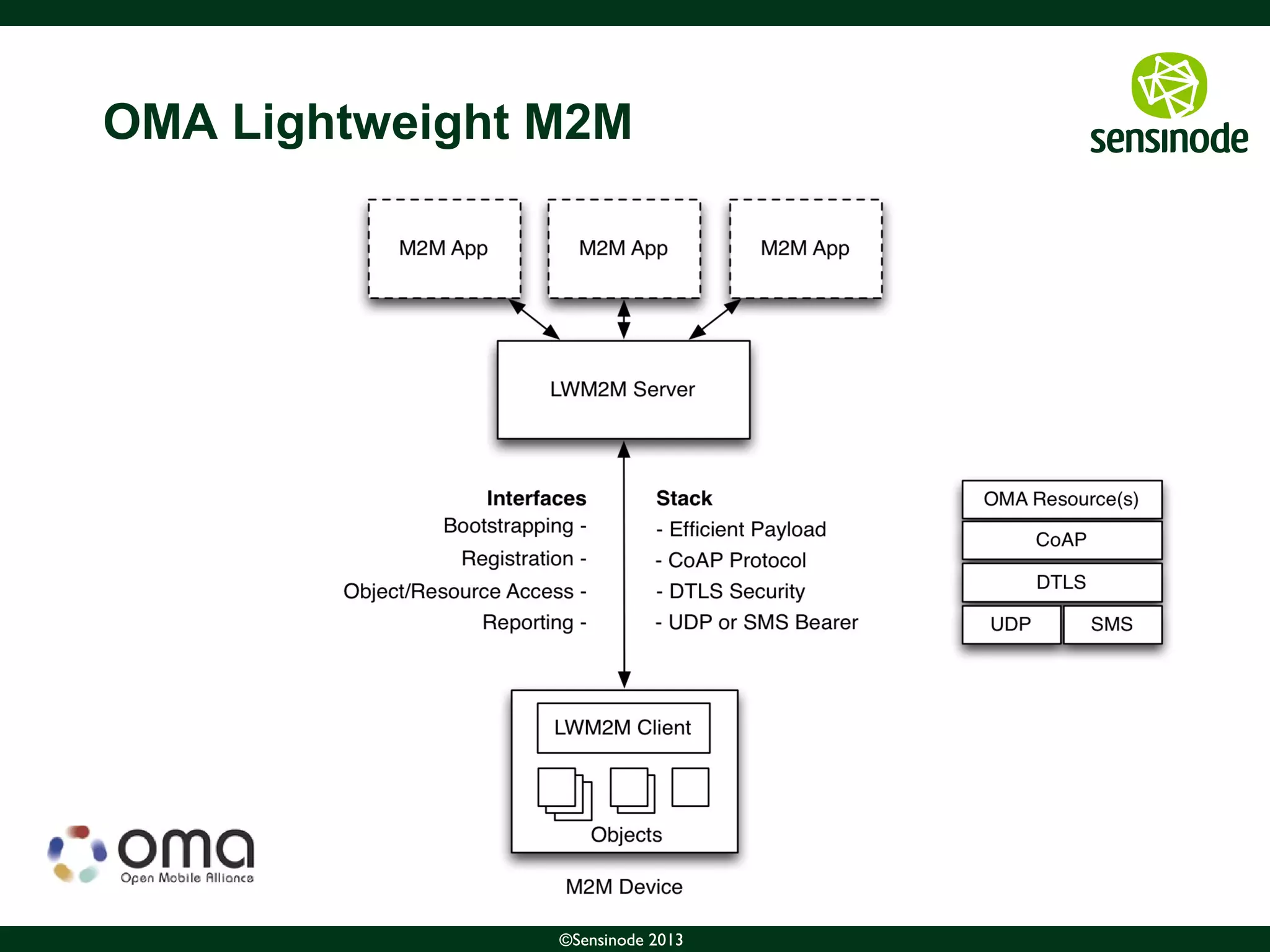
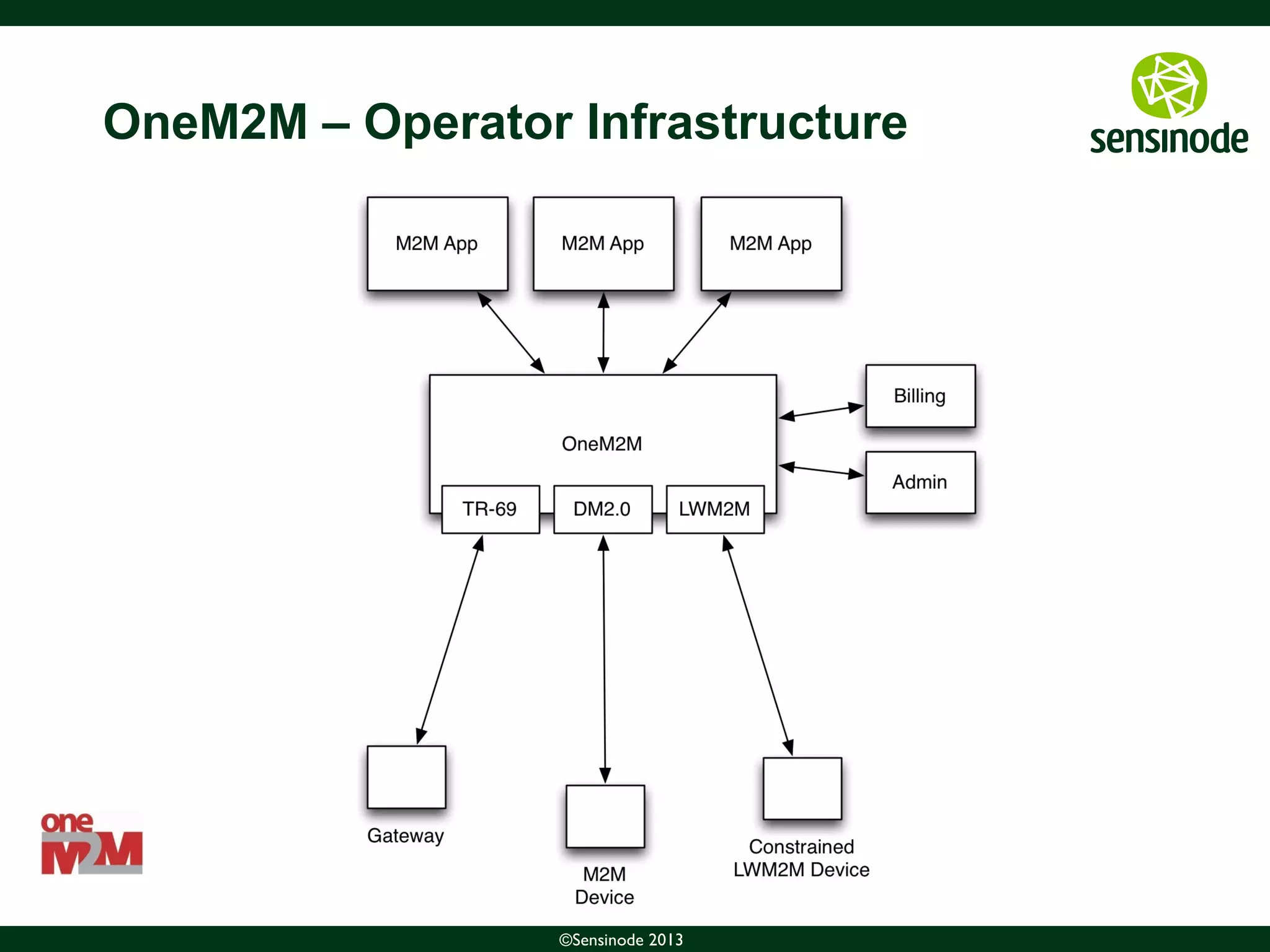
The document discusses the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart cities. It notes that as more devices become internet-connected, standards like IPv6, 6LoWPAN, and CoAP will be important to enable interoperability. The Web of Things uses these standards and protocols like CoAP to provide web services at the network edge for IoT applications. Sensinode is a provider of end-to-end IoT software solutions and plays a key role in several IoT standardization efforts.