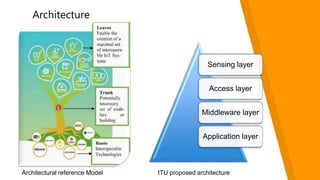
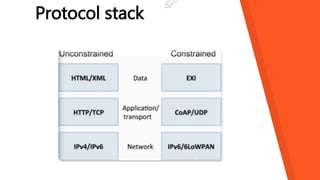
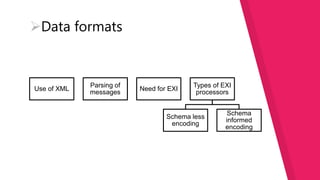
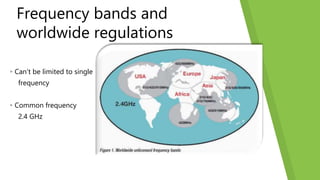
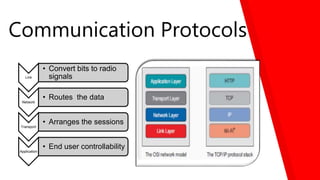
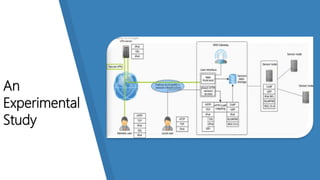
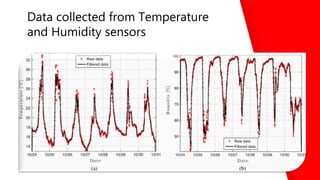
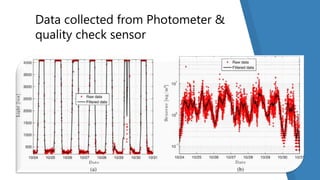
This document discusses how the Internet of Things can be used to create smart cities. It outlines different IoT architectures including sensing, access, middleware and application layers. It also discusses using a web service approach with REST and CoAP protocols. The document describes using IoT in areas like structural health, waste management, air quality monitoring and traffic congestion monitoring. It then details an experimental study collecting environmental data and monitoring public street lighting using sensors and forming a 6LoWPAN network.