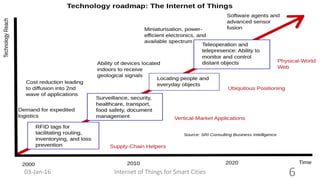
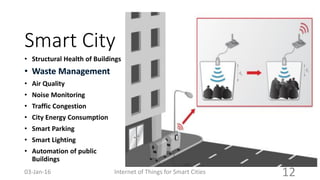
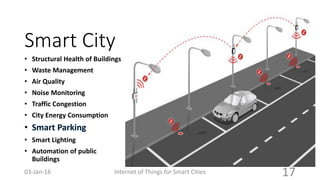
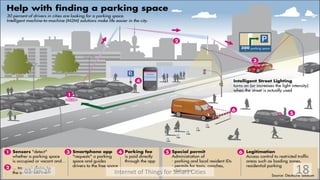
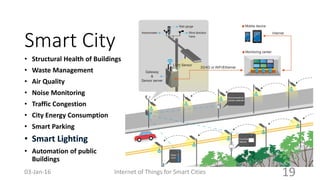
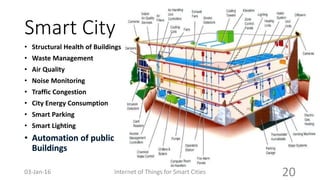
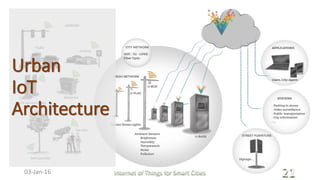
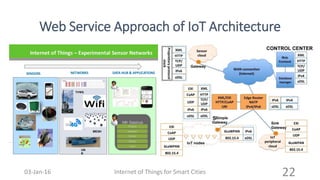
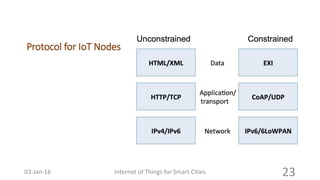
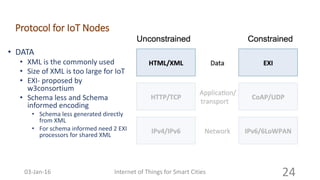
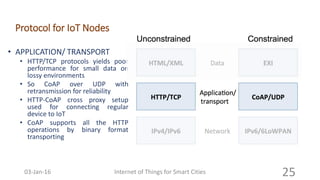
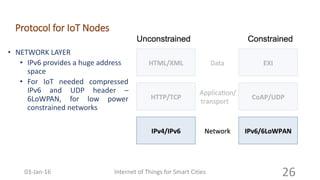
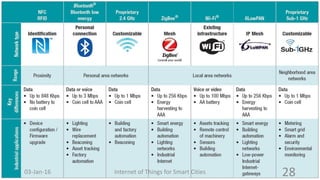
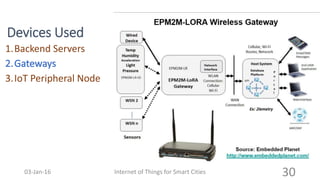
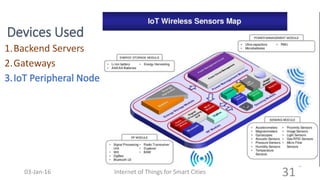
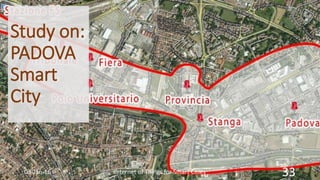
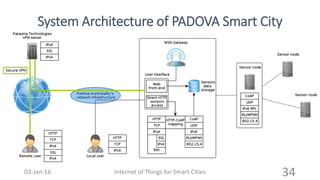
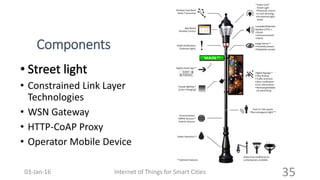
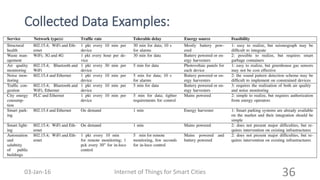
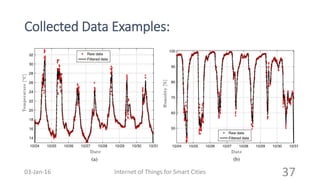
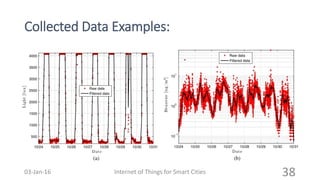
This document discusses the concept of smart cities and the role of the Internet of Things. It begins with an overview of smart city concepts and urban IoT architecture. It then describes an experimental study of the PADOVA smart city project in Italy. This includes details on the system architecture used in PADOVA and examples of data collected. The document concludes that IoT solutions are available for smart cities and emerging technologies are expanding the market for related products. It provides references on IoT for smart cities and convergence of technologies.