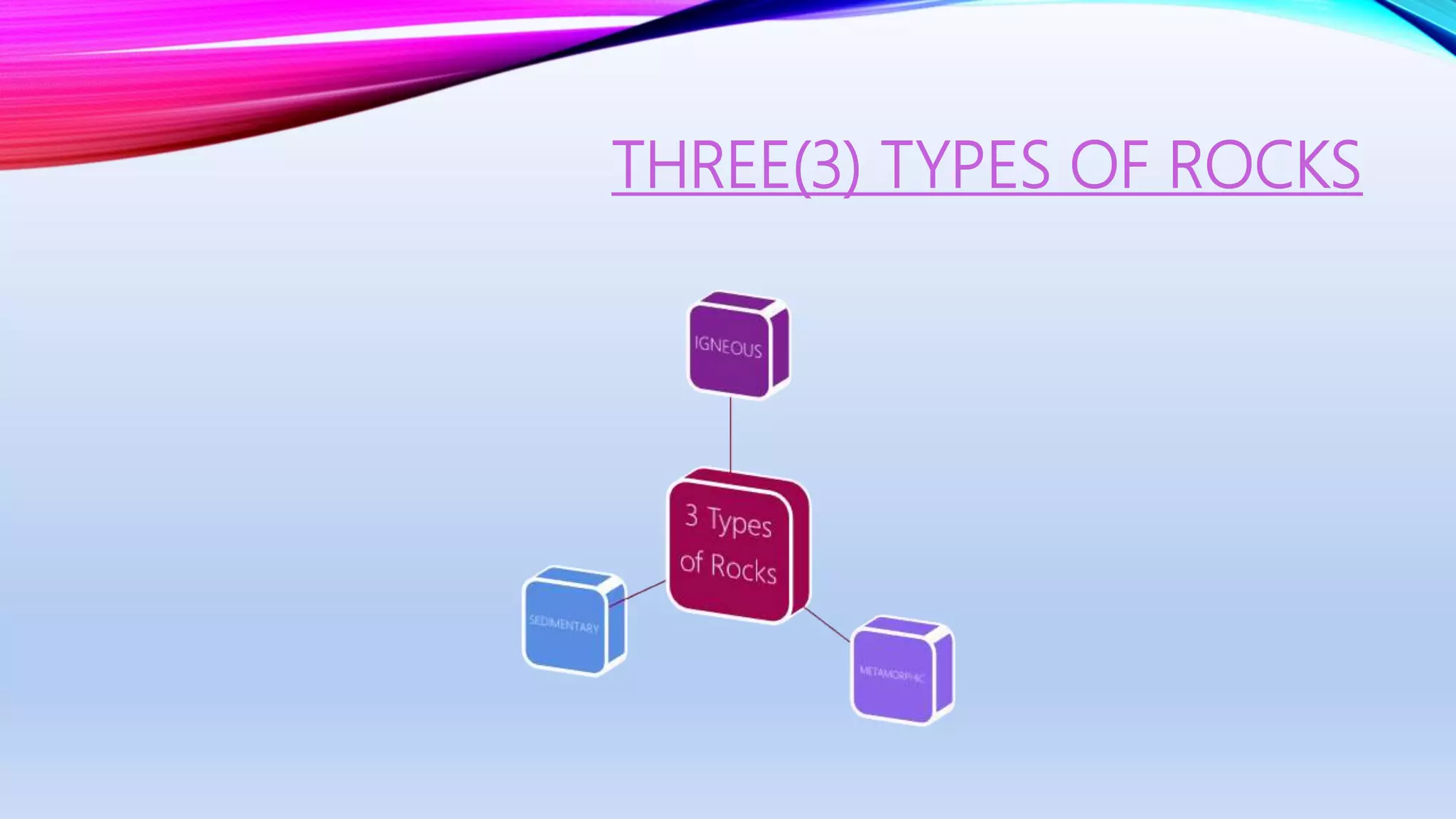
There are three main types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooled magma and are categorized as either extrusive or intrusive based on if they cool above or below ground. Sedimentary rocks form from the compaction and cementation of sediments and sometimes contain fossils. Metamorphic rocks form from changes to existing igneous or sedimentary rocks through heat and pressure, creating new rock types with interlocking crystals. The document provides examples and characteristics of each rock type.