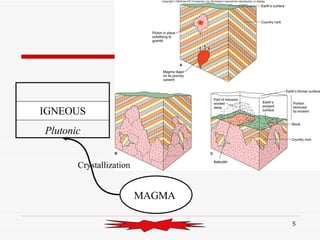
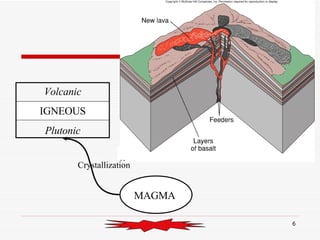
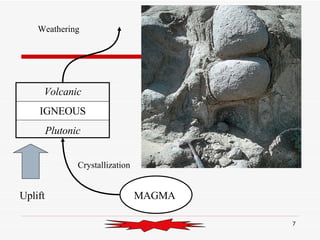
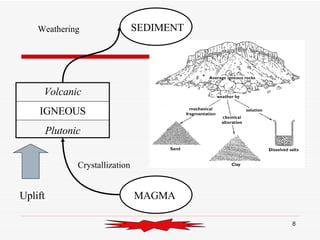
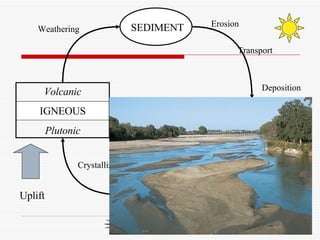
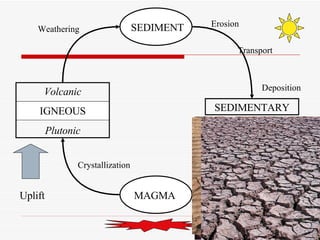
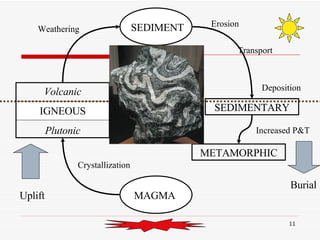
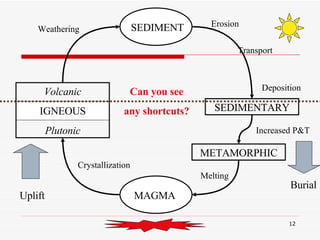
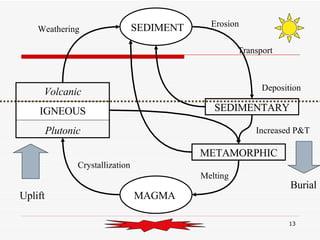
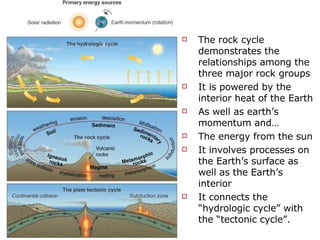
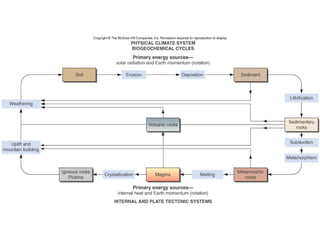
The document discusses the rock cycle and the relationships between the three main rock groups: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, either deep underground or at the surface. Sedimentary rocks form at the surface from eroded materials that are transported and deposited. Metamorphic rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by heat, pressure, and fluids deep underground. The rock cycle demonstrates how rocks are continuously being formed and reformed through geological processes both at the surface and in Earth's interior.