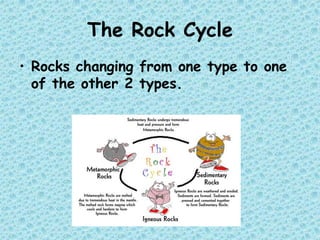
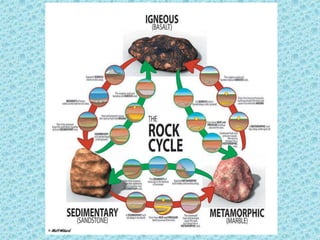
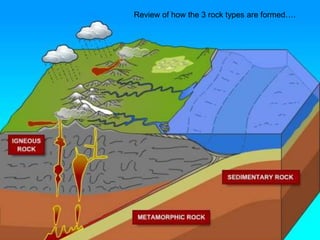
The document is a lesson on rocks that discusses the three main types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. It explains that igneous rocks form from the cooling of magma or lava, sedimentary rocks form from compressed sediments, and metamorphic rocks form from intense heat and pressure changing other rock types. The rock cycle is also described, showing how rocks can change between the three types over time.