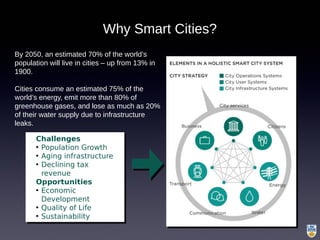
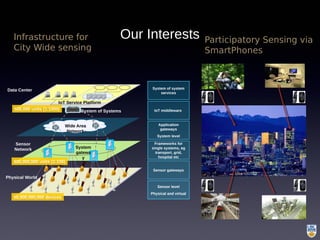
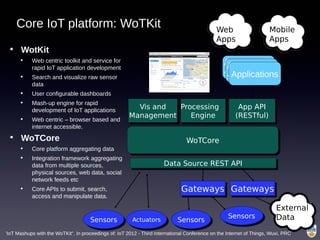
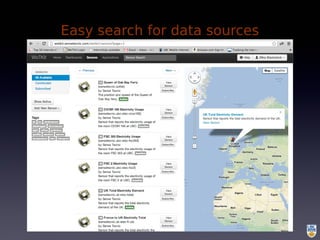
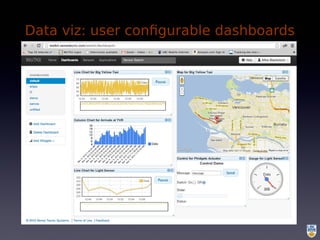
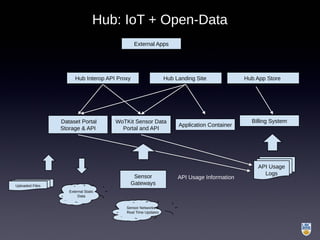
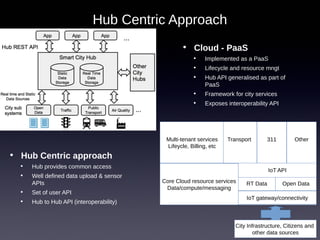
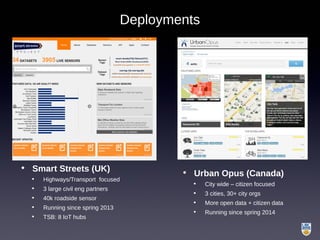
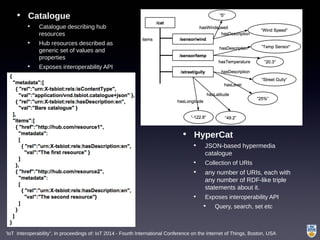
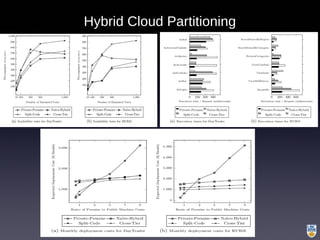
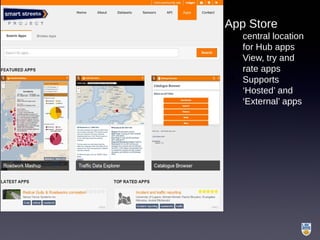
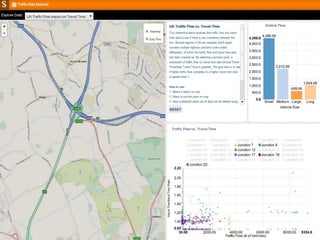
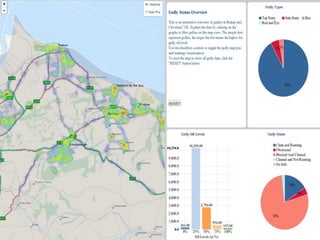
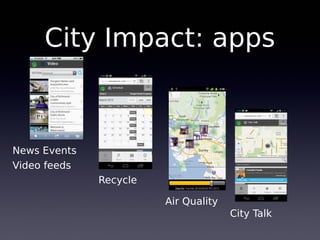
The document discusses the integration of IoT in smart cities, highlighting the growth and challenges faced by urban environments as population density increases. It outlines the system architecture, including data aggregation platforms and various smart city applications, while addressing interoperability issues and hybrid cloud solutions. Key examples of deployment projects, such as Smart Streets in the UK and Urban Opus in Canada, illustrate the practical implementation of these concepts.