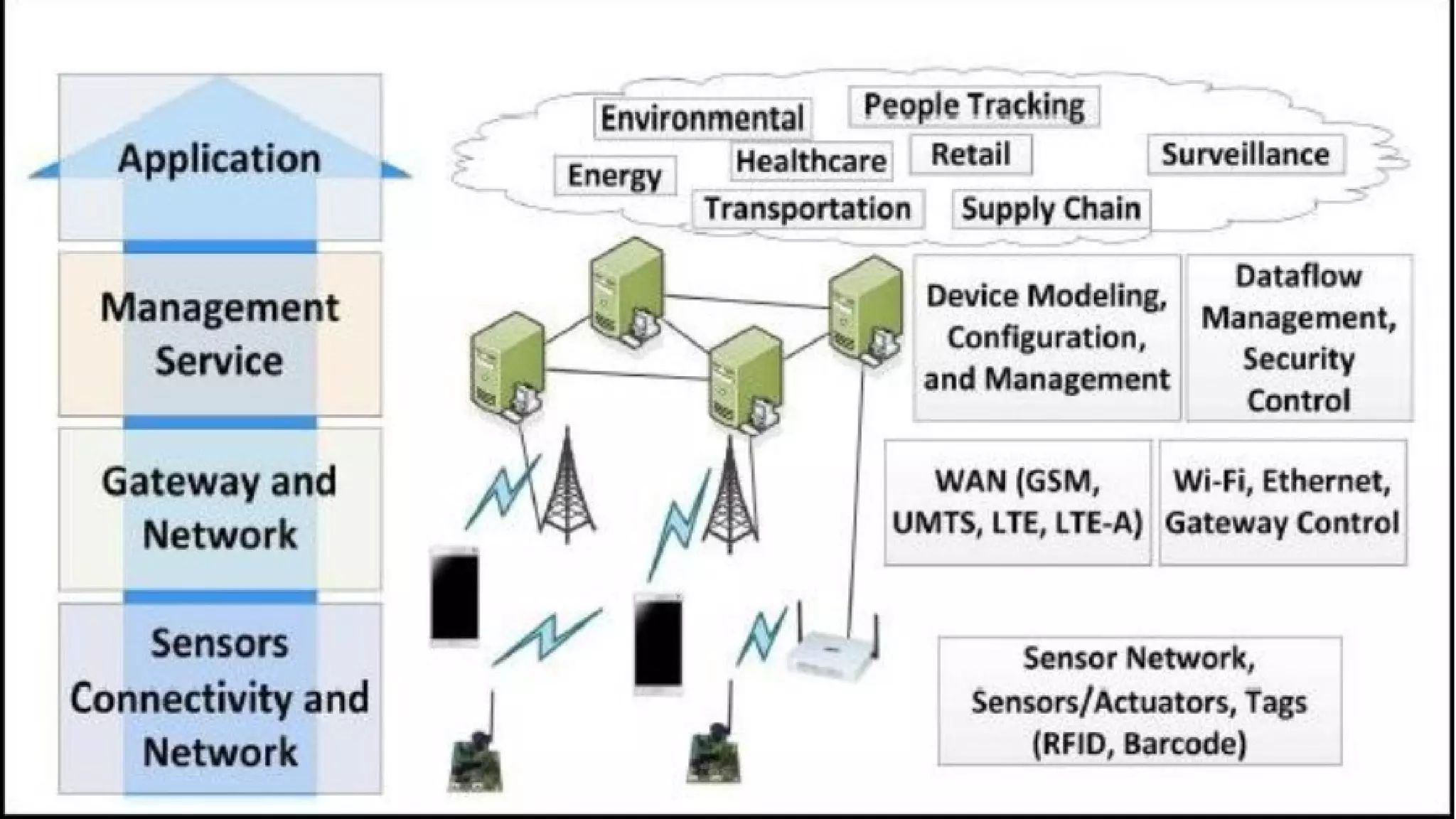
The document discusses the future of the Internet of Things (IoT). It defines IoT as connecting physical devices to exchange data and integrate the physical world into computer systems. The architecture of IoT is described as having four layers - a sensor layer to collect real-time data, a gateway layer to support communication, a service layer to analyze data, and an application layer for user interfaces. Challenges of IoT include scalability, standardization, and data volumes. Applications are in smart homes, cities, grids, cars, health, and supply chains. The future of IoT is vast due to advances enabling integration across devices.